|
Elyakim Rubinstein High Court Judge
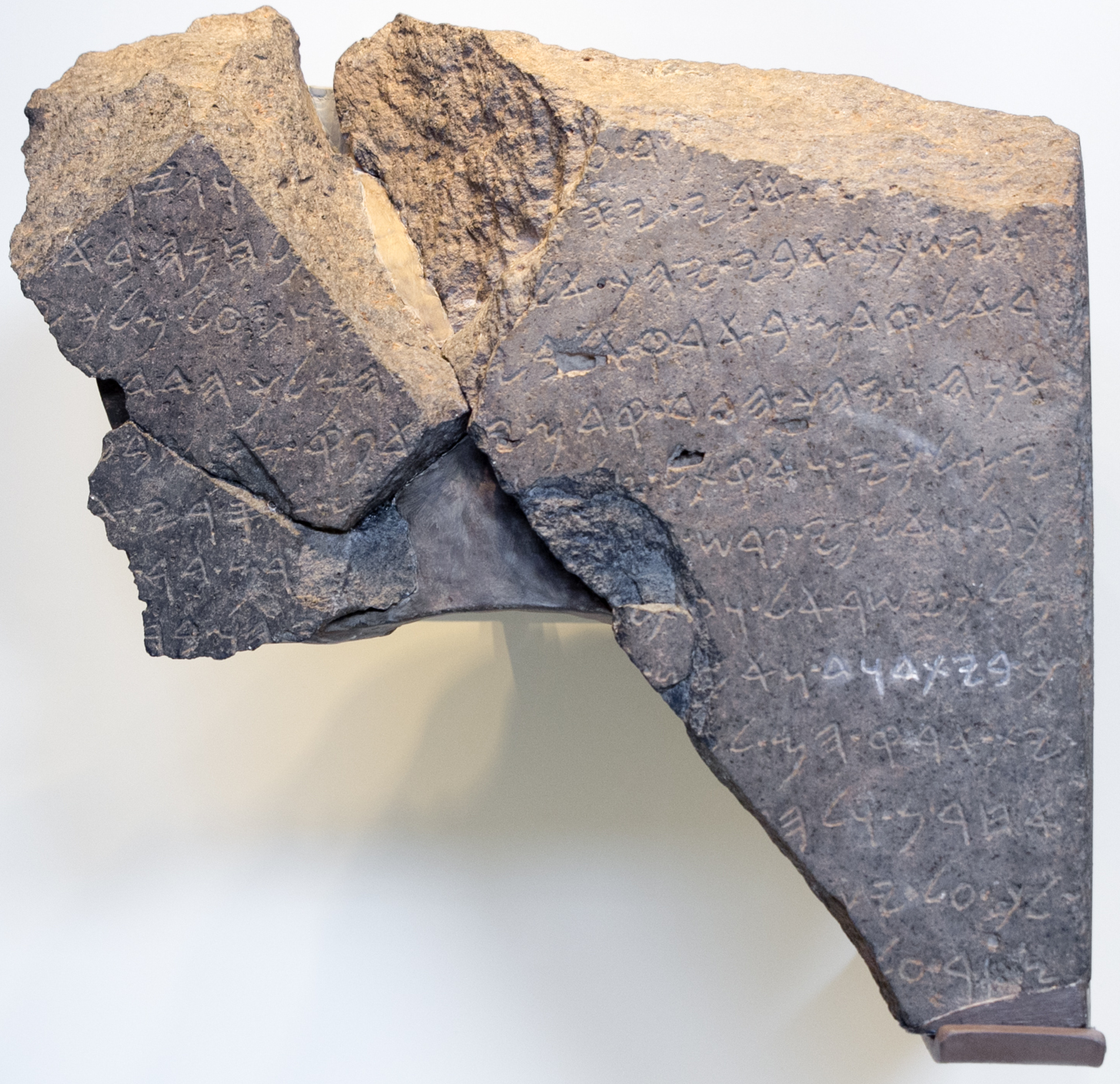
Eliakim () is a moshav in northern Israel. Located in the Menashe Heights, it falls under the jurisdiction of Megiddo Regional Council. In it had a population of . History The village was established in 1949 as a moshav by Jewish refugees from Yemen on the lands of the depopulated Palestinian village of Umm az-Zinat, and was named after Jehoiakim (who was originally named Eliakim), a King of Judah (2 Kings 23:34). In 1970 it was converted to a communal settlement, but returned to being a moshav in 2008. Archaeology A large burial cave was unearthed at Eliakim, featuring a poorly executed inscription above its entrance, using the Samaritan script, which reads "El'azar son of Azariah". The cave houses three burial troughs and a loculus. Notable residents *Boaz Mauda, winner of season 5 of Kokhav Nolad ''Kokhav Nolad'' (; meaning "A Star Is Born") was an Israeli reality television show searching for talented new vocalists, based on the British ''Pop Idol'' model. Since i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yemenite Jews
Yemenite Jews, also known as Yemeni Jews or Teimanim (from ; ), are a Jewish diaspora group who live, or once lived, in Yemen, and their descendants maintaining their customs. After several waves of antisemitism, persecution, the vast majority of Yemenite Jews aliyah, emigrated to Israel in Operation Magic Carpet (Yemen), Operation Magic Carpet between June 1949 and September 1950. Most Yemenite Jews in Israel, Yemenite Jews now live in Israel, with smaller communities in the United States and elsewhere. As of 2024, only one Jew, Levi Marhabi, remains in Yemen, although ''Ynet'' cited local sources stating that the actual number is five. Yemenite Jews observe a unique religious tradition that distinguishes them from Ashkenazi Jews, Sephardic Jews, and Jewish ethnic divisions, other Jewish groups. They have been described as "the most Jewish of all Jews" and "the ones who have preserved the Hebrew language the best". Yemenite Jews are considered Mizrahi Jews, Mizrahi or "Eastern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
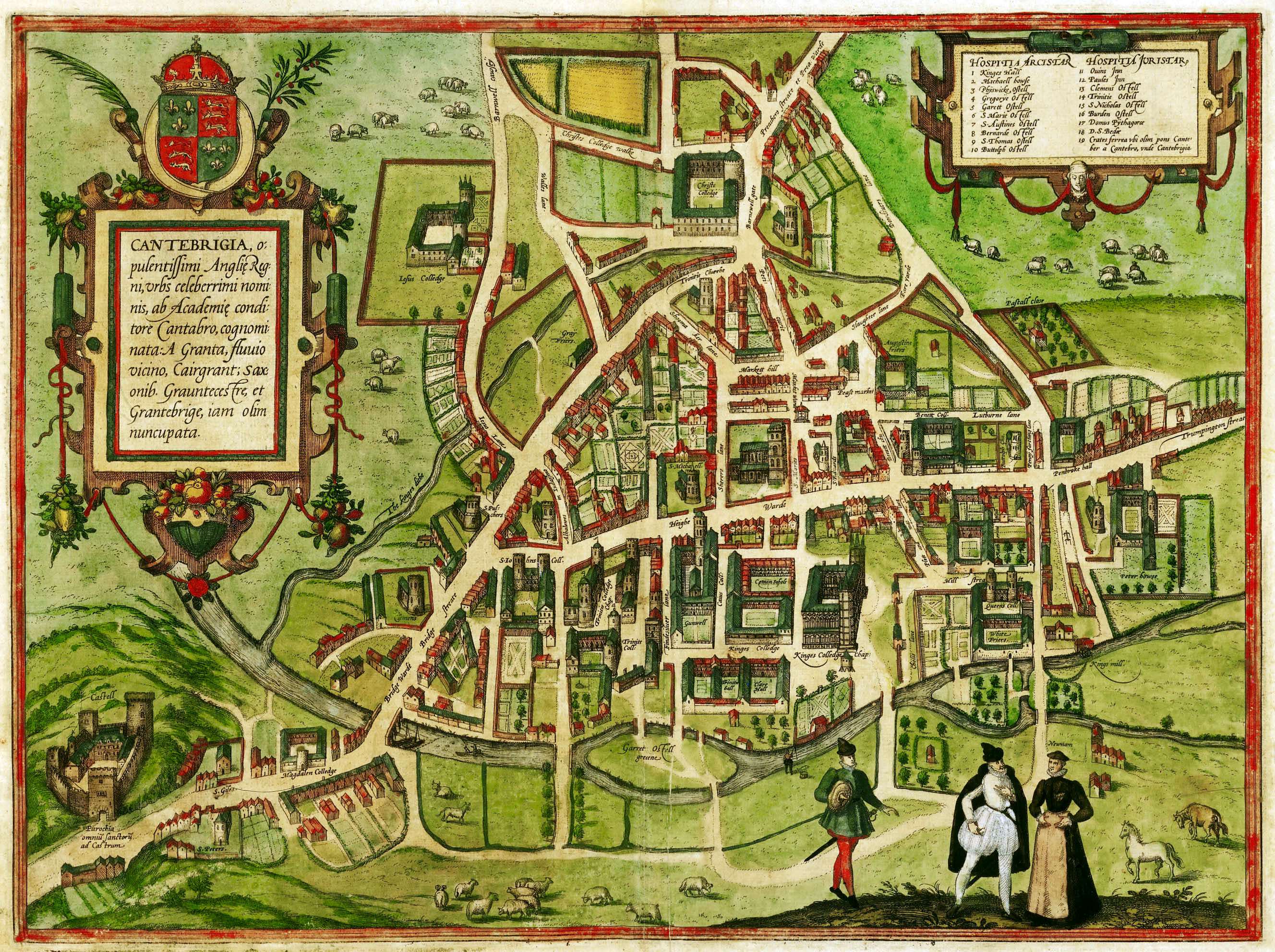
Cambridge University Press
Cambridge University Press was the university press of the University of Cambridge. Granted a letters patent by King Henry VIII in 1534, it was the oldest university press in the world. Cambridge University Press merged with Cambridge Assessment to form Cambridge University Press and Assessment under Queen Elizabeth II's approval in August 2021. With a global sales presence, publishing hubs, and offices in more than 40 countries, it published over 50,000 titles by authors from over 100 countries. Its publications include more than 420 academic journals, monographs, reference works, school and university textbooks, and English language teaching and learning publications. It also published Bibles, runs a bookshop in Cambridge, sells through Amazon, and has a conference venues business in Cambridge at the Pitt Building and the Sir Geoffrey Cass Sports and Social Centre. It also served as the King's Printer. Cambridge University Press, as part of the University of Cambridge, was a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Populated Places In Northern District (Israel)
Population is a set of humans or other organisms in a given region or area. Governments conduct a census to quantify the resident population size within a given jurisdiction. The term is also applied to non-human animals, microorganisms, and plants, and has specific uses within such fields as ecology and genetics. Etymology The word ''population'' is derived from the Late Latin ''populatio'' (a people, a multitude), which itself is derived from the Latin word ''populus'' (a people). Use of the term Social sciences In sociology and population geography, population refers to a group of human beings with some predefined feature in common, such as location, race, ethnicity, nationality, or religion. Ecology In ecology, a population is a group of organisms of the same species which inhabit the same geographical area and are capable of interbreeding. The area of a sexual population is the area where interbreeding is possible between any opposite-sex pair within the are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moshavim
A moshav (, plural ', "settlement, village") is a type of Israeli village or town or Jewish settlement, in particular a type of cooperative agricultural community of individual farms settler, pioneered by the Labour Zionists between 1904 and 1914, during what is known as the Second Aliyah, second wave of ''aliyah''. A resident or a member of a moshav can be called a "moshavnik" (). There is an umbrella organization, the Moshavim Movement. The moshavim are similar to kibbutzim with an emphasis on communitarian, individualist labour. They were designed as part of the Zionist state-building programme following the green revolution in the Mandatory Palestine, British Mandate of Palestine during the early 20th century, but in contrast to the collective farming kibbutzim, farms in a moshav tended to be individually owned but of fixed and equal size. Workers produced crops and other goods on their properties through individual or pooled labour with the profit and foodstuffs go ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kokhav Nolad
''Kokhav Nolad'' (; meaning "A Star Is Born") was an Israeli reality television show searching for talented new vocalists, based on the British ''Pop Idol'' model. Since its debut on Israeli Channel 2 in 2003, Kokhav Nolad has become popular and turned out many new musical stars. The show was hosted by Zvika Hadar. Summary Format The format of ''Kokhav Nolad'' was similar to Pop Idol and its spinoffs, like American Idol, but was independently produced and not a licensed adaptation. The contest was open to aspiring singers, most of them in their late teens and early 20s, who appeared before a panel of judges, who evaluated their performances. The audience was then asked to vote for their favorite singer. In every round, whoever gets the fewest votes leaves the competition until only one is left, who is declared the winner. ''Kokhav Nolad'' was preceded by another program called '' Lo Nafsik Lashir'', in which the participants competed in their knowledge of Hebrew songs, not o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boaz Mauda
Boaz Ma'uda (; born April 23, 1987) is an Israeli singer and songwriter. He won the fifth season of ''Kokhav Nolad'', the Israeli version of ''Pop Idol'', and represented Israel in the Eurovision Song Contest 2008, finishing in 9th place. His voice has been described as somewhere between David D'Or and Dana International. Early life Boaz was born and raised in moshav Elyakim, where he still lives. He is the youngest son of his mother, who became disabled from complications of his birth. He is of Yemenite Jewish descent. Career ''Kochav Nolad'' Without any history in the music industry, and unknown to Boaz, he was signed up by a friend for the auditions of the fifth season of Kochav Nolad. During the show, Boaz sang many Mizrahi and acoustic songs. His voice was loved by the audience and judges. At the finals on August 29, 2007, Boaz competed against Marina Maximillian Blumin and Shlomi Bar'el. On that evening, he performed two songs: "Señorita" with veteran Israeli sin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samaritan Script
The Samaritan Hebrew script, or simply Samaritan script, is used by the Samaritans for religious writings, including the Samaritan Pentateuch, writings in Samaritan Hebrew, and for commentaries and translations in Samaritan Aramaic language, Samaritan Aramaic and occasionally Arabic language, Arabic. Samaritan is a direct descendant of the Paleo-Hebrew alphabet, which was a variety of the Phoenician alphabet. Paleo-Hebrew is the alphabet in which large parts of the Hebrew Bible were originally penned according to the consensus of most scholars, who also believe that these scripts are descendants of the Proto-Sinaitic script. Paleo-Hebrew script was used by the ancient Israelites, both Jews and Samaritans. The better-known "square script" Hebrew alphabet which has been traditionally used by Jews since the Babylonian exile is a stylized version of the Aramaic alphabet called Ashurit (כתב אשורי). Historically, the Aramaic alphabet became distinct from Phoenician/Paleo-Heb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Judah
The Kingdom of Judah was an Israelites, Israelite kingdom of the Southern Levant during the Iron Age. Centered in the highlands to the west of the Dead Sea, the kingdom's capital was Jerusalem. It was ruled by the Davidic line for four centuries. Jews are named after Judah, and primarily descend from people who lived in the region. The Hebrew Bible depicts the Kingdom of Judah as one of the two successor states of the Kingdom of Israel (united monarchy), United Kingdom of Israel, a term denoting the united monarchy under biblical kings Saul, David, and Solomon and covering the territory of Judah and Kingdom of Israel (Samaria), Israel. However, during the 1980s, Biblical minimalism, some biblical scholars began to argue that the archaeological evidence for an extensive kingdom before the late 8th century BCE is too weak, and that the methodology used to obtain the evidence is flawed. In the 10th and early 9th centuries BCE, the territory of Judah might have been limited ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jehoiakim
Jehoiakim, also sometimes spelled Jehoikim was the eighteenth and antepenultimate King of Judah from 609 to 598 BC. He was the second son of King Josiah () and Zebidah, the daughter of Pedaiah of Rumah. His birth name was Eliakim. Background After Josiah's death, Jehoiakim's younger brother Jehoahaz (also known as Shallum) was proclaimed king, but after three months Pharaoh Necho II deposed him, making Eliakim king in his place. When placed on the throne, his name was changed to "Jehoiakim". Jehoiakim reigned for eleven years, until 598 BCDan Cohn-Sherbok, ''The Hebrew Bible'', Continuum International, 1996, page x. and was succeeded by his son Jeconiah (also known as Jehoiachin), who reigned for only three months. Reign Jehoiakim was appointed king by Necho II, king of Egypt, in 609 BC, after Necho's return from the battle in Harran, three months after he had killed King Josiah at Megiddo. Necho deposed Jehoiakim's younger brother Jehoahaz after a reign of only three mont ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cambridge
Cambridge ( ) is a List of cities in the United Kingdom, city and non-metropolitan district in the county of Cambridgeshire, England. It is the county town of Cambridgeshire and is located on the River Cam, north of London. As of the 2021 United Kingdom census, the population of the City of Cambridge was 145,700; the population of the wider built-up area (which extends outside the city council area) was 181,137. (2021 census) There is archaeological evidence of settlement in the area as early as the Bronze Age, and Cambridge became an important trading centre during the Roman Britain, Roman and Viking eras. The first Town charter#Municipal charters, town charters were granted in the 12th century, although modern city status was not officially conferred until 1951. The city is well known as the home of the University of Cambridge, which was founded in 1209 and consistently ranks among the best universities in the world. The buildings of the university include King's College Chap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Institute For Palestine Studies
The Institute for Palestine Studies (IPS) is the oldest independent nonprofit public service research institute in the Arab world. It was established and incorporated in Beirut, Lebanon, in 1963 and has since served as a model for other such institutes in the region. It is the only institute solely concerned with analyzing and documenting Palestinian affairs and the Arab–Israeli conflict. It also publishes scholarly journals and has published more than 600 books, monographs, and documentary collections in English, Arabic and French—as well as its quarterly academic journals: '' Journal of Palestine Studies'', ''Jerusalem Quarterly'', and ''Majallat al-Dirasat al-Filistiniyyah''. IPS's Library in Beirut is the largest in the Arab world specializing in Palestinian affairs, the Arab–Israeli conflict, and Judaica. It is led by a board of trustees comprising some forty scholars, businessmen, and public figures representing almost all Arab countries. The institute currently mai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |