|
Eltanin Fault System
The Eltanin Fault System (Eltanin Fracture Zone) is a series of six or seven dextral transform faults that offset the Pacific-Antarctic Ridge, a spreading zone between the Pacific Plate and the Antarctic Plate. The affected zone of the Pacific-Antarctic Ridge is about 800 km long, between 56° S, 145° W and 54.5° S, 118.5° W, southwest of Easter Island, and about as far as one can get from land on planet Earth (48°52.6′S 123°23.6′W). However, the total offset is about 1600 km. The two major faults in the Eltanin Fracture Zone are the Heezen Fault and the Tharp Fault. Others related faults include the Vacquier Transform Fault, the Menard Transform Fault, and the Udintsev Fault. See also * Hollister Ridge Notes Further reading * * * * * * * Geology of the Southern Ocean Geology of the Pacific Ocean Seismic faults Geology of Antarctica {{tectonics-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
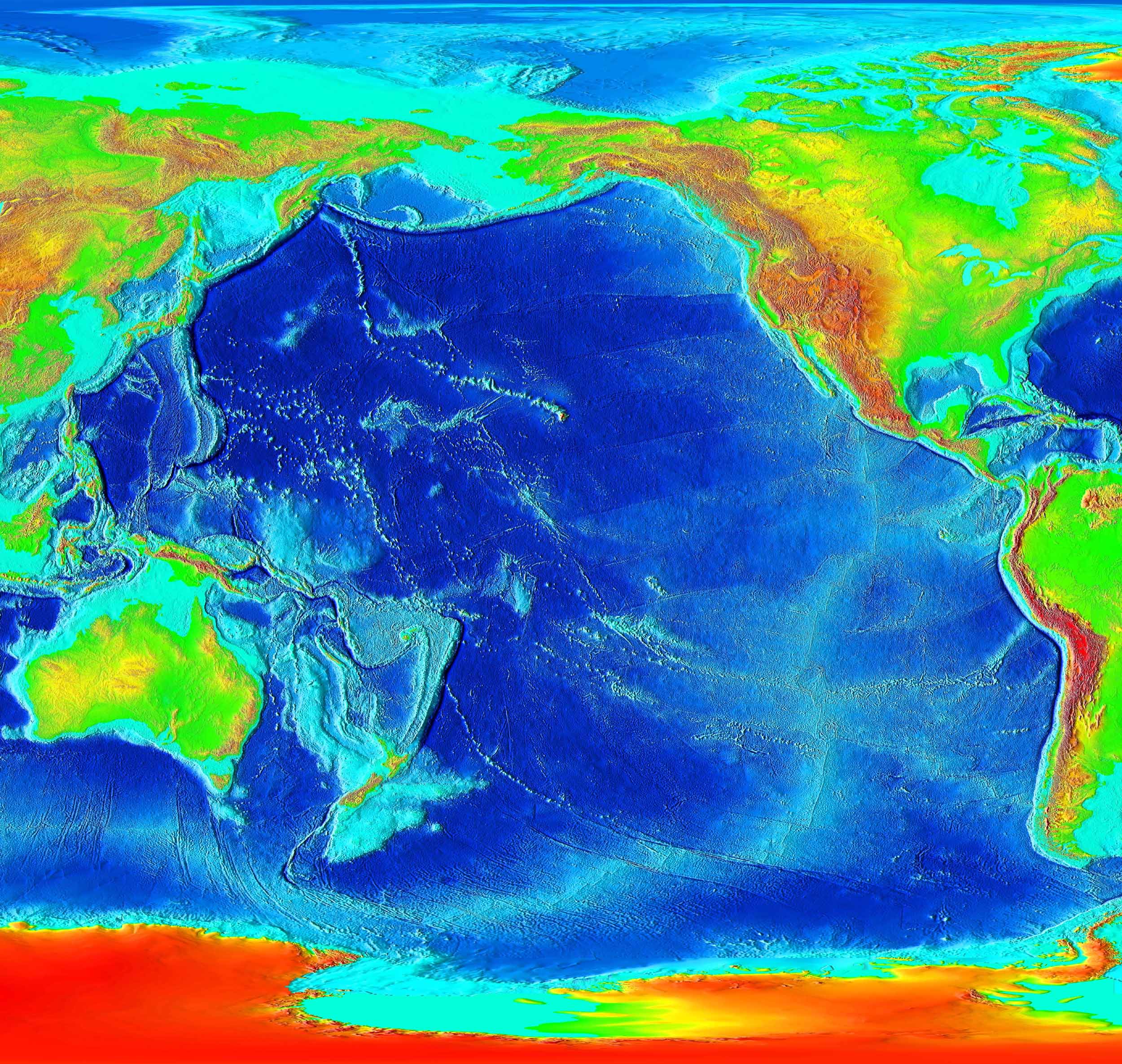
Pacific Elevation2
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean (or, depending on definition, to Antarctica) in the south, and is bounded by the continents of Asia and Oceania in the west and the Americas in the east. At in area (as defined with a southern Antarctic border), this largest division of the World Ocean—and, in turn, the Hydrosphere, hydrosphere—covers about 46% of Earth's water surface and about 32% of its total surface area, larger than Earth's entire land area combined .Pacific Ocean . ''Encyclopædia Britannica, Britannica Concise.'' 2008: Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc. The centers of both the Land and water hemispheres, Water Hemisphere and the Western Hemisphere, as well as the Pole of inaccessibility#Oceanic pole of ina ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pacific-Antarctic Ridge
The Pacific-Antarctic Ridge (PAR) is a divergent tectonic plate boundary located on the seafloor of the South Pacific Ocean, separating the Pacific Plate from the Antarctic Plate. It is regarded as the southern section of the East Pacific Rise in some usages, generally south of the Challenger Fracture Zone and stretching to the Macquarie Triple Junction south of New Zealand. The Louisville Ridge Stretching for 4,300 km north-west from the Pacific-Antarctic Ridge to the Osbourn Seamount at Tonga and Kermadec Junction is a long line of seamounts called the Louisville Ridge – the longest such chain in the Pacific – thought to have formed from the Pacific Plate sliding over a long-lived center of upwelling magma called the Louisville hotspot. See also * Hollister Ridge * Oceanic ridge A mid-ocean ridge (MOR) is a seafloor mountain system formed by plate tectonics. It typically has a depth of about and rises about above the deepest portion of an ocean basin. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pacific Plate
The Pacific Plate is an oceanic tectonic plate that lies beneath the Pacific Ocean. At , it is the largest tectonic plate. The plate first came into existence 190 million years ago, at the triple junction between the Farallon, Phoenix, and Izanagi Plates. The Pacific Plate subsequently grew to where it underlies most of the Pacific Ocean basin. This reduced the Farallon Plate to a few remnants along the west coast of North America and the Phoenix Plate to a small remnant near the Drake Passage, and destroyed the Izanagi Plate by subduction under Asia. The Pacific Plate contains an interior hot spot forming the Hawaiian Islands. Boundaries The north-eastern side is a divergent boundary with the Explorer Plate, the Juan de Fuca Plate and the Gorda Plate forming respectively the Explorer Ridge, the Juan de Fuca Ridge and the Gorda Ridge. In the middle of the eastern side is a transform boundary with the North American Plate along the San Andreas Fault, and a boundary w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antarctic Plate
The Antarctic Plate is a tectonic plate containing the continent of Antarctica, the Kerguelen Plateau, and some remote islands in the Southern Ocean and other surrounding oceans. After breakup from Gondwana (the southern part of the supercontinent Pangea), the Antarctic plate began moving the continent of Antarctica south to its present isolated location, causing the continent to develop a much colder climate. The Antarctic Plate is bounded almost entirely by extensional mid-ocean ridge systems. The adjoining plates are the Nazca Plate, the South American Plate, the African Plate, the Somali Plate, the Indo-Australian Plate, the Pacific Plate, and, across a transform boundary, the Scotia Plate. The Antarctic Plate has an area of about . It is Earth's fifth-largest tectonic plate. The Antarctic Plate's movement is estimated to be at least per year towards the Atlantic Ocean. Subduction beneath South America The Antarctic Plate started to subduct beneath South America 14 mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Easter Island
Easter Island ( rap, Rapa Nui; es, Isla de Pascua) is an island and special territory of Chile in the southeastern Pacific Ocean, at the southeasternmost point of the Polynesian Triangle in Oceania. The island is most famous for its nearly 1,000 extant monumental statues, called '' moai'', which were created by the early Rapa Nui people. In 1995, UNESCO named Easter Island a World Heritage Site, with much of the island protected within Rapa Nui National Park. Experts disagree on when the island's Polynesian inhabitants first reached the island. While many in the research community cited evidence that they arrived around the year 800, there is compelling evidence presented in a 2007 study that places their arrival closer to 1200. The inhabitants created a thriving and industrious culture, as evidenced by the island's numerous enormous stone ''moai'' and other artifacts. However, land clearing for cultivation and the introduction of the Polynesian rat led to gradual defo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hollister Ridge
Hollister Ridge is a group of seamounts in the Pacific Ocean. They lie west from the Pacific-Antarctic Ridge and form three ridges that form a line; one of the ridges rises to a depth of and in the past formed an island. The seamounts are composed out of basaltic and other rocks and their ages range from about 2.5 million years ago to latest Pleistocene; an acoustic swarm recorded in the southern Pacific Ocean in 1991-1992 is considered to be the manifestation of a historical eruption of the Hollister Ridge. The origin of the Hollister Ridge is unclear, with various proposed mechanisms involving the neighbouring Pacific-Antarctic Ridge, crustal weaknesses and the Louisville hotspot. History The ridge was discovered either by gravimetry from satellites or by the research ship ''Eltanin'' in 1965 and first named "Hollister Ridge" in a 1995 publication. Rock samples were taken at the ridge in 1996. Geography and geomorphology The Hollister Ridge is an aseismic ridge in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geophysical Journal International
''Geophysical Journal International'' is a monthly peer-reviewed scientific journal published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Royal Astronomical Society and the Deutsche Geophysikalische Gesellschaft (German Geophysical Society). The journal publishes original research papers, research notes, letters, and book reviews. It was established in 1922. The editor-in-chief An editor-in-chief (EIC), also known as lead editor or chief editor, is a publication's editorial leader who has final responsibility for its operations and policies. The highest-ranking editor of a publication may also be titled editor, managing ... is Joerg Renner ( Ruhr University Bochum). The journal covers research on all aspects of theoretical, computational, applied and observational geophysics. History The journal was formerly entitled ''Geophysical Journal'' (Oxford) from January 1988 to June 1989. The ''Geophysical Journal'' was itself formed by the merger of three other publications: ''Ge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geology Of The Southern Ocean
Geology () is a branch of natural science concerned with Earth and other astronomical objects, the features or rocks of which it is composed, and the processes by which they change over time. Modern geology significantly overlaps all other Earth sciences, including hydrology, and so is treated as one major aspect of integrated Earth system science and planetary science. Geology describes the structure of the Earth on and beneath its surface, and the processes that have shaped that structure. It also provides tools to determine the relative and absolute ages of rocks found in a given location, and also to describe the histories of those rocks. By combining these tools, geologists are able to chronicle the geological history of the Earth as a whole, and also to demonstrate the age of the Earth. Geology provides the primary evidence for plate tectonics, the evolutionary history of life, and the Earth's past climates. Geologists broadly study the properties and processes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geology Of The Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean evolved in the Mesozoic from the Panthalassic Ocean, which had formed when Rodinia rifted apart around 750 Ma. The first ocean floor which is part of the current Pacific Plate began 160 Ma to the west of the central Pacific and subsequently developed into the largest oceanic plate on Earth. The East Pacific Rise near Easter Island is the fastest spreading mid-ocean ridge, with a spreading rate of over 15 cm/yr. The Pacific Plate moves generally towards the northwest at between 7 and 11 cm/yr while the Juan De Fuca Plate has an east-northeasterly movement of some 4 cm/yr. Most subduction zones around the rim of the Pacific are directed away from a large area in the southern Pacific. At the core–mantle boundary below this area there is a large low-shear velocity province (LLSVP). Most of Pacific hotspots are located above the LLSVP while the longest Pacific hotspot tracks are located at or near its boundaries pointing at the posi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seismic Faults
Seismology (; from Ancient Greek σεισμός (''seismós'') meaning "earthquake" and -λογία (''-logía'') meaning "study of") is the scientific study of earthquakes and the propagation of elastic waves through the Earth or through other planet-like bodies. It also includes studies of earthquake environmental effects such as tsunamis as well as diverse seismic sources such as volcanic, tectonic, glacial, fluvial, oceanic, atmospheric, and artificial processes such as explosions. A related field that uses geology to infer information regarding past earthquakes is paleoseismology. A recording of Earth motion as a function of time is called a seismogram. A seismologist is a scientist who does research in seismology. History Scholarly interest in earthquakes can be traced back to antiquity. Early speculations on the natural causes of earthquakes were included in the writings of Thales of Miletus (c. 585 BCE), Anaximenes of Miletus (c. 550 BCE), Aristotle (c. 340 BCE), and Zhan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)