|
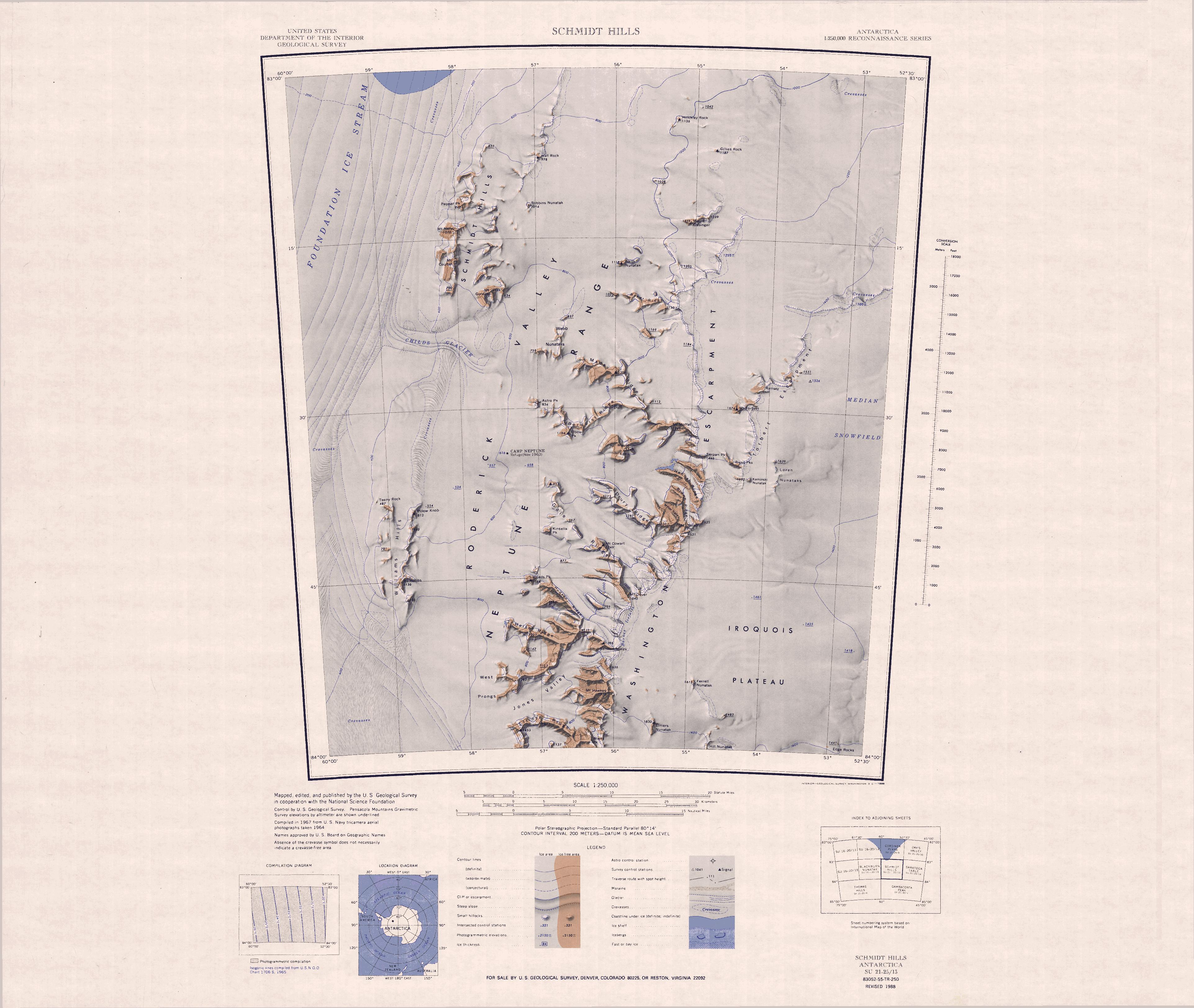
Elmers Nunatak
The Iroquois Plateau () is a large, mainly ice-covered plateau situated east of the southern part of the Washington Escarpment in the Pensacola Mountains, Antarctica. Mapping and name The Iroquois Plateau was mapped by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) from surveys and United States Navy air photographs in 1956–66. It was named by the United States Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names after the Bell UH-1 Iroquois helicopter which has greatly facilitated field operations in Antarctica. Location The Iroquois Plateau is in the Neptune Range. It is east of the Washington Escarpment and south of the Median Snowfield. Scattered nunataks on the plateau include Elmers Nunatak, Ferrell Nunatak, Hill Nunatak and the Edge Rocks. Features Elmers Nunatak . A prominent nunatak southeast of Mount Hawkes. Named by US-ACAN for Elmer H. Smith, aerographer with the wintering parties at Ellsworth Station in 1958 and McMurdo Station in 1961. Ferrell Nunatak . A nunatak protrudin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neptune Range
The Neptune Range () is a mountain range, long, lying west-southwest of Forrestal Range in the central part of the Pensacola Mountains, Antarctica. The range comprises Washington Escarpment with its associated ridges, valleys and peaks, the Iroquois Plateau, the Schmidt and the Williams Hills. Exploration and name The Neptune Range was discovered and photographed on 13 January 1956 on a United States Navy transcontinental plane flight from McMurdo Sound to Weddell Sea and return. It was named by United States US-ACAN after the Navy P2V-2N "Neptune" aircraft with which this flight was made. The entire Pensacola Mountains were mapped by United States Geological Survey (USGS) in 1967 and 1968 from ground surveys and United States Navy tricamera aerial photographs taken in 1964. Location The Neptune Range runs from south to north to the east if the Foundation Ice Stream. Childs Glacier flows west from the range to join the ice stream, The Academy Glacier flows northwest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pensacola Mountains
The Pensacola Mountains () are a large group of mountain ranges and peaks that extend in a northeast–southwest direction in the Transantarctic Mountains System, Queen Elizabeth Land region of Antarctica. They comprise the Argentina Range, Forrestal Range, Dufek Massif, Cordiner Peaks, Neptune Range, Patuxent Range, Rambo Nunataks and Pecora Escarpment. These mountain units lie astride the extensive Foundation Ice Stream and Support Force Glacier which drain northward to the Ronne Ice Shelf. Discovery and naming The Pensacola Mountains were discovered and photographed on 13 January 1956 in the course of a transcontinental nonstop plane flight by personnel of United States Navy Operation Deep Freeze I from McMurdo Sound to Weddell Sea and return. They were named by the United States Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names (US-ACAN) for the U.S. Naval Air Station, Pensacola, Florida, in commemoration of the historic role of that establishment in training aviators of the United St ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plateau
In geology and physical geography, a plateau (; ; : plateaus or plateaux), also called a high plain or a tableland, is an area of a highland consisting of flat terrain that is raised sharply above the surrounding area on at least one side. Often one or more sides have deep hills or escarpments. Plateaus can be formed by a number of processes, including upwelling of volcanic magma, extrusion of lava, and erosion by water and glaciers. Plateaus are classified according to their surrounding environment as intermontane, piedmont, or continental. A few plateaus may have a small flat top while others have wider ones. Formation Plateaus can be formed by a number of processes, including upwelling of volcanic magma, extrusion of lava, plate tectonics movements, and erosion by water and glaciers. Volcanic Volcanic plateaus are produced by volcanic activity. They may be formed by upwelling of volcanic magma or extrusion of lava. The underlining mechanism in forming p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Washington Escarpment
The Neptune Range () is a mountain range, long, lying west-southwest of Forrestal Range in the central part of the Pensacola Mountains, Antarctica. The range comprises Washington Escarpment with its associated ridges, valleys and peaks, the Iroquois Plateau, the Schmidt and the Williams Hills. Exploration and name The Neptune Range was discovered and photographed on 13 January 1956 on a United States Navy transcontinental plane flight from McMurdo Sound to Weddell Sea and return. It was named by United States US-ACAN after the Navy P2V-2N "Neptune" aircraft with which this flight was made. The entire Pensacola Mountains were mapped by United States Geological Survey (USGS) in 1967 and 1968 from ground surveys and United States Navy tricamera aerial photographs taken in 1964. Location The Neptune Range runs from south to north to the east if the Foundation Ice Stream. Childs Glacier flows west from the range to join the ice stream, The Academy Glacier flows northw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Geological Survey
The United States Geological Survey (USGS), founded as the Geological Survey, is an agency of the U.S. Department of the Interior whose work spans the disciplines of biology, geography, geology, and hydrology. The agency was founded on March 3, 1879, to study the landscape of the United States, its natural resources, and the natural hazards that threaten it. The agency also makes maps of planets and moons, based on data from U.S. space probes. The sole scientific agency of the U.S. Department of the Interior, USGS is a fact-finding research organization with no regulatory responsibility. It is headquartered in Reston, Virginia, with major offices near Lakewood, Colorado; at the Denver Federal Center; and in NASA Research Park in California. In 2009, it employed about 8,670 people. The current motto of the USGS, in use since August 1997, is "science for a changing world". The agency's previous slogan, adopted on its hundredth anniversary, was "Earth Science in the Pub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Navy
The United States Navy (USN) is the naval warfare, maritime military branch, service branch of the United States Department of Defense. It is the world's most powerful navy with the largest Displacement (ship), displacement, at 4.5 million tons in 2021. It has the world's largest aircraft carrier fleet, with List of aircraft carriers in service, eleven in service, one undergoing trials, two new carriers under construction, and six other carriers planned as of 2024. With 336,978 personnel on active duty and 101,583 in the Ready Reserve, the U.S. Navy is the third largest of the United States military service branches in terms of personnel. It has 299 deployable combat vessels and about 4,012 operational aircraft as of 18 July 2023. The U.S. Navy is one of six United States Armed Forces, armed forces of the United States and one of eight uniformed services of the United States. The United States Navy traces its origins to the Continental Navy, which was established during ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Advisory Committee On Antarctic Names
The Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names (ACAN or US-ACAN) is an advisory committee of the United States Board on Geographic Names responsible for recommending commemorative names for features in Antarctica. History The committee was established in 1943 as the Special Committee on Antarctic Names (SCAN). It became the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names in 1947. Fred G. Alberts was Secretary of the Committee from 1949 to 1980. By 1959, a structured nomenclature was reached, allowing for further exploration, structured mapping of the region and a unique naming system. A 1990 ACAN gazeeter of Antarctica listed 16,000 names. Description The United States does not recognise territorial boundaries within Antarctica, so ACAN assigns names to features anywhere within the continent, in consultation with other national nomenclature bodies where appropriate, as defined by the Antarctic Treaty System. The research and staff support for the ACAN is provided by the United States Geologi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bell UH-1 Iroquois
The Bell UH-1 Iroquois (nicknamed "Huey") is a utility military helicopter designed and produced by the American aerospace company Bell Helicopter. It is the first member of the prolific Huey family, as well as the first turbine-powered helicopter in service with the United States military. Development of the Iroquois started in the early 1950s, a major impetus being a requirement issued by the United States Army for a new medical evacuation and utility helicopter. The Bell 204, first flown on 20 October 1956, was warmly received, particularly for the performance of its single turboshaft engine over piston engine-powered counterparts. An initial production contract for 100 ''HU-1A''s was issued in March 1960. In response to criticisms over the rotorcraft's power, Bell quickly developed multiple models furnished with more powerful engines; in comparison to the prototype's Lycoming YT53-L-1 (LTC1B-1) engine, producing , by 1966, the Lycoming T53-L-13, capable of , was bein ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
C83052s5 Schmidt Hills
C83 may refer to: *Byron Airport, a public airport serving Contra Costa County, California, USA. * '' Corydoras loxozonus'', a freshwater catfish. * Ruy Lopez The Ruy Lopez (; ), also called the Spanish Opening or Spanish Game, is a chess opening characterised by the moves: :1. e4 e5 :2. Nf3 Nc6 :3. Bb5 The Ruy Lopez remains one of the most popular chess openings, featuring many variations. In ... chess openings ECO code * Diffuse non-Hodgkin's lymphoma ICD-10 code * HMS Southampton (C83), a 1934 British Royal Navy cruiser * Labour Standards (Non-Metropolitan Territories) Convention, 1947 code * Caldwell 83 ( NGC 4945), a spiral galaxy in the constellation Centaurus C-83 may refer to : * C-83 Coupe, an aircraft {{Letter-NumberCombDisambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Median Snowfield
Torbert Escarpment () is an escarpment, long, marking the west margin of Median Snowfield in the Neptune Range, Pensacola Mountains, Antarctica. Mapping and name The Torbert Escarpment was mapped by United States Geological Survey (USGS) from surveys and United States Navy air photographs in 1956–66. It was named by the United States Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names (US-ACAN) after Mount Torbert, the salient feature along its edge. Location The Torbert Escarpment faces west in the northeast of the Neptune Range. It runs roughly north–south between the Median Snowfield to the east, and the north end of the Washington Escarpment to the west. Festures include, from south to north, Rivas Peaks, Mount Torbert and Ramsey Cliff. Nearby features to the east include Kaminski Nunatak, Loren Nunataks and Median Snowfield. Features Features and nearby features include: Kaminski Nunatak . A cone-shaped nunatak southeast of Rivas Peaks. Named by US-ACAN for Francis Kamins ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nunatak
A nunatak (from Inuit language, Inuit ) is the summit or ridge of a mountain that protrudes from an ice field or glacier that otherwise covers most of the mountain or ridge. They often form natural pyramidal peaks. Isolated nunataks are also called glacial islands, and smaller nunataks rounded by glacial action may be referred to as rognons. The word is of Greenlandic language, Greenlandic origin and has been used in English since the 1870s. Description The term ''nunatak'' is typically used in areas where a permanent ice sheet is present and the ridge protrudes above the sheet.J. J. Zeeberg, ''Climate and Glacial History of the Novaya Zemlya Archipelago, Russian Arctic''. pp. 82–84 Nunataks present readily identifiable landmark reference points in glaciers or ice caps and are often named. While some are isolated, they can also form dense clusters, such as Queen Louise Land in Greenland. Nunataks are generally angular and jagged, hampering the formation of glacial ice on thei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mount Hawkes
Mount Hawkes () is, at , the highest mountain along the Washington Escarpment, standing at the east side of Jones Valley in the Neptune Range of the Pensacola Mountains, Antarctica. Discovery and name Mount Hawkes was discovered and photographed on January 13, 1956, in the course of the trans-Antarctic nonstop plane flight by personnel of United States Navy Operation Deep Freeze I from McMurdo Sound to the Weddell Sea and return. It was named by the United States Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names for Commander William M. Hawkes of the United States Navy, who was the co-pilot of the P2V-2N Neptune aircraft making this flight. The Hawkes Heights are also named for Hawkes, who was assigned to Air Development Squadron Six (VX-6) in 1955–56. Location Mount Hawkes is towards the south of the Washington Escarpment, which runs from south to north through the length of the Neptune Range. The Jones Valley is to its west and the Iroquois Plateau is to its east. Gambacorta Pea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |