|
Ellerslie Railway Station
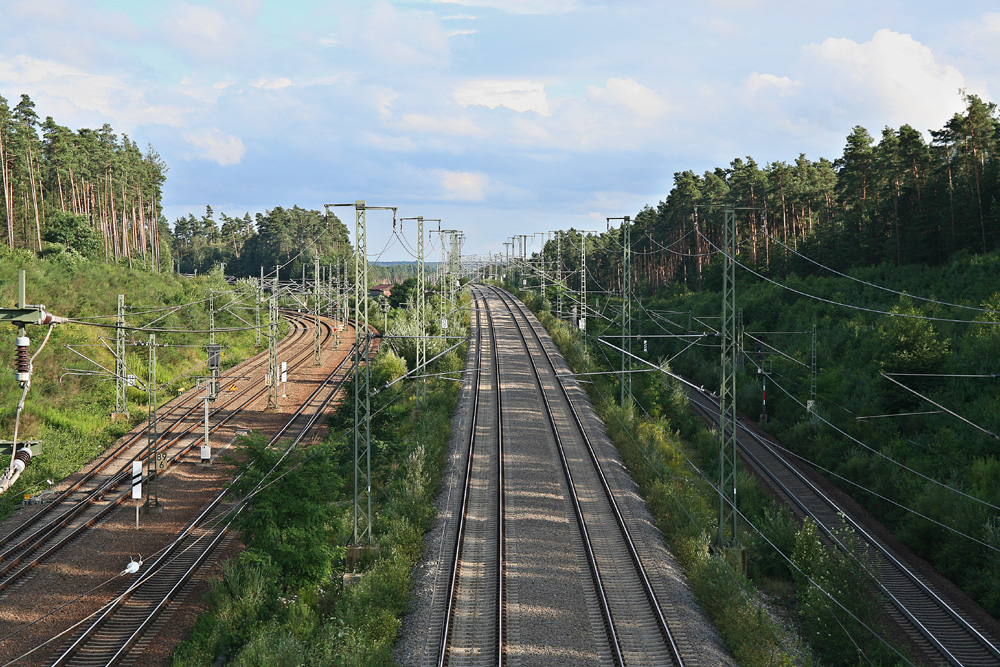
Ellerslie railway station serves the Southern and Onehunga Lines of the Auckland railway network in New Zealand. It was opened in 1873. It has an island platform and is south of Greenlane and north of Penrose. Access to Station Access to the station at the northern end was by a ramp down from the footbridge crossing the SH1 Southern Motorway between Main Highway, Ellerslie and Kalmia Street. At the southern end of the station there is a subway between Findlay Street and Sultan Street. History The station was on the railway line between Auckland and Onehunga via Newmarket, Ellerslie and Penrose, built by Brogden & Co. Completion was delayed by bankruptcy of a sub contractor. A trial passenger run was made on 24 October 1873 and, in November, passengers were carried to a point near the cricket ground, though there was no station. A temporary platform was then built. However, it wasn't until 20 December 1873 that the line opened with great public celebration, though only ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Newmarket, New Zealand
Newmarket is an Auckland suburb to the south-east of the central business district. With its high building density, especially of retail shops, it is considered New Zealand's premier retailing area, and a rival of local competitor Auckland CBD. While as early as 1873, Newmarket has been referred to as a 'suburb' of Auckland, in fact until the amalgamation of the borough councils into Auckland City Council in 1989, local governance was by the Newmarket Borough Council, with its own Mayor. The borough, while one of the smallest in the Auckland Region, was also one of the busiest. This is especially true of Broadway, the main street, which has large shopping centres and smaller retail tenancies (with a total of over 400 stores as of mid-2010), two movie theatres, and numerous restaurants, bars and cafés. History Māori beginnings Tāmaki Māori called this area, particularly the south of the current Newmarket, Te Tī Tūtahi, 'the cabbage tree standing alone' or 'the cab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Remuera Railway Station
Remuera railway station is a station serving the suburb of Remuera in Auckland, New Zealand. It is served by the Southern Line and the Onehunga Line, and consists of an island platform which is accessed by a ramp from the Market Road motorway overbridge. The station was opened in 1873. It includes a weatherboard and tile station building, typical of those designed by George Troup. Services Auckland One Rail, on behalf of Auckland Transport, operates suburban services on the Southern Line and Onehunga Line. All Southern Line services stop at Remuera. Since 26 August 2018, Onehunga Line services stop only in the evenings. The typical weekday off-peak timetable in trains per hour (tph) is: *3 tph to Britomart *3 tph to Papakura See also * List of Auckland railway stations This is a list of the railway stations in the public transport network of Auckland. It includes closed and planned stations. Auckland has 13 fare zones, with some zone overlap areas. The ro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Signalling Block System
Signalling block systems enable the safe and efficient operation of railways by preventing collisions between trains. The basic principle is that a track is broken up into a series of sections or "blocks". Only one train may occupy a block at a time, and the blocks are sized to allow a train to stop within them. That ensures that a train always has time to stop before getting dangerously close to another train on the same line. The block system is referred to in the UK as the ''method of working'', in the US as the ''method of operation'', and in Australia as ''safeworking''. In most situations, a system of signals is used to control the passage of trains between the blocks. When a train enters a block, signals at both ends change to indicate that the block is occupied, typically using red lamps or indicator flags. When a train first enters a block, the rear of the same train has not yet left the previous block, so both blocks are marked as occupied. That ensures there is sligh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Passing Loop
A passing loop (UK usage) or passing siding (North America) (also called a crossing loop, crossing place, refuge loop or, colloquially, a hole) is a place on a single line railway or tramway, often located at or near a station, where trains or trams travelling in opposite directions can pass each other. Trains/trams going in the same direction can also overtake, provided that the signalling arrangement allows it. A passing loop is double-ended and connected to the main track at both ends, though a dead end siding known as a refuge siding, which is much less convenient, can be used. A similar arrangement is used on the gauntlet track of cable railways and funiculars, and in passing places on single-track roads. Ideally, the loop should be longer than all trains needing to cross at that point. Unless the loop is of sufficient length to be dynamic, the first train to arrive must stop or move very slowly, while the second to arrive may pass at speed. If one train is too lo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Troup (architect)
Sir George Alexander Troup (21 October 1863 – 4 October 1941) was a New Zealand architect, engineer and statesman. He was nicknamed "Gingerbread George" after his most famous design, the Dunedin Railway Station in the Flemish Renaissance style (he preferred his alternative design in the Scottish Baronial style). He was the first official architect of the New Zealand Railways. He designed many other stations, including Lower Hutt and Petone. Early life and education He was born in London, England. His family returned to Edinburgh, Scotland soon after he was born. His widowed mother sent him to Robert Gordon's College, Aberdeen, where he was entitled to free board and tuition as the son of an Aberdeen burgess. He trained as an architect and engineer under C.E. Calvert in Edinburgh, and in 1882 was employed as a draughtsman by architect J.J.A. Chesser. Career He emigrated to New Zealand in 1884. Joining the Survey Department when he arrived in Dunedin, he worked in remote ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Onehunga Branch
The Onehunga Branch railway line is a section of the Onehunga Line in Auckland, New Zealand. It was constructed by the Auckland Province, Auckland Provincial Government and opened from Penrose Train Station, Penrose to Onehunga Train Station, Onehunga on 24 December 1873, and extended to Onehunga Wharf on 28 November 1878. It is in length and is single-track only. After being closed to passenger traffic on 19 January 1973 and mothballed in 2007, the line was reopened on 18 September 2010 with regular passenger services beginning on 19 September 2010. History Construction and original services The Onehunga Branch was part of one of the first government-funded railways in New Zealand. The Auckland and Drury Railway Act 1863 was passed by Parliament "to enable the Superintendent of the Province of Auckland to construct a Railway between the Towns of Auckland and Drury with a Branch to Onehunga in the said Province." Along with a further 10 km north to Auckland (now ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Branch Line
A branch line is a phrase used in railway terminology to denote a secondary railway line which branches off a more important through route, usually a main line. A very short branch line may be called a spur line. Industrial spur An industrial spur is a type of secondary track used by railroads to allow customers at a location to load and unload railcars without interfering with other railroad operations. Industrial spurs can vary greatly in length and railcar capacity depending on the requirements of the customer the spur is serving. In heavily industrialized areas, it is not uncommon for one industrial spur to have multiple sidings to several different customers. Typically, spurs are serviced by local trains responsible for collecting small numbers of railcars and delivering them to a larger yard, where these railcars are sorted and dispatched in larger trains with other cars destined to similar locations. Because industrial spurs generally have less capacity and traffi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North Auckland Line
The North Auckland Line (designation NAL) is a major section of New Zealand's national rail network, and is made up of the following parts: the portion of track that runs northward from Westfield Junction to Newmarket Station; from there, westward to Waitakere; from there, northward to Otiria via Whangārei. The first section was opened in 1868 and the line was completed in 1925. The line, or sections of it, have been known at various times as the Kaipara Line, the Waikato-Kaipara Line, the Kaipara Branch and the North Auckland Main Trunk. North Auckland Line is a designation for the section of track, not a service route. The southernmost portion from Westfield Junction to Newmarket was originally built as part of the North Island Main Trunk railway, with Newmarket serving as the junction of the two lines. The North Island Main Trunk was re-routed in 1930 via the Westfield Deviation through Glen Innes and Panmure. Westfield-Newmarket was then incorporated into the North ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North Island Main Trunk
The North Island Main Trunk (NIMT) is the main railway line in the North Island of New Zealand, connecting the capital city Wellington with the country's largest city, Auckland. The line is long, built to the New Zealand rail gauge of and serves the large cities of Palmerston North and Hamilton. Most of the NIMT is single track with frequent passing loops, but has double track - * between Wellington and Waikanae, except for of single-track through tunnels between North Junction ( from Wellington) and South Junction, ( from Wellington), on the Pukerua Bay to Paekakariki section, * between Hamilton and Te Kauwhata (except for the single-track Waikato River Bridge at Ngāruawāhia), and * between Meremere and Auckland Britomart. Around (approximately 65%) of the line is electrified in three separate sections: one section at 1600 V DC between Wellington and Waikanae, and two sections at 25 kV AC: between Palmerston North and Te Rapa (Hamilton) and between Papakura ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pleasure Garden
A pleasure garden is a park or garden that is open to the public for recreation and entertainment. Pleasure gardens differ from other public gardens by serving as venues for entertainment, variously featuring such attractions as concert halls, bandstands, amusement rides, zoos, and menageries. Historically a "pleasure garden" or '' pleasure ground'' meant private flower gardens, shrub gardens or formal wooded areas such as bosquets, that were planted for enjoyment, with ornamental plants and neat paths for walking. These were distinguished from the areas in a large garden planted as lawns or a landscaped park, or the "useful" areas of the kitchen garden and woodland. Thus most modern gardens would have been called "pleasure gardens", especially in the 17th and 18th centuries. The two meanings of the term, as the ornamental parts of a garden, and as a commercial place of entertainment, coexisted in English from at least the 17th century. History Public pleasure garde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Graham (New Zealand Politician)
Robert Graham (15 May 1820 – 26 May 1885) was a 19th-century New Zealand politician in the Auckland area. Early life Graham was born in 1820 in the parish of Barony in Glasgow, Scotland. His parents were Barbara Stirling Rennie and the farmer and coal merchant Robert Graham. His brother was David Graham. Political career He represented the Southern Division electorate (containing Waikato, Coromandel, the Bay of Plenty, and East Cape) in the 2nd New Zealand Parliament from 1855 to 1860, and then represented the Franklin electorate in the 3rd Parliament and the 4th Parliament from 1861 to 1868, when he resigned. He was the fifth Superintendent of Auckland Auckland (pronounced ) ( mi, Tāmaki Makaurau) is a large metropolitan city in the North Island of New Zealand. The most populous urban area in the country and the fifth largest city in Oceania, Auckland has an urban population of about I ... from 1862 to 1865. Prior to this, he had represented the So ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)