|
Elisa Acuña
Elisa Acuña Rossetti (also Rosete, Rosseti, 1872-1946) was a Mexican anarchist and educator, feminist and journalist, revolutionary and leader of the Mexican Cultural Missions against illiteracy. Early life María Elisa Brígida Lucía Acuña Rosetti was born 8 October 1872 in Mineral del Monte, Hidalgo, Mexico to Antonio Acuña and Mauricia Rosete. Though there were several configurations of her name which appear in records, she signed her name as Elisa Acuña Rosseti. At age 13, she began teaching basic reading, writing, arithmetic, national history, pedagogy and drawing, in the rural schools of the area. She witnessed much poverty and discrimination, which had a profound effect on her development. Pre-revolutionary radicalism In 1900, she graduated with teaching credentials and the following year she joined the Liberal Club "Ponciano Arriaga" created by Camilo Arriaga. The club members were ardent supporters of the brothers Ricardo and Enrique Flores Magón, anarchist journ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mineral Del Monte
Mineral del Monte, commonly called Real del Monte () or El Real, is a small mining town, and one of the 84 municipalities of Hidalgo, in the State of Hidalgo in east-central Mexico. It is located at an altitude of . As of 2005, the municipality had a total population of 11,944 — with Mauricio Rodriguez Téllez as head of the municipal council. History The Mine District of Pachuca—Real del Monte has a long and rich heritage. The mines in the district are conservatively estimated to have produced 1.2 billion Troy ounces of silver and 6.2 million ounces of gold. That is 6% of the silver mined throughout the world during the last five centuries. Some of the mines have continued limited production until the present day. Gold and silver were discovered after the Spanish conquest of Mexico in the 1520s. The Colonial Spanish began mining in the 16th century in the Pachuca area, but the mines were suffering from flooding by 1725. In 1741, Pedro Romero de Terreros and Jose Alej ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
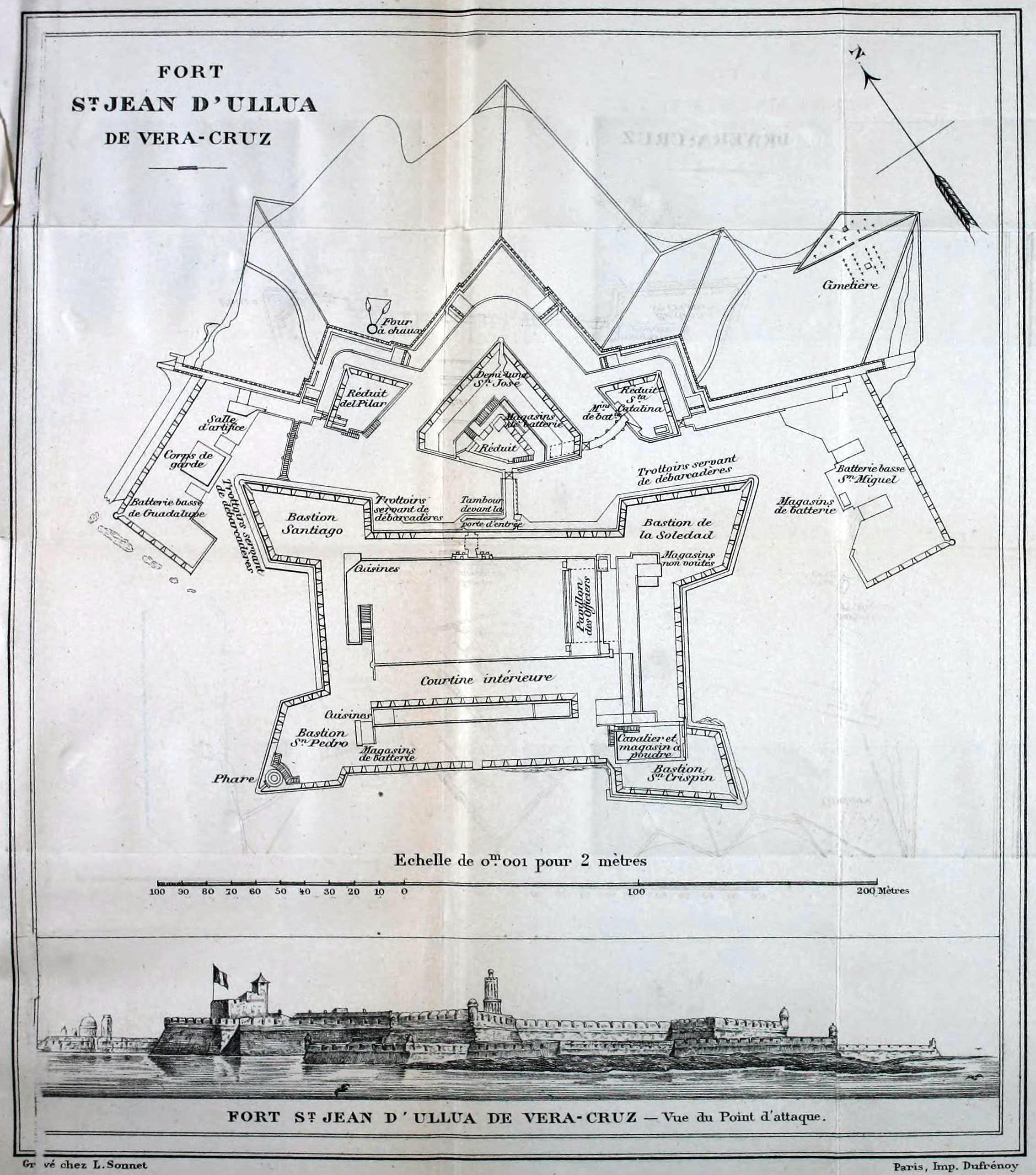
San Juan De Ulúa
San Juan de Ulúa, also known as Castle of San Juan de Ulúa, is a large complex of fortresses, prisons and one former palace on an island of the same name in the Gulf of Mexico overlooking the seaport of Veracruz, Mexico. Juan de Grijalva's 1518 expedition named the island. On Easter Sunday 1519, Hernan Cortés met with Tendile and Pitalpitoque, emissaries from Moctezuma II's Aztec Empire.Diaz, B., 1963, The Conquest of New Spain, London: Penguin Books, It was built between 1535 and 1769. There is a local museum of the fortress, inaugurated in 1984. History The fort was constructed during the period of Spanish colonial rule, with construction being initiated in 1535 by the Spanish authorities. The boundaries of the fort were repeatedly expanded several times during its existence. In 1568, the Spanish forces stationed on the fortress succeeded in trapping a privateer fleet under the command of John Hawkins in the fortress's harbour. The commanders under Hawk ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1872 Births
Year 187 ( CLXXXVII) was a common year starting on Sunday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Quintius and Aelianus (or, less frequently, year 940 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 187 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years. Events By place Roman Empire * Septimius Severus marries Julia Domna (age 17), a Syrian princess, at Lugdunum (modern-day Lyon). She is the youngest daughter of high-priest Julius Bassianus – a descendant of the Royal House of Emesa. Her elder sister is Julia Maesa. * Clodius Albinus defeats the Chatti, a highly organized German tribe that controlled the area that includes the Black Forest. By topic Religion * Olympianus succeeds Pertinax as bishop of Byzantium (until 198). Births * Cao Pi, Chinese emperor of the Cao Wei st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pachuca
Pachuca (; ote, Nju̱nthe), formally known as Pachuca de Soto, is the capital and largest city of the Mexican state of Hidalgo. It is located in the south-central part of the state. Pachuca de Soto is also the name of the municipality of which the city serves as municipal seat. Pachuca is located about from Mexico City via Mexican Federal Highway 85. There is no consensus about the origin of the name ''Pachuca''. It has been traced to the word ''pachoa'' (strait; opening), ''Pachoacan'' (place of government; place of silver and gold), and ''patlachuican'' (place of factories; place of tears). The official name of Pachuca is Pachuca de Soto in honor of congressman Manuel Fernando Soto, who is given credit for the creation of Hidalgo state. Its nickname of "La bella airosa" (Beautiful Airy City) comes from the strong winds that blow into the valley through the canyons to the north of the city. In the indigenous Otomi language, Pachuca is known as . The area had been long inh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zacatecas
, image_map = Zacatecas in Mexico (location map scheme).svg , map_caption = State of Zacatecas within Mexico , coordinates = , coor_pinpoint = , coordinates_footnotes = , subdivision_type = Country , subdivision_name = Mexico , subdivision_type1 = Capital , subdivision_name1 = Zacatecas , subdivision_type2 = Municipalities , subdivision_name2 = 58 , established_title = Admission , established_date = December 23, 1823 , established_title2 = Order , established_date2 = 10th , founder = , seat_type = , seat = , government_footnotes = , leader_party = , leader_title = Governor , leader_name = David Monreal Ávila , leader_title1 = Senators , leader_name1 = , leader_title2 = Deputies , leader_name2 = , unit_ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
San Luis Potosí
San Luis Potosí (), officially the Free and Sovereign State of San Luis Potosí ( es, Estado Libre y Soberano de San Luis Potosí), is one of the 32 states which compose the Federal Entities of Mexico. It is divided in 58 municipalities and its capital city is San Luis Potosí City. Located in Central Mexico, San Luis Potosí is bordered by seven other Mexican states: Nuevo León to the north; Tamaulipas to the north-east; Veracruz to the east; Hidalgo, Querétaro and Guanajuato to the south; and Zacatecas to north-west. In addition to the capital city, other major cities in the state include Ciudad Valles, Matehuala, Rioverde, and Tamazunchale. History In pre-Columbian times, the territory now occupied by the state of San Luis Potosí contained parts of the cultural areas of Mesoamerica and Aridoamerica. Its northern and western-central areas were inhabited by the Otomi and Chichimeca tribes. These indigenous groups were nomadic hunter-gatherers. Although many indi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aguascalientes
Aguascalientes (; ), officially the Free and Sovereign State of Aguascalientes ( es, Estado Libre y Soberano de Aguascalientes), is one of the 32 states which comprise the Federal Entities of Mexico. At 22°N and with an average altitude of above sea level it is predominantly of semi-arid climate ( Bhs and Bhk), and it is located in the northern part of the Bajío region, in north-central Mexico, bordered by Zacatecas to the north, east and west, and by Jalisco to the south. As of 2019, Aguascalientes has a population of 1.4 million inhabitants, most of whom live in its capital city, also named Aguascalientes. Its name means "hot waters" and originated from the abundance of hot springs originally found in the area. The demonym for the state's inhabitants is ''hidrocálido'' or ''aguascalentense''. Aguascalientes is one of the smallest states of Mexico, either by population or land, being the 27th most populated state and the 29th biggest state by area; nonetheless, it is the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Secretariat Of Public Education (Mexico)
The Mexican Secretariat of Public Education ( in Spanish ''Secretaría de Educación Pública'', ''SEP'') is a federal government authority with cabinet representation and the responsibility for overseeing the development and implementation of national educational policy and school standards in Mexico. Its headquarters has several buildings distributed throughout the country, but its main offices, initially confined to the Old Dominican Convent of the Holy Incarnation in the oldest borough of Mexico City, have extended to the House of the Marqués de Villamayor, (also known as the ''Casa de los adelantados de Nueva Galicia'', built in 1530), the Old House of don Cristóbal de Oñate, a three-time governor and general captain of New Galicia (also built in 1530), and the Old Royal Customs House (built in 1730–1731). Some of the buildings were decorated with mural paintings by Diego Rivera and other notable exponents of the Mexican muralist movement of the twentieth century, Da ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Venustiano Carranza
José Venustiano Carranza de la Garza (; 29 December 1859 – 21 May 1920) was a Mexican wealthy land owner and politician who was Governor of Coahuila when the constitutionally elected president Francisco I. Madero was overthrown in a February 1913 right-wing military coup. Known as the ''Primer Jefe'' or "First Chief" of the Constitutionalist faction in the Mexican Revolution, Carranza was a shrewd civilian politician. He supported Madero's challenge to the Díaz regime in the 1910 elections, but became a critic of Madero once Díaz was overthrown in May 1911. Madero did appoint him the governor of Coahuila. When Madero was murdered during the February 1913 counter-revolutionary coup, Carranza drew up the Plan of Guadalupe, a purely political plan to oust Madero's usurper, General Victoriano Huerta. As a sitting governor when Madero was overthrown, Carranza held legitimate power and he became the leader of the northern coalition opposed to Huerta. The Constitutionalist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Puebla
Puebla ( en, colony, settlement), officially Free and Sovereign State of Puebla ( es, Estado Libre y Soberano de Puebla), is one of the 32 states which comprise the Federal Entities of Mexico. It is divided into 217 municipalities and its capital is the city of Puebla. It is located in East-Central Mexico. It is bordered by the states of Veracruz to the north and east, Hidalgo, México, Tlaxcala and Morelos to the west, and Guerrero and Oaxaca to the south. The origins of the state lie in the city of Puebla, which was founded by the Spanish in this valley in 1531 to secure the trade route between Mexico City and the port of Veracruz. By the end of the 18th century, the area had become a colonial province with its own governor, which would become the State of Puebla, after the Mexican War of Independence in the early 19th century. Since that time the area, especially around the capital city, has continued to grow economically, mostly through industry, despite being the scen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emiliano Zapata
Emiliano Zapata Salazar (; August 8, 1879 – April 10, 1919) was a Mexican revolutionary. He was a leading figure in the Mexican Revolution of 1910–1920, the main leader of the people's revolution in the Mexican state of Morelos, and the inspiration of the agrarian movement called '' Zapatismo''. Zapata was born in the rural village of Anenecuilco in Morelos, in an era when peasant communities came under increasing repression from the small-landowning class who monopolized land and water resources for sugarcane production with the support of dictator Porfirio Díaz (President from 1877 to 1880 and 1884 to 1911). Zapata early on participated in political movements against Díaz and the landowning '' hacendados'', and when the Revolution broke out in 1910 he became a leader of the peasant revolt in Morelos. Cooperating with a number of other peasant leaders, he formed the Liberation Army of the South, of which he soon became the undisputed leader. Zapata's forces contributed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Victoriano Huerta
José Victoriano Huerta Márquez (; 22 December 1854 – 13 January 1916) was a general in the Mexican Federal Army and 39th President of Mexico, who came to power by coup against the democratically elected government of Francisco I. Madero with the aid of other Mexican generals and the U.S. Ambassador to Mexico. His violent seizure of power set off a new wave of armed conflict in the Mexican Revolution. After a military career under President Porfirio Díaz and Interim President Francisco León de la Barra, Huerta became a high-ranking officer during the presidency of Madero during the first phase of the Mexican Revolution (1911–13). In February 1913 Huerta joined a conspiracy against Madero, who entrusted him to control a revolt in Mexico City. The Ten Tragic Days – actually fifteen days – saw the forced resignation of Madero and his vice president and their murders. The coup was backed by the nascent German Empire as well as the United States under the Taft admin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |