|
Eli Siegel
Eli Siegel (August 16, 1902 – November 8, 1978) was a poet, critic, and educator. He founded Aesthetic Realism, a philosophical movement based in New York City. An idea central to Aesthetic Realism—that every person, place or thing in reality has something in common with all other things—was expressed in the title poem of his first volume, '' Hot Afternoons Have Been in Montana: Poems''. His second volume was ''Hail, American Development''. Siegel's philosophic works include ''Self and World: An Explanation of Aesthetic Realism,'' ''Definitions, and Comment: Being a Description of the World,'' and ''The Aesthetic Nature of the World''. His teaching of Aesthetic Realism spanned almost four decades and included thousands of extemporaneous lectures on poetry, the arts and sciences, religion, economics, and national ethics, as well as lessons to individuals and general classes which showed that questions of everyday life are aesthetic and ethical. His lecture on the poetry of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dvinsk
Daugavpils (see also other names) is a state city in southeastern Latvia, located on the banks of the Daugava River, from which the city derives its name. The parts of the city to the north of the river belong to the historical Latvian region of Latgale, and those to the south lie in Selonia. It is the second-largest city in the country after the capital Riga, which is located some northwest and is the ninth most populous city in the Baltic states. Daugavpils is located relatively close to Belarus and Lithuania (distances of and , respectively), and some from the Latvian border with Russia. Daugavpils is a major railway junction and industrial centre, and was an historically important garrison city lying approximately midway between Riga and Minsk, and between Warsaw and Saint Petersburg. Daugavpils, then called Dyneburg, was the capital of Polish Livonia while in Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. Following the first partition of Poland in 1772, the city became part of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poetry
Poetry (from the Greek language, Greek word ''poiesis'', "making") is a form of literature, literary art that uses aesthetics, aesthetic and often rhythmic qualities of language to evoke meaning (linguistics), meanings in addition to, or in place of, Denotation, literal or surface-level meanings. Any particular instance of poetry is called a poem and is written by a poet. Poets use a variety of techniques called poetic devices, such as assonance, alliteration, Phonaesthetics#Euphony and cacophony, euphony and cacophony, onomatopoeia, rhythm (via metre (poetry), metre), and sound symbolism, to produce musical or other artistic effects. They also frequently organize these effects into :Poetic forms, poetic structures, which may be strict or loose, conventional or invented by the poet. Poetic structures vary dramatically by language and cultural convention, but they often use Metre (poetry), rhythmic metre (patterns of syllable stress or syllable weight, syllable (mora) weight ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Journal Of Aesthetics And Art Criticism
''The Journal of Aesthetics and Art Criticism'' is a quarterly peer-reviewed academic journal covering the study of aesthetics and art criticism. It was published by Wiley-Blackwell Wiley-Blackwell is an international scientific, technical, medical, and scholarly publishing business of John Wiley & Sons. It was formed by the merger of John Wiley & Sons Global Scientific, Technical, and Medical business with Blackwell Publish ... on behalf of the American Society for Aesthetics up to January 2021 when it shifted to Oxford University Press. External links * * Aesthetics journals Wiley-Blackwell academic journals Quarterly journals Academic journals established in 1941 English-language journals Academic journals associated with learned and professional societies {{aesthetics-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polarity
Polarity may refer to: Science *Electrical polarity, direction of electrical current *Polarity (mutual inductance), the relationship between components such as transformer windings *Polarity (projective geometry), in mathematics, a duality of order two * Polarity in embryogenesis, the animal and vegetal poles within a blastula *Cell polarity, differences in the shape, structure, and function of cells *Chemical polarity, in chemistry, a separation of electric charge *Magnetic polarity, north or south poles of a magnet *Polar reciprocation, a concept in geometry also known as polarity * Trilinear polarity, a concept in geometry of the triangle *Polarity of a literal, in mathematical logic Humanities *Polarity (international relations), a description of the distribution of power within the international system *Polarity of gender, when a word takes the opposite grammatical gender than expected *Polarity item, in linguistics, the sensitiveness of some expression to negative or affirma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Contraries
In term logic (a branch of philosophical logic), the square of opposition is a diagram representing the relations between the four basic categorical propositions. The origin of the square can be traced back to Aristotle's tractate ''On Interpretation'' and its distinction between two oppositions: contradiction and contrariety. However, Aristotle did not draw any diagram; this was done several centuries later by Boethius. Summary In traditional logic, a proposition (Latin: ''propositio'') is a spoken assertion (''oratio enunciativa''), not the meaning of an assertion, as in modern philosophy of language and logic. A ''categorical proposition'' is a simple proposition containing two terms, subject () and predicate (), in which the predicate is either asserted or denied of the subject. Every categorical proposition can be reduced to one of four logical forms, named , , , and based on the Latin ' (I affirm), for the affirmative propositions and , and ' (I deny), for the nega ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Martin Buber
Martin Buber (; , ; ; 8 February 1878 – 13 June 1965) was an Austrian-Israeli philosopher best known for his philosophy of dialogue, a form of existentialism centered on the distinction between the I and Thou, I–Thou relationship and the I–It relationship. Born in Vienna, Buber came from a family of observant Jews, but broke with Jewish custom to pursue secular studies in philosophy. He produced writings about Zionism and worked with various bodies within the Zionist movement extensively over a nearly 50-year period spanning his time in Europe and the Near East. In 1923, Buber wrote his famous essay on existence, ''I and Thou, Ich und Du'' (later translated into English as ''I and Thou''), and in 1925 he began translating the Hebrew Bible into the German language. He was nominated for the Nobel Prize in Literature ten times, and the Nobel Peace Prize seven times. Biography Martin (Hebrew language, Hebrew name: ''מָרְדֳּכַי,'' ''Mordechai'') Buber was born in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hegel
Georg Wilhelm Friedrich Hegel (27 August 1770 – 14 November 1831) was a 19th-century German idealism, German idealist. His influence extends across a wide range of topics from metaphysical issues in epistemology and ontology, to political philosophy and the aesthetics, philosophy of art and philosophy of religion, religion. Born in 1770 in Stuttgart, Holy Roman Empire, during the transitional period between the Age of Enlightenment#German states, Enlightenment and the German Romanticism, Romantic movement in the Germanic regions of Europe, Hegel lived through and was influenced by the French Revolution and the Napoleonic wars. His fame rests chiefly upon the ''The Phenomenology of Spirit, Phenomenology of Spirit'', the ''Science of Logic'', and his Teleology, teleological account of history. Throughout his career, Hegel strove to correct what he argued were untenable Mind–body dualism, dualisms endemic to modern philosophy (typically by drawing upon the resources of ancient ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Immanuel Kant
Immanuel Kant (born Emanuel Kant; 22 April 1724 – 12 February 1804) was a German Philosophy, philosopher and one of the central Age of Enlightenment, Enlightenment thinkers. Born in Königsberg, Kant's comprehensive and systematic works in epistemology, metaphysics, ethics, and aesthetics have made him one of the most influential and highly discussed figures in modern Western philosophy. In his doctrine of transcendental idealism, Kant argued that space and time are mere "forms of intuition" that structure all experience and that the objects of experience are mere "appearances". The nature of things as they are in themselves is unknowable to us. Nonetheless, in an attempt to counter the philosophical doctrine of Philosophical skepticism, skepticism, he wrote the ''Critique of Pure Reason'' (1781/1787), his best-known work. Kant drew a parallel to the Copernican Revolution#Immanuel Kant, Copernican Revolution in his proposal to think of the objects of experience as confo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aristotle
Aristotle (; 384–322 BC) was an Ancient Greek philosophy, Ancient Greek philosopher and polymath. His writings cover a broad range of subjects spanning the natural sciences, philosophy, linguistics, economics, politics, psychology, and the arts. As the founder of the Peripatetic school of philosophy in the Lyceum (classical), Lyceum in Athens, he began the wider Aristotelianism, Aristotelian tradition that followed, which set the groundwork for the development of modern science. Little is known about Aristotle's life. He was born in the city of Stagira (ancient city), Stagira in northern Greece during the Classical Greece, Classical period. His father, Nicomachus (father of Aristotle), Nicomachus, died when Aristotle was a child, and he was brought up by a guardian. At around eighteen years old, he joined Plato's Platonic Academy, Academy in Athens and remained there until the age of thirty seven (). Shortly after Plato died, Aristotle left Athens and, at the request ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heraclitus
Heraclitus (; ; ) was an Ancient Greece, ancient Greek Pre-Socratic philosophy, pre-Socratic philosopher from the city of Ephesus, which was then part of the Achaemenid Empire, Persian Empire. He exerts a wide influence on Western philosophy, both Ancient philosophy, ancient and Modern philosophy, modern, through the works of such authors as Plato, Aristotle, Georg Wilhelm Friedrich Hegel, Hegel, Friedrich Nietzsche, Nietzsche, and Martin Heidegger, Heidegger. Little is known of Heraclitus's life. He wrote a single work, only Literary fragment, fragments of which have survived. Even in ancient times, his Paradox#In philosophy, paradoxical philosophy, appreciation for Word play, wordplay, and cryptic, oracular epigrams earned him the epithets "the dark" and "the obscure". He was considered arrogant and depressed, a Misanthropy, misanthrope who was subject to melancholia. Consequently, he became known as "the weeping philosopher" in contrast to the ancient ancient atomism, atom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Library Journal
''Library Journal'' is an American trade publication for librarians. It was founded in 1876 by Melvil Dewey. It reports news about the library world, emphasizing public libraries, and offers feature articles about aspects of professional practice. It also reviews library-related materials and equipment. Each year since 2008, the Journal has assessed public libraries and awarded stars in their Star Libraries program. Its "Library Journal Book Review" does pre-publication reviews of several hundred popular and academic books each month. With a circulation of approximately 100,000, ''Library Journal'' has the highest circulation of any librarianship journal, according to Ulrich's. ''Library Journal's'' original publisher was Frederick Leypoldt, whose company became R. R. Bowker. Reed International later merged into Reed Elsevier and purchased Bowker in 1985; they published ''Library Journal'' until 2010, when it was sold to Media Source Inc., owner of the Junior Library G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
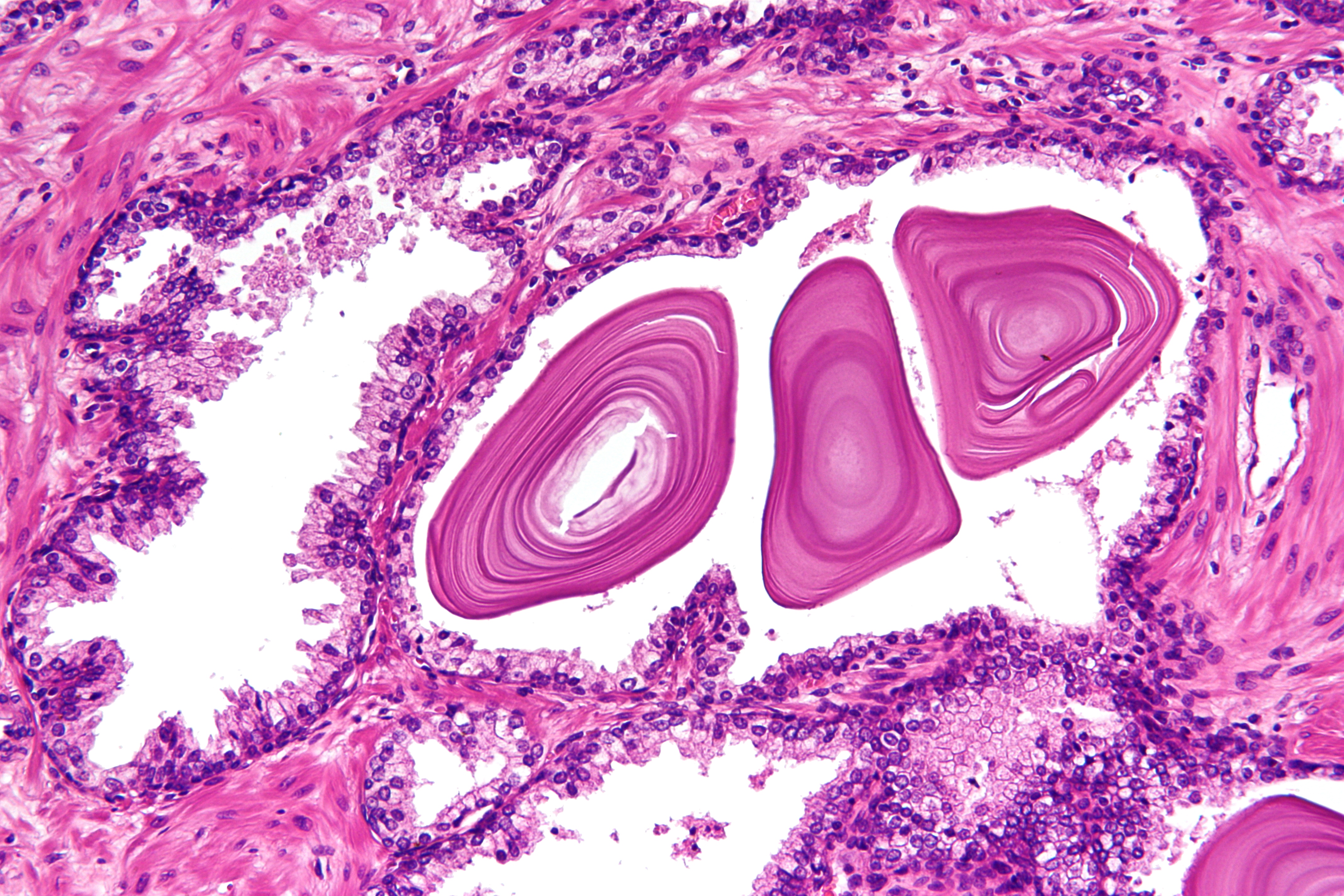
Prostate
The prostate is an male accessory gland, accessory gland of the male reproductive system and a muscle-driven mechanical switch between urination and ejaculation. It is found in all male mammals. It differs between species anatomically, chemically, and physiologically. Anatomically, the prostate is found below the bladder, with the urethra passing through it. It is described in gross anatomy as consisting of lobes and in microanatomy by zone. It is surrounded by an elastic, fibromuscular capsule and contains glandular tissue, as well as connective tissue. The prostate produces and contains fluid that forms part of semen, the substance emitted during ejaculation as part of the male human sexual response cycle, sexual response. This prostatic fluid is slightly Alkalinity, alkaline, milky or white in appearance. The alkalinity of semen helps neutralize the acidity of the vagina, vaginal tract, prolonging the lifespan of sperm. The prostatic fluid is expelled in the first part of ej ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |