|
Elementaves
Elementaves is a proposed clade of birds, comprising a diverse group of birds who occupy various different ecological niches. They include the clades Phaethoquornithes and Strisores, as well as the Gruimorphae and Opisthocomiformes. According to Stiller ''et al.'' (2024), it is one of the four major subclades of Neoaves and sister to Telluraves. The clade's name refers to the classical elements The classical elements typically refer to earth, water, air, fire, and (later) aether which were proposed to explain the nature and complexity of all matter in terms of simpler substances. Ancient cultures in Greece, Angola, Tibet, India, ..., reflecting its members' varying adaptations to earth, air, and water. References Neognathae {{improve categories, date=April 2024 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neoaves
Neoaves is a clade that consists of all modern bird Birds are a group of warm-blooded vertebrates constituting the class (biology), class Aves (), characterised by feathers, toothless beaked jaws, the Oviparity, laying of Eggshell, hard-shelled eggs, a high Metabolism, metabolic rate, a fou ...s (Neornithes or Aves) with the exception of Palaeognathae (ratites and kin) and Galloanserae (ducks, chickens and kin). This group is defined in the '' PhyloCode'' by George Sangster and colleagues in 2022 as "the most inclusive crown clade containing '' Passer domesticus'', but not '' Gallus gallus''". Almost 95% of the roughly 10,000 known species of extant birds belong to the Neoaves. The early diversification of the various neoavian groups occurred very rapidly around the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event, and attempts to resolve their relationships with each other have resulted initially in much controversy. Phylogeny The early diversification of the various neoavia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Larus Pacificus
The Pacific gull (''Larus pacificus'') is a gull, native to the coasts of Australia. It is moderately common between Carnarvon in the west, and Sydney in the east, although it has become scarce in some parts of the south-east, as a result of competition from the kelp gull, which has "self-introduced" since the 1940s. Much larger than the ubiquitous silver gull, and much less common, Pacific gulls are usually seen alone or in pairs, loafing around the shoreline, steadily patrolling high above the edge of the water, or sometimes flying high on the breeze to drop a shellfish or sea urchin onto rocks. Diet The gulls' diet consists of a number various fish species and invertebrates. They frequently consume crabs, most often the species '' Ovalipes australiensis'' and '' Paragrapsus gaimardii.'' They also commonly eat ''Platycephalus bassensis'' (sand flatheads) and cephalopods, both of which are sourced from their regular consumption of waste from fish which have been cleaned on wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paleocene
The Paleocene ( ), or Palaeocene, is a geological epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from about 66 to 56 mya (unit), million years ago (mya). It is the first epoch of the Paleogene Period (geology), Period in the modern Cenozoic Era (geology), Era. The name is a combination of the Ancient Greek ''palaiós'' meaning "old" and the Eocene Epoch (which succeeds the Paleocene), translating to "the old part of the Eocene". The epoch is bracketed by two major events in Earth's history. The K–Pg extinction event, brought on by an asteroid impact (Chicxulub impact) and possibly volcanism (Deccan Traps), marked the beginning of the Paleocene and killed off 75% of species, most famously the non-avian dinosaurs. The end of the epoch was marked by the Paleocene–Eocene Thermal Maximum (PETM), which was a major climatic event wherein about 2,500–4,500 gigatons of carbon were released into the atmosphere and ocean systems, causing a spike in global temperatures and ocean acidification. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clade
In biology, a clade (), also known as a Monophyly, monophyletic group or natural group, is a group of organisms that is composed of a common ancestor and all of its descendants. Clades are the fundamental unit of cladistics, a modern approach to taxonomy adopted by most biological fields. The common ancestor may be an individual, a population, or a species (extinct or Extant taxon, extant). Clades are nested, one in another, as each branch in turn splits into smaller branches. These splits reflect evolutionary history as populations diverged and evolved independently. Clades are termed ''monophyletic'' (Greek: "one clan") groups. Over the last few decades, the cladistic approach has revolutionized biological classification and revealed surprising evolutionary relationships among organisms. Increasingly, taxonomists try to avoid naming Taxon, taxa that are not clades; that is, taxa that are not Monophyly, monophyletic. Some of the relationships between organisms that the molecul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Opisthocomidae
Opisthocomidae is a family of birds, the only named family within the order Opisthocomiformes. The only living representative is the hoatzin (''Opisthocomus hoazin'') which lives in the Amazon and the Orinoco delta in South America. Several fossil species have been identified, including one from Africa and one from Europe. Phylogeny The phylogeny below is based on the work of Hughes & Baker 1999 and Mayr & De Pietri 2014. Traditionally classified among the fowl-like birds (Galliformes), recent studies have favored Opisthocomidae's placement within the Neoaves. Taxonomy * Family Opisthocomidae Swainson 1837Mikko's Phylogeny Archiv ** Genus ?†'' Foro (bird), Foro'' Olson 1992 (mid-Eocene, USA) - cuculiform? *** Species †'' Foro panarium'' Olson 1992 ** Genus ?†'' Onychopteryx'' Cracraft 1971 (Early Eocene of Argentina) – falconid? A ''nomen dubium'' *** Species †'' Onychopteryx simpsoni'' Cracraft 1971 ** Genus †'' Protoazin'' Mayr & De Pietri 2014 (late Eocene of Fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gruimorphae
Gruimorphae is a clade of birds that contains the orders Charadriiformes (plovers, gulls, and allies) and Gruiformes (cranes and rails) identified by molecular analysis. This grouping has had historical support, as various charadriiform families such as the families Pedionomidae and Turnicidae were classified as gruiforms. It may also have support from the fossil record since the discovery of '' Nahmavis'' from the Early Eocene of North America. The relationship between these birds is due to similar anatomical and behavioral characteristics. A morphological study went further to suggest that the gruiforms might be paraphyletic in respect to the shorebirds, with the rails being closely related to the buttonquail Buttonquail or hemipodes are members of a small family of birds, Turnicidae, which resemble, but are not closely related to, the quails of Phasianidae. They inhabit warm grasslands in Asia, Africa, Europe, and Australia. There are 18 species in ...s. References ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strisores
Strisores ( ), sometimes called nightbirds, is a clade of birds that includes the living family (biology), families and order (biology), orders Caprimulgidae (nightjars, nighthawks and allies), Nyctibiidae (potoos), Steatornithidae (oilbirds), Podargidae (frogmouths), Apodiformes (swifts and hummingbirds), as well as the Aegotheliformes (owlet-nightjars) whose distinctness was only recently realized. The Apodiformes (which include the "Trochiliformes" of the Sibley-Ahlquist taxonomy) and the Aegotheliformes form the Apodimorphae, Daedalornithes. Description The material evidence for this group is very equivocal; the most ancient Strisores are quite nondescript tree-dwellers but already tend towards peculiarly apomorphic feet, and no Cretaceous fossils are known. Torpor and other metabolic peculiarities are frequently found in this group, perhaps more often than in any other bird lineage. The synapomorphies that define this clade are the ''ossa maxillaria'' separated by a large c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phaethoquornithes
Phaethoquornithes is a clade of birds that contains Eurypygimorphae and Aequornithes, which was first recovered by genome analysis in 2014. Members of Eurypygimorphae were originally classified in the obsolete group Metaves, and Aequornithes were classified as the sister taxon to Musophagiformes or Gruiformes. This group has also been informally called Ardeae. Older classifications have used Ardeae in a different sense, as a suborder of Ciconiiformes containing herons and related species. George Sangster and colleagues in 2022 named and defined this clade in the ''PhyloCode'' as the least inclusive crown clade containing '' Phaethon aethereus'' and '' Pelecanus onocrotalus'', but not '' Apus apus'', '' Charadrius hiaticula'', '' Musophaga violacea'', or ''Passer domesticus''. Cladogram A cladogram (from Greek language, Greek ''clados'' "branch" and ''gramma'' "character") is a diagram used in cladistics to show relations among organisms. A cladogram is not, however, an P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clade
In biology, a clade (), also known as a Monophyly, monophyletic group or natural group, is a group of organisms that is composed of a common ancestor and all of its descendants. Clades are the fundamental unit of cladistics, a modern approach to taxonomy adopted by most biological fields. The common ancestor may be an individual, a population, or a species (extinct or Extant taxon, extant). Clades are nested, one in another, as each branch in turn splits into smaller branches. These splits reflect evolutionary history as populations diverged and evolved independently. Clades are termed ''monophyletic'' (Greek: "one clan") groups. Over the last few decades, the cladistic approach has revolutionized biological classification and revealed surprising evolutionary relationships among organisms. Increasingly, taxonomists try to avoid naming Taxon, taxa that are not clades; that is, taxa that are not Monophyly, monophyletic. Some of the relationships between organisms that the molecul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bird
Birds are a group of warm-blooded vertebrates constituting the class (biology), class Aves (), characterised by feathers, toothless beaked jaws, the Oviparity, laying of Eggshell, hard-shelled eggs, a high Metabolism, metabolic rate, a four-chambered heart, and a strong yet lightweight Bird skeleton, skeleton. Birds live worldwide and range in size from the bee hummingbird to the common ostrich. There are over 11,000 living species and they are split into 44 Order (biology), orders. More than half are passerine or "perching" birds. Birds have Bird wing, wings whose development varies according to species; the only known groups without wings are the extinct moa and elephant birds. Wings, which are modified forelimbs, gave birds the ability to fly, although further evolution has led to the Flightless bird, loss of flight in some birds, including ratites, penguins, and diverse endemism, endemic island species. The digestive and respiratory systems of birds are also uniquely a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Telluraves
Telluraves (also called land birds or core landbirds) is a recently defined clade of birds defined by their arboreality. Based on most recent genetic studies, the clade unites a variety of bird groups, including the australavians (passerines, parrots, seriemas, and falcons) as well as the afroavians (including the Accipitrimorphae – eagles, hawks, buzzards, vultures etc. – owls and woodpeckers, among others). This grouping was defined in the ''PhyloCode'' by George Sangster and colleagues in 2022 as "the least inclusive crown clade containing '' Accipiter nisus'' and '' Passer domesticus''". They appear to be the sister group of the Phaethoquornithes. Given that the most basal extant members of both Afroaves (Accipitrimorphae, Strigiformes) and Australaves (Cariamiformes, Falconiformes) are birds of prey, it has been suggested that the last common ancestor of all Telluraves may have been an apex predator, and possibly also a bird of prey. Other researchers are ske ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
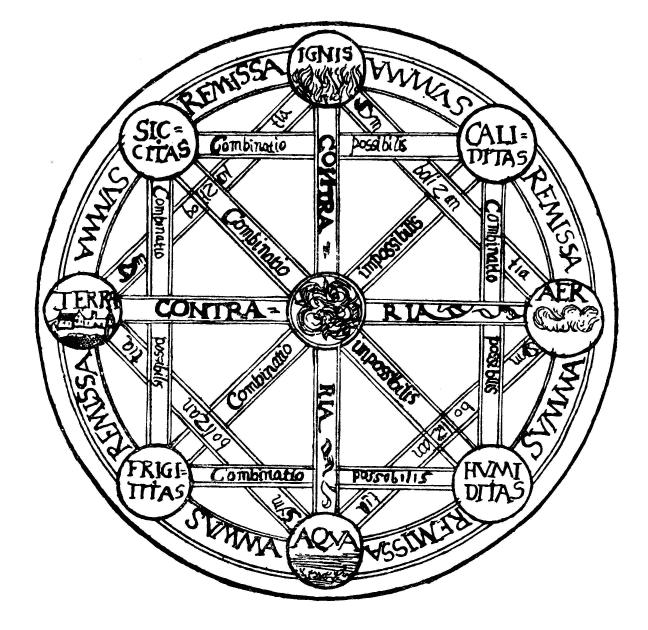
Classical Element
The classical elements typically refer to Earth (classical element), earth, Water (classical element), water, Air (classical element), air, Fire (classical element), fire, and (later) Aether (classical element), aether which were proposed to explain the nature and complexity of all matter in terms of simpler Substance theory, substances. Ancient cultures in Ancient Greece, Greece, Angola, Ancient Tibet, Tibet, Ancient India, India, and Mali had similar lists which sometimes referred, in local languages, to "air" as "wind", and to "aether" as "space". These different cultures and even individual philosophers had widely varying explanations concerning their attributes and how they related to observable phenomena as well as cosmology. Sometimes these theories overlapped with mythology and were personification, personified in deities. Some of these interpretations included atomism (the idea of very small, indivisible portions of matter), but other interpretations considered the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |