|
Elektronika B3-34
Elektronika B3-34 (Cyrillic: Электроника Б3-34) was a Soviet programmable calculator. It was released in 1980 and was sold for 85 rubles. B3-34 used reverse Polish notation and had 98 bytes of instruction memory, four stack user registers and 14 addressable registers. Each register could store up to 8 mantissa or significand digits and two exponent digits in the range to . The first Soviet programmable stationary calculator the ISKRA 123, using mains power, was released at the beginning of the 1970s. The first programmable battery-powered pocket calculator Elektronika B3-21 was developed by the end of 1977 and released at the beginning of 1978. Its successor, B3-34, wasn't backward compatible with B3-21. The instruction set, hardware architecture and microcode of the B3-34 defined the standard of the later Soviet programmable hand-held and office-desk calculators: MK-61, MK-52, MK-54, MK-56. Model numbers do not follow any special order: MK-54 is a slightly upgrad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
EEPROM
EEPROM or E2PROM (electrically erasable programmable read-only memory) is a type of non-volatile memory. It is used in computers, usually integrated in microcontrollers such as smart cards and remote keyless systems, or as a separate chip device, to store relatively small amounts of data by allowing individual bytes to be erased and reprogrammed. EEPROMs are organized as arrays of floating-gate transistors. EEPROMs can be programmed and erased in-circuit, by applying special programming signals. Originally, EEPROMs were limited to single-byte operations, which made them slower, but modern EEPROMs allow multi-byte page operations. An EEPROM has a limited life for erasing and reprogramming, reaching a million operations in modern EEPROMs. In an EEPROM that is frequently reprogrammed, the life of the EEPROM is an important design consideration. Flash memory is a type of EEPROM designed for high speed and high density, at the expense of large erase blocks (typically 512 b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
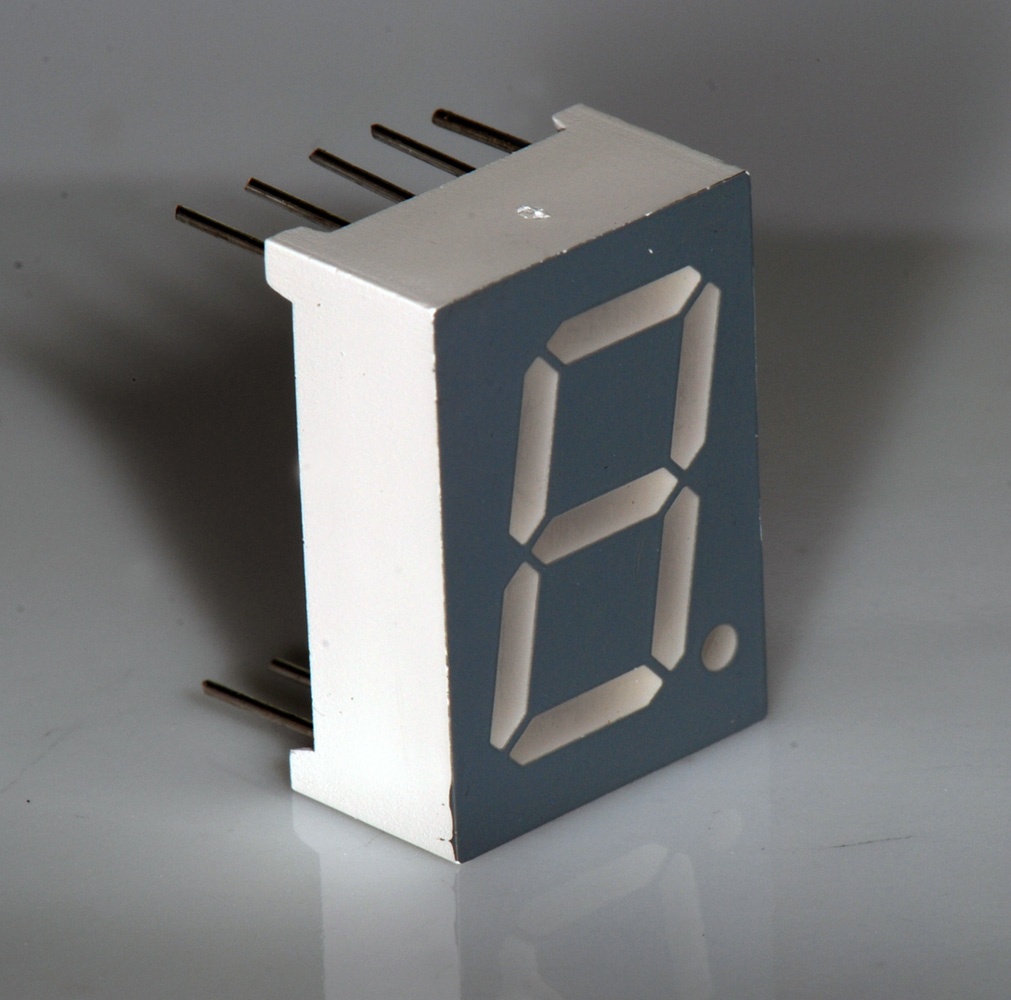
Seven-segment Display
A seven-segment display is a display device for Arabic numerals, less complex than a device that can show more characters such as dot matrix displays. Seven-segment displays are widely used in digital clocks, electronic meters, basic calculators, and other electronic devices that display numerical information. History Seven-segment representation of figures can be found in patents as early as 1903 (in ), when Carl Kinsley invented a method of telegraphically transmitting letters and numbers and having them printed on tape in a segmented format. In 1908, F. W. Wood invented an 8-segment display, which displayed the number 4 using a diagonal bar (). In 1910, a seven-segment display illuminated by incandescent bulbs was used on a power-plant boiler room signal panel. They were also used to show the dialed telephone number to operators during the transition from manual to automatic telephone dialing. They did not achieve widespread use until the advent of light-emitting diode, LEDs in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elektronika MK-18M
The Elektronika MK-18M () was a scientific calculator manufactured in the Soviet Union. It was released in 1986. Technical specifications Source: * Display: vacuum fluorescent display, green color, contains 8 digits + minus sign + error sign * Power: 4 x AA batteries or AC adapter (with charging function) with 3-pin connector, power consumption ≤0.7W * 20 buttons * Case: aluminium + plastic * Supported numbers range: ±(10E-7)...±(10E8-1) * Size: 170x86.5x27 mm, weighing around 350 grams Novelty The Elektronika MK-18M calculator has no new novel functionality. Despite this, the aluminum casing was an improvement from previous models' plastic casing. In addition, the model was produced at Billur (Ganja, Azerbaijan, Kirovograd), in contrast to the Elektronica B3-18 and B3-18A models which were manufactured at Angstrem (company), Angstrem (Zelenograd) and NPO Elektronika (Boguchar, Voronezh Region). See also * Elektronika B3-34 References Computer-related introductions i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calculator Spelling
Calculator spelling is an Unintended consequences, unintended characteristic of the seven-segment display traditionally used by calculators, in which, when read upside-down, the digits resemble letters of the Latin alphabet. Each digit may be mapped to one or more letters, creating a limited but functional subset of the alphabet, sometimes referred to as ''beghilos'' (or ''beghilosz''). Applications Aside from novelty and amusement, calculator spelling has limited utility. The popularity of pagers in the 1990s gave rise to a form of leetspeak called "pager-speak." Students, in particular, experimented with calculators to discover new words. English version : The "original" attributed example of calculator spelling, which dates from the 1970s, is 5318008, which when turned over spells "wikt:boobies, BOOBIES". Another early example of calculator spelling offered the sequence 0.7734, which becomes "hello", or could also be written as 0.1134. The 1979 album ''Five Three One - Doub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Novosibirsk
Novosibirsk is the largest city and administrative centre of Novosibirsk Oblast and the Siberian Federal District in Russia. As of the 2021 Russian census, 2021 census, it had a population of 1,633,595, making it the most populous city in Siberia and the list of cities and towns in Russia by population, third-most populous city in Russia after Moscow and Saint Petersburg. Additionally, it is the largest city in the Asian part of Russia and the most populous city in the country that does not have the status of a Federal subjects of Russia, federal subject. Novosibirsk is located in southwestern Siberia, on the banks of the Ob River. Novosibirsk was founded in 1893 on the Ob River crossing point of the future Trans-Siberian Railway, where the Novosibirsk Rail Bridge was constructed. Originally named Novonikolayevsk ("New Nicholas") in honor of Nicholas II of Russia, Emperor Nicholas II, the city rapidly grew into a major transport, commercial, and industrial hub. Novosibirsk was r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microcode
In processor design, microcode serves as an intermediary layer situated between the central processing unit (CPU) hardware and the programmer-visible instruction set architecture of a computer. It consists of a set of hardware-level instructions that implement the higher-level machine code instructions or control internal finite-state machine sequencing in many digital processing components. While microcode is utilized in Intel and AMD general-purpose CPUs in contemporary desktops and laptops, it functions only as a fallback path for scenarios that the faster hardwired control unit is unable to manage. Housed in special high-speed memory, microcode translates machine instructions, state machine data, or other input into sequences of detailed circuit-level operations. It separates the machine instructions from the underlying electronics, thereby enabling greater flexibility in designing and altering instructions. Moreover, it facilitates the construction of complex multi-step inst ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nauka I Zhizn
''Nauka i Zhizn'' (''Science and Life'', ) is a science magazine first issued during the years 1890–1900 in Russian Empire, and then since 1934 in the Soviet Union (and continued in the Russian Federation today). See also *Tekhnika Molodezhi ''Tekhnika Molodezhi'' (, "Technology for the Youth") is a Soviet, and eventually Russian popular science magazine which has been published monthly since 1933. History and profile ''Tekhnika Molodezhi'' was established in 1933. During the Soviet ... "Technology for the Youth" * Znanie — Sila "Knowledge is Power" References External links''Nauka i Zhizn'' website 1890 establishments in the Russian Empire Magazines established in 1890 Magazines published in Moscow Magazines published in the Soviet Union Popular science magazines Russian-language magazines Science and technology magazines published in Russia Science and technology in the Soviet Union {{Europe-sci-mag-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
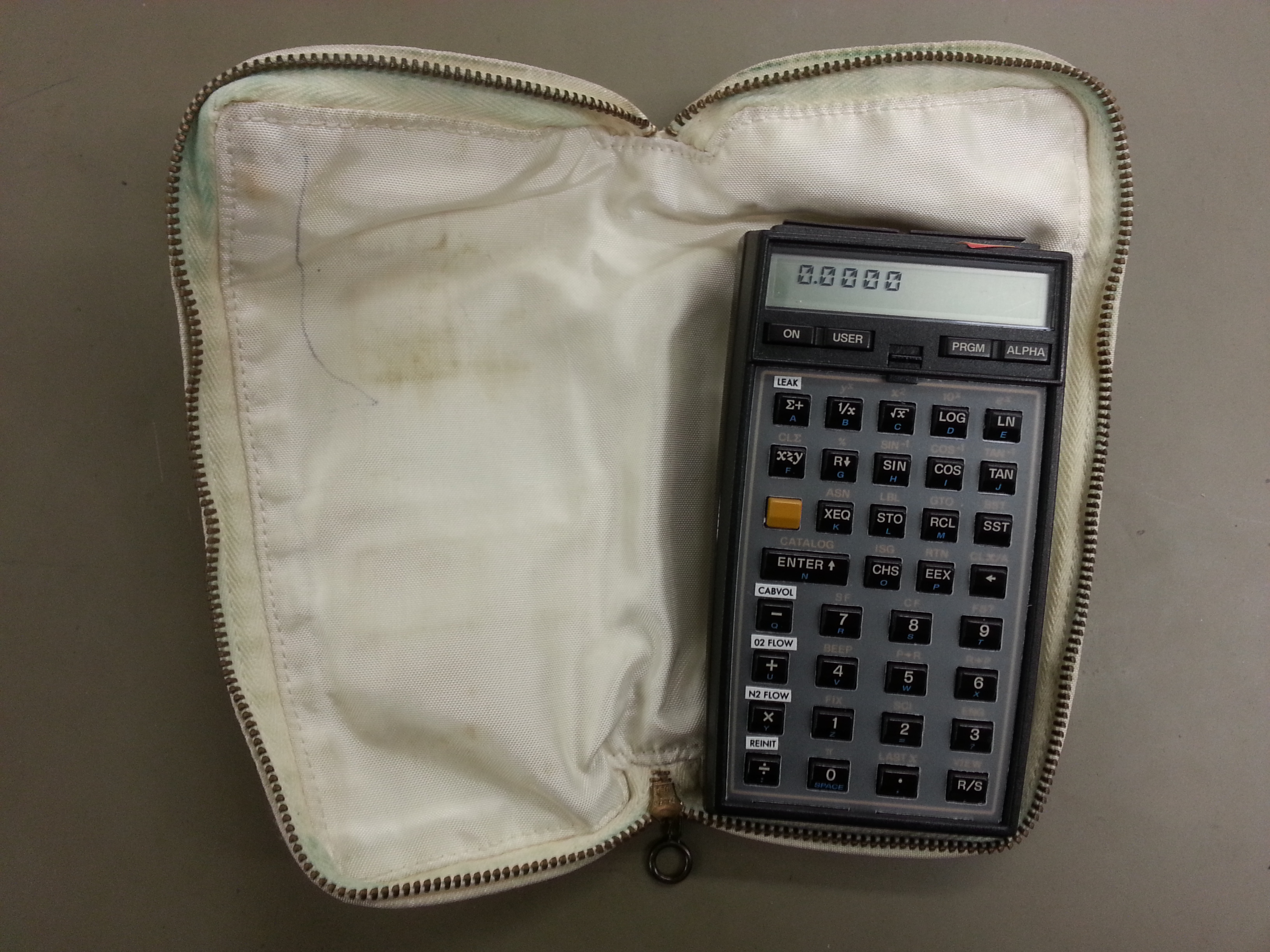
HP-41
The HP-41C series are programmable, expandable, continuous memory handheld RPN calculators made by Hewlett-Packard from 1979 to 1990. The original model, HP-41C, was the first of its kind to offer alphanumeric display capabilities. Later came the HP-41CV and HP-41CX, offering more memory and functionality. The alphanumeric "revolution" The alphanumeric LCD screen of the HP-41C revolutionized the way a pocket calculator could be used, providing user friendliness (for its time) and expandability (keyboard-unassigned functions could be spelled out alphabetically). By using an alphanumeric display, the calculator could tell the user what was going on: it could display error messages, such as showing ("DATA ERROR") upon attempting to divide by zero instead of simply displaying a blinking zero; it could also specifically prompt the user for arguments ("ENTER RADIUS") instead of just displaying a question mark. Earlier calculators needed a key, or key combination, for every av ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synthetic Programming (HP-41)
__NOTOC__ Synthetic programming (SP) is an advanced technique for programming the HP-41C and Elektronika B3-34 calculators, involving creating instructions (or combinations of instructions and operands) that cannot be obtained using the standard capabilities of the calculator. Some HP-41C instructions are coded in memory using multiple bytes. Some of these sequence of bytes correspond to instructions the calculator is able to execute, but these cannot be entered in the program memory using conventional program entry methods (''i.e.'' using the calculator as described in the user's manual). Synthetic programming uses a bug in the calculator firmware to enter those byte sequences as a sequence of other instructions, then partially skipping halfway through the first instruction, so that the calculator believes the end of the first instruction is actually the beginning of a new one. This was called ''byte jumper'' or ''byte grabber''. It is not clear if the creators behind the HP- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soyuz TM-7
Soyuz TM-7 was a crewed Soyuz spaceflight to Mir.The mission report is available here: http://www.spacefacts.de/mission/english/soyuz-TM7.htm It launched on 26 November 1988, at 15:49:34, and was the start of the fourth long duration expedition to Mir, Mir EO-4. The crew would join the third crew member of EO-4, cosmonaut/physician Valeri Polyakov, who was on Mir for the second half of EO-3. Also launched by Soyuz TM-7 was French astronaut Jean-Loup Chrétien, who would take part in the 24-day French mission known as Mir Aragatz. The spacecraft Soyuz TM-7 remained docked to Mir for the duration of EO-4. At the end of EO-4 in April 1989, due to delays in the launch schedule, Mir was left uncrewed, and all three EO-4 crew members were transported back to Earth. Crew Backup crew * Aleksandr Viktorenko * Aleksandr Serebrov * Michel Tognini Mission parameters *Mass: 7,000 kg 15,400 lb *Perigee: 194 km (120 mi) *Apogee: 235 km (146 mi) *Inclination: 51.6 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |