|
Eleazar Ben Shammua
Eleazar ben Shammua or Eleazar I (Hebrew: אלעזר בן שמוע) was a rabbi of the 2nd century (4th generation of tannaim), frequently cited in rabbinic writings as simply Rabbi Eleazar (Bavli) or Rabbi Lazar רִבִּי לָֽעְזָר (Yerushalmi). He was of priestly descent and rich, and acquired great fame as a teacher of traditional law. Biography Eleazar ben Shammua was a student of Rabbi Akiva, but was not ordained by him due to the Hadrianic persecution. After Akiva's death, however, Judah ben Bava ordained Eleazar, together with Rabbi Meir, Jose ben Halafta, Judah bar Ilai, and Shimon bar Yochai, at a secluded spot between Usha and Shefa-Amr. The ordainer was detected in the act and brutally slain, but the ordained escaped, and eventually became the custodians and disseminators of Jewish tradition. Mention is made of a controversy between Eleazar and Rabbi Meir at Ardiska. He also maintained halakhic discussions with Judah bar Ilai and Jose ben Halafta, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hebrew
Hebrew (; ''ʿÎbrit'') is a Northwest Semitic languages, Northwest Semitic language within the Afroasiatic languages, Afroasiatic language family. A regional dialect of the Canaanite languages, it was natively spoken by the Israelites and remained in regular use as a first language until after 200 CE and as the Sacred language, liturgical language of Judaism (since the Second Temple period) and Samaritanism. The language was Revival of the Hebrew language, revived as a spoken language in the 19th century, and is the only successful large-scale example of Language revitalization, linguistic revival. It is the only Canaanite language, as well as one of only two Northwest Semitic languages, with the other being Aramaic, still spoken today. The earliest examples of written Paleo-Hebrew alphabet, Paleo-Hebrew date back to the 10th century BCE. Nearly all of the Hebrew Bible is written in Biblical Hebrew, with much of its present form in the dialect that scholars believe flourish ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Usha (city)
Usha () was an ancient Jewish town in the western part of Galilee. It was identified in the late 19th century by Victor Guérin, who found the ruins on which the Arab village of Hawsha was built.Guerin, 1880, pp415416. Partially translated in Conder and Kitchener, 1881, SWP I, p311/ref> The modern kibbutz of Usha, Israel is located several kilometers to the west. The site is close to the town of Kiryat Ata."1,400-year-old Byzantine Hammer and Nails Discovered in Ancient Jewish Village of Usha" Ruth Schuster for ''Haaretz'', 30 Oct 2019. Accessed 29 Jan 2024. History and archaeology ...
|
Johanan Bar Nappaha
:''See Johanan (name) for more rabbis by this name''. Johanan bar Nappaha ( Yoḥanan bar Nafḥa or Napaḥa), also known simply as Rabbi Yochanan or Johanan bar Nafcha (180–279 CE), was a leading rabbi and second-generation '' Amora'' during the Talmudic era. Johanan's opinions are quoted widely across the Jerusalem and Babylonian Talmuds. The compilation of the Jerusalem Talmud is generally ascribed to him. Name He is generally cited as "Johanan," but sometimes by his cognomen only, which he himself uses once; but he is never cited by both together. Opinions vary on whether "bar Nappaha" (literally "son f theblacksmith") derives from his father's profession, from the name of his ancestral region, or perhaps represents a physical or psychological quality. Biography Early years Johanan's early years were spent in Sepphoris in the Roman-ruled Galilee (then part of Syria Palaestina province). He traced his descent from the tribe of Joseph. His father, a blacksmith, died ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abba Arikha
Rav Abba bar Aybo (; 175–247 CE), commonly known as Abba Arikha () or simply as Rav (), was a Jewish amora of the 3rd century. He was born and lived in Kafri, Asoristan, in the Sasanian Empire. In Sura, Arikha established the systematic study of the rabbinic traditions, which, using the Mishnah as a foundational text, led to the compilation of the Talmud. With him began the long period of ascendancy of the prestigious Talmudic academies in Babylonia around the year 220. In the Talmud, he is frequently associated with Samuel of Nehardea, a fellow amora with whom he debated many issues. Biography His surname, Arikha (English: ''the Tall''), he owed to his height, which exceeded that of his contemporaries. Others, reading Arekha, consider it an honorary title, like "Lecturer". In the traditional literature, he is referred to almost exclusively as Rav, "the Master" (both by contemporaries and latter generations), just as his teacher, Judah ha-Nasi, was known simply as ''Rab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Talmud
The Talmud (; ) is the central text of Rabbinic Judaism and the primary source of Jewish religious law (''halakha'') and Jewish theology. Until the advent of Haskalah#Effects, modernity, in nearly all Jewish communities, the Talmud was the centerpiece of Jewish culture, Jewish cultural life and was foundational to "all Jewish thought and aspirations", serving also as "the guide for the daily life" of Jews. The Talmud includes the teachings and opinions of thousands of rabbis on a variety of subjects, including halakha, Jewish ethics, Jewish philosophy, philosophy, Jewish customs, customs, Jewish history, history, and Jewish folklore, folklore, and many other topics. The Talmud is a commentary on the Mishnah. This text is made up of 63 Masekhet, tractates, each covering one subject area. The language of the Talmud is Jewish Babylonian Aramaic. Talmudic tradition emerged and was compiled between the destruction of the Second Temple in 70 CE and the Arab conquest in the early seve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Judah Ha-Nasi
Judah ha-Nasi (, ''Yəhūḏā hanNāsīʾ''; Yehudah HaNasi or Judah the Prince or Judah the President) or Judah I, known simply as Rebbi or Rabbi, was a second-century rabbi (a tanna of the fifth generation) and chief redactor and editor of the ''Mishnah''. He lived from approximately 135 to 217 CE. He was a key leader of the Jewish community in Roman-occupied Judea after the Bar Kokhba revolt. Name and titles The title '' nasi'' was used for presidents of the Sanhedrin. He was the first ''nasi'' to have this title added permanently to his name; in traditional literature he is usually called "Rabbi Yehuda ha-Nasi." Often though (and always in the Mishnah) he is simply called ''Rabbi'' "my teacher" (), the master par excellence. He is occasionally called ''Rabbenu'' "our master". He is also called "Rabbenu HaQadosh" "our holy master" () due to his deep piety. Biography Youth Judah was born in 135 in the newly-established Roman province of Syria Palaestina to Rabbi Sime ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mekhilta
Mekhilta (, IPA /məˈχiltɑ/, "a collection of rules of interpretation"; corresponding to the Mishnaic Hebrew ' 'measure', 'rule'), is used to denote a compilation of exegesis in Judaism, attributed to or written by any of several authors. The Mekhilta include: * The Mekhilta of Rabbi Ishmael, on the Book of Exodus * The Mekhilta of Rabbi Shimon ben Yochai, on the Book of Exodus * The Mekhilta le-Sefer Devarim, on the Book of Deuteronomy See also * Midrash halakha ''Midrash halakha'' () was the ancient Judaic rabbinic method of Torah study that expounded upon the traditionally received 613 Mitzvot (commandments) by identifying their sources in the Hebrew Bible, and by interpreting these passages as proo ..., a mekhilta that is seen as binding {{Authority control Exegesis Sifrei Kodesh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moed
Moed (, "Festivals") is the second Order of the Mishnah, the first written recording of the Oral Torah of the Jewish people (also the Tosefta and Talmud). Of the six orders of the Mishna, Moed is the third shortest. The order of Moed consists of 12 tractates: # ''Shabbat'' or ''Shabbath'' () ("Sabbath") deals with the 39 prohibitions of "work" on the Shabbat. 24 chapters. # ''Eruvin'' (ערובין) ("Mixtures") deals with the Eruv or Sabbath-bound - a category of constructions/delineations that alter the domains of the Sabbath for carrying and travel. 10 chapters. # '' Pesahim'' (פסחים) (" Passover Festivals") deals with the prescriptions regarding the Passover and the paschal sacrifice. 10 chapters. # '' Shekalim'' (שקלים) ("Shekels") deals with the collection of the half-Shekel as well as the expenses and expenditure of the Temple. 8 chapters # '' Yoma'' (יומא) ("The Day")—also called "Kippurim" or "Yom ha-Kippurim" ("Day of Atonement")—deals with the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
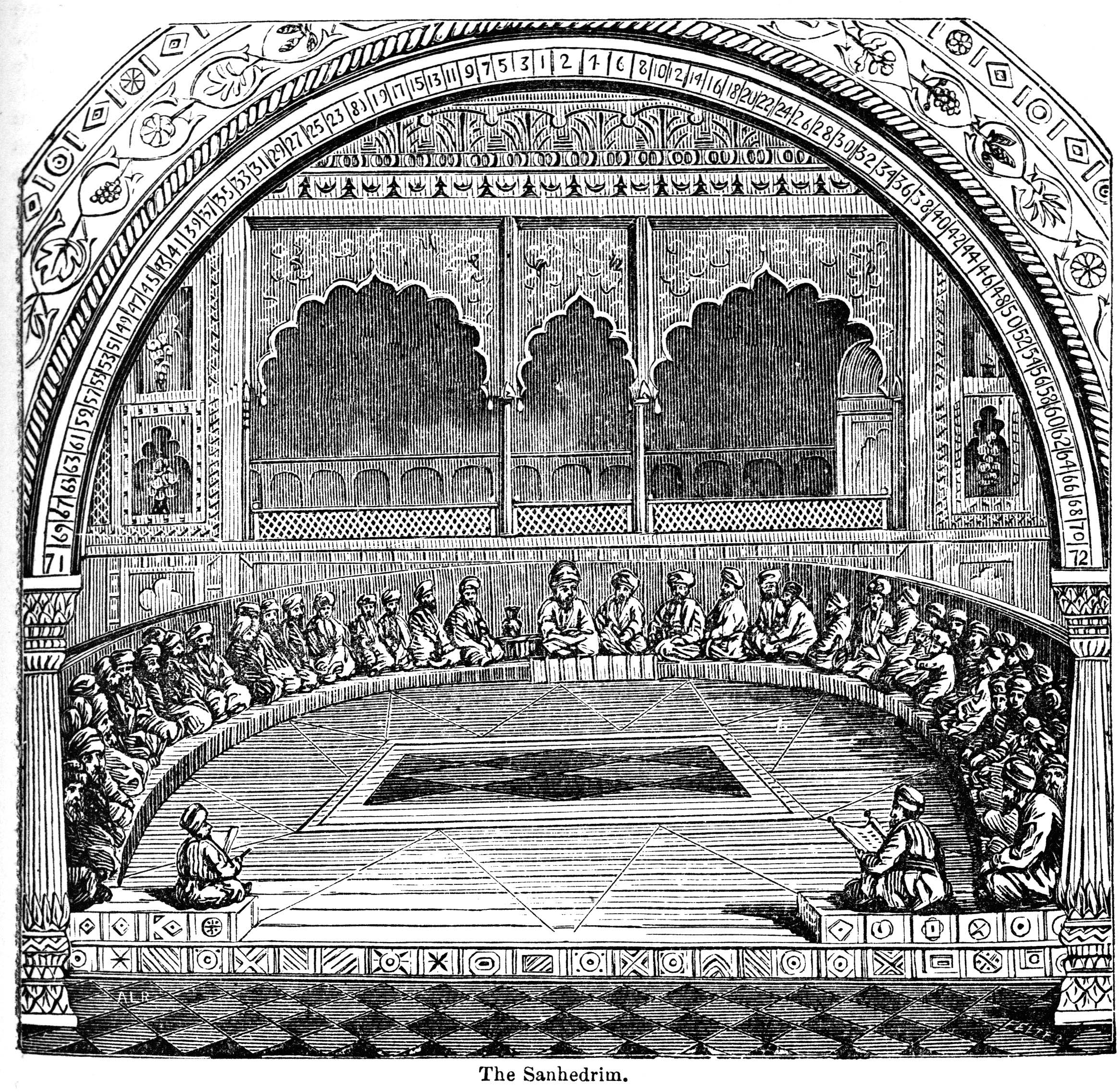
Sanhedrin
The Sanhedrin (Hebrew and Middle Aramaic , a loanword from , 'assembly,' 'sitting together,' hence ' assembly' or 'council') was a Jewish legislative and judicial assembly of either 23 or 70 elders, existing at both a local and central level in the ancient Land of Israel. There were two classes of Rabbinite courts called sanhedrins: Greater and Lesser. A lesser Sanhedrin of 23 judges was appointed to sit as a tribunal in each city. There was only one Great Sanhedrin of 70 judges, which, among other roles, acted as a supreme court, taking appeals from cases that lesser courts decided. In general usage, ''the Sanhedrin'' without qualifier usually refers to the Great Sanhedrin, which was presided over by the Nasi, who functioned as its head or representing president, and was a member of the court; the Av Beit Din or the chief of the court, who was second to the Nasi and 69 general members. In the Second Temple period, the Great Sanhedrin met in the Temple in Jerusalem, in a bu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yoma
Yoma (Aramaic: יומא, lit. "The Day") is the fifth tractate of '' Seder Moed'' ('Order of Festivals') of the ''Mishnah'' and of the ''Talmud''. It is concerned mainly with the laws of the Jewish holiday Yom Kippur, on which Jews atone for their sins from the previous year. It consists of eight chapters and has a Gemara ('Completion') from both the Jerusalem Talmud and the Babylonian Talmud. Content The first chapter is regarding the seven days before Yom Kippur in which the Kohen Gadol is separated from his wife and moves into a chamber on the Beit HaMikdash, sprinkled with water from the Red Heifer and taught the laws relating to the Yom Kippur sacrifices. The second through seventh chapters deal with the order of services on Yom Kippur, both those specific to Yom Kippur and the daily sacrifices. Some of the issues addressed include those of the lottery employed to assign services to Kohanim, laws regarding the scapegoat, and the incense sacrifices performed by the Kohe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |