|
El Capitan (Montana)
El Capitan is a mountain summit in the Bitterroot Range of Montana. The peak is located in the Selway-Bitterroot Wilderness on land managed by the Bitterroot National Forest. The summit lies 12 miles west of the town of Darby, Montana, and three miles east of the Idaho–Montana border. The highest point of the Central Bitterroot Range is line parent Trapper Peak, 9.3 miles south-southeast. Climate Based on the Köppen climate classification, the peak is located in a subarctic climate The subarctic climate (also called subpolar climate, or boreal climate) is a climate with long, cold (often very cold) winters, and short, warm to cool summers. It is found on large landmasses, often away from the moderating effects of an ocean, ge ... zone characterized by long, usually very cold winters, and mild summers. Winter temperatures can drop below −10 °F with wind chill factors below −30 °F. Gallery File:SelwayBitterrootWilderness LonesomeBachelorAndElCapitan.jpg, Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ravalli County, Montana
Ravalli County is a county in the southwestern part of the U.S. state of Montana. As of the 2020 census, the population was 44,174. Its county seat is Hamilton. Ravalli County is part of a north–south mountain valley bordered by the Sapphire Mountains on the East and the Bitterroot Mountains on the West. It is often referred to as the Bitterroot Valley, which is named for the Bitterroot Flower. The county is on the Pacific Ocean side of the Continental Divide, which follows the Idaho-Montana border from Wyoming until Ravalli County. Here, it turns east into Montana, between Chief Joseph Pass and Lost Trail Pass, and follows the Ravalli County- Beaverhead County border. History Ravalli County was once home to the Bitterroot Salish tribe. The tribe was first encountered in 1805 by the Lewis and Clark Expedition, which noted their friendly nature. The Catholic Church took an interest in creating a mission in the area, and in 1841 founded St. Mary's Mission, subsequently ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 U.S. state, states, a Washington, D.C., federal district, five major unincorporated territories, nine United States Minor Outlying Islands, Minor Outlying Islands, and 326 Indian reservations. The United States is also in Compact of Free Association, free association with three Oceania, Pacific Island Sovereign state, sovereign states: the Federated States of Micronesia, the Marshall Islands, and the Palau, Republic of Palau. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by area, third-largest country by both land and total area. It shares land borders Canada–United States border, with Canada to its north and Mexico–United States border, with Mexico to its south and has maritime borders with the Bahamas, Cuba, Russia, and other nations. With a population of over 333 million, it is the List of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bitterroot Range
The Bitterroot Range is a mountain range and a subrange of the Rocky Mountains that runs along the border of Montana and Idaho in the northwestern United States. The range spans an area of and is named after the bitterroot (''Lewisia rediviva''), a small pink flower that is the state flower of Montana. History In 1805, the Corps of Discovery, led by Meriwether Lewis and William Clark and aided by Sacajawea of the Shoshone Native American tribe, crossed the Bitterroot Range several times. Lewis first crossed the mountains at Lemhi Pass on August 12, then returned across the pass to meet Clark. The entire expedition then crossed the pass to the Salmon River valley, and the next month entered the Bitterroot Valley from the south via either Lost Trail Pass or Chief Joseph Pass. It then crossed Lolo Pass to the west. The mountains were crossed by the Chicago, Milwaukee, St. Paul and Pacific Railroad (the "Milwaukee Road"). Ranges According to the U.S. Board on Geogra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Geological Survey
The United States Geological Survey (USGS), formerly simply known as the Geological Survey, is a scientific agency of the United States government. The scientists of the USGS study the landscape of the United States, its natural resources, and the natural hazards that threaten it. The organization's work spans the disciplines of biology, geography, geology, and hydrology. The USGS is a fact-finding research organization with no regulatory responsibility. The agency was founded on March 3, 1879. The USGS is a bureau of the United States Department of the Interior; it is that department's sole scientific agency. The USGS employs approximately 8,670 people and is headquartered in Reston, Virginia. The USGS also has major offices near Lakewood, Colorado, at the Denver Federal Center, and Menlo Park, California. The current motto of the USGS, in use since August 1997, is "science for a changing world". The agency's previous slogan, adopted on the occasion of its hundredth an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Summit
A summit is a point on a surface that is higher in elevation than all points immediately adjacent to it. The topographic terms acme, apex, peak (mountain peak), and zenith are synonymous. The term (mountain top) is generally used only for a mountain peak that is located at some distance from the nearest point of higher elevation. For example, a big, massive rock next to the main summit of a mountain is not considered a summit. Summits near a higher peak, with some prominence or isolation, but not reaching a certain cutoff value for the quantities, are often considered ''subsummits'' (or ''subpeaks'') of the higher peak, and are considered part of the same mountain. A pyramidal peak is an exaggerated form produced by ice erosion of a mountain top. Summit may also refer to the highest point along a line, trail, or route. The highest summit in the world is Mount Everest with a height of above sea level. The first official ascent was made by Tenzing Norgay and Sir Edmund Hillary. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
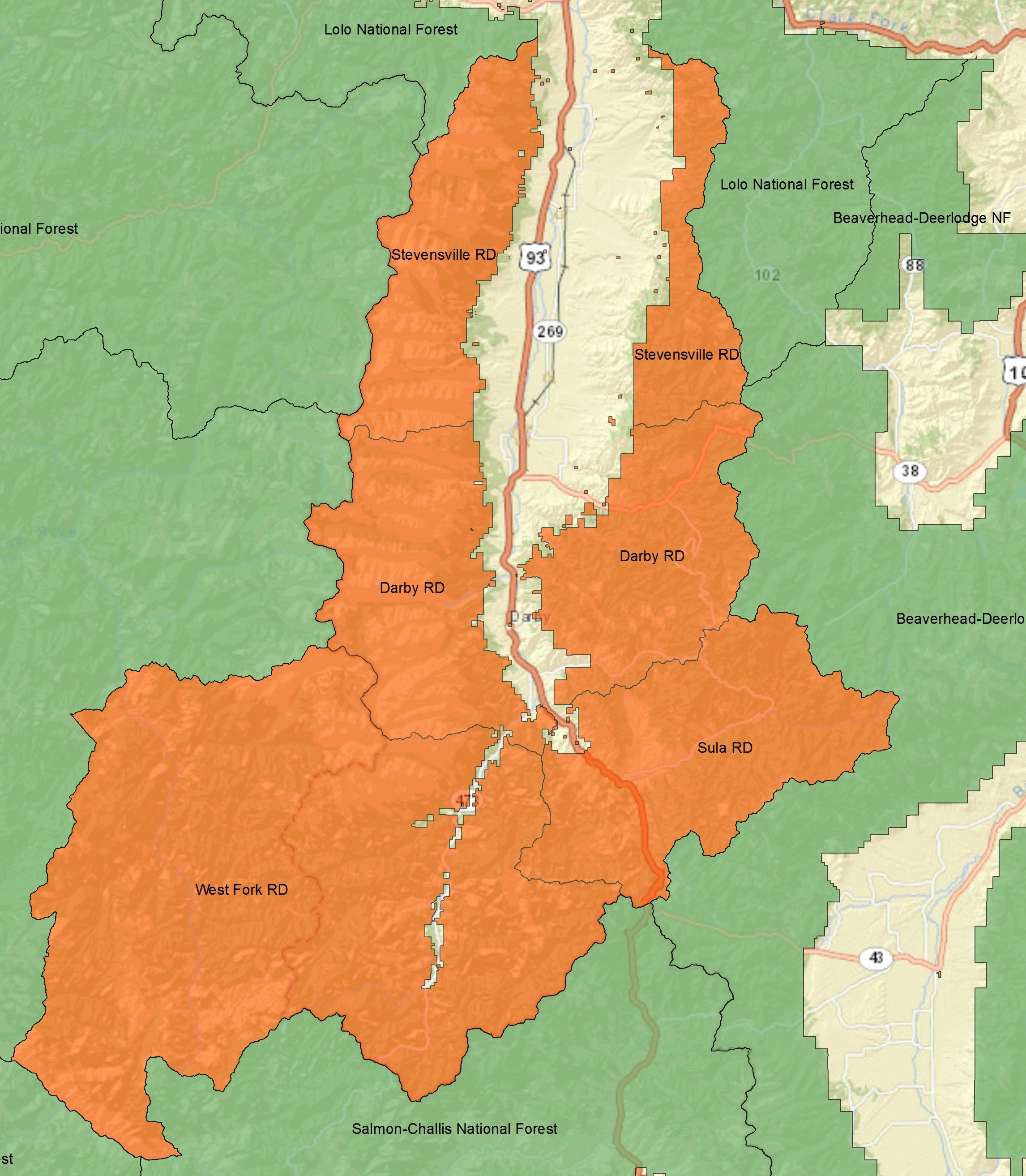
Bitterroot National Forest
Bitterroot National Forest comprises 1.587 million acres (6,423 km²) in west-central Montana and eastern Idaho, of the United States. It is located primarily in Ravalli County, Montana (70.26% of the forest), but also has acreage in Idaho County, Idaho (29.24%), and Missoula County, Montana (0.49%). Founded in 1898, the forest is located in the Bitterroot and Sapphire Mountains with elevations ranging from 2,200 feet (650 m) along the Salmon River in Idaho to 10,157 foot (3,100 m) Trapper Peak. Roughly half the forest (743,000 acres, 3,000 km²) make up part or all of three distinct Wilderness areas. These areas include the Anaconda-Pintler, Selway-Bitterroot and Frank Church River of No Return Wildernesses. The distinction is that in wilderness areas, no roads, logging, mining or other construction is permitted and all access must be done either on foot or horseback; even bicycles are not permitted. Hunting, however is allowed forest-wide including wilderness ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Darby, Montana
Darby ( Salish: snk̓ʷɫxʷexʷem̓i, "Place Where They Would Lift Something") is a town in Ravalli County, Montana, United States. The population was 783 at the 2020 census. Darby is located near the southwestern border of Montana and Idaho, along the Continental Divide. Officially established in 1889, the town was named after James W. Darby who signed the post office application. Geography Darby is located at (46.022030, -114.179603). According to the United States Census Bureau, the town has a total area of , all land. The area south of Darby is called ''nɫpapʔá'' in Salish. Climate This climatic region is typified by large seasonal temperature differences, with warm to hot (and often humid) summers and cold (sometimes severely cold) winters. According to the Köppen Climate Classification system, Darby has a humid continental climate, abbreviated "Dfb" on climate maps. Visitors to Darby may wish to seek shelter during thunderstorms. In July 2012, "A cowboy and two s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Line Parent
A peak's line parent is the closest higher peak on the highest ridge leading away from the peak's "key col". A col is the lowest point on the ridge between two summits and is roughly synonymous with pass, gap, saddle and notch. The highest col of a peak is its key col. If there is more than one ridge which can be followed to a higher peak then the line parent is the peak closest to the key col. Usually, a line parent must meet some prominence criteria, which might vary depending on the author and the location of the peak. There are at least two other kinds of peak parentage. Island parentage, which is also referred to as encirclement or topographic parentage; and source parentage. See also * Topographic prominence In topography, prominence (also referred to as autonomous height, relative height, and shoulder drop in US English, and drop or relative height in British English) measures the height of a mountain or hill's summit relative to the lowest cont ... References ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trapper Peak (Montana)
Trapper Peak is the highest point in the Bitterroot Mountains, part of the larger Bitterroot Range in western Montana. It rises over above the nearby Bitterroot Valley. The peak is located within the Central Bitterroot Range, a subrange of the Bitterroot Mountains and within the Selway-Bitterroot Wilderness Area of the Bitterroot National Forest Bitterroot National Forest comprises 1.587 million acres (6,423 km²) in west-central Montana and eastern Idaho, of the United States. It is located primarily in Ravalli County, Montana (70.26% of the forest), but also has acreage in Idah .... A trail to the peak climbs from the end of a Forest Service road. References External links * * Bitterroot Range Mountains of Montana Mountains of Ravalli County, Montana Bitterroot National Forest {{RavalliCountyMT-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Köppen Climate Classification
The Köppen climate classification is one of the most widely used climate classification systems. It was first published by German-Russian climatologist Wladimir Köppen (1846–1940) in 1884, with several later modifications by Köppen, notably in 1918 and 1936. Later, the climatologist Rudolf Geiger (1894–1981) introduced some changes to the classification system, which is thus sometimes called the Köppen–Geiger climate classification system. The Köppen climate classification divides climates into five main climate groups, with each group being divided based on seasonal precipitation and temperature patterns. The five main groups are ''A'' (tropical), ''B'' (arid), ''C'' (temperate), ''D'' (continental), and ''E'' (polar). Each group and subgroup is represented by a letter. All climates are assigned a main group (the first letter). All climates except for those in the ''E'' group are assigned a seasonal precipitation subgroup (the second letter). For example, ''Af'' i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subarctic Climate
The subarctic climate (also called subpolar climate, or boreal climate) is a climate with long, cold (often very cold) winters, and short, warm to cool summers. It is found on large landmasses, often away from the moderating effects of an ocean, generally at latitudes from 50° to 70°N, poleward of the humid continental climates. Subarctic or boreal climates are the source regions for the cold air that affects temperate latitudes to the south in winter. These climates represent Köppen climate classification ''Dfc'', ''Dwc'', ''Dsc'', ''Dfd'', ''Dwd'' and ''Dsd''. Description This type of climate offers some of the most extreme seasonal temperature variations found on the planet: in winter, temperatures can drop to below and in summer, the temperature may exceed . However, the summers are short; no more than three months of the year (but at least one month) must have a 24-hour average temperature of at least to fall into this category of climate, and the coldest month should a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |