|
Ekaterina Scherbachenko
Ekaterina Nikolayevna Scherbachenko (, ''Yekaterina Shcherbachenko''; born 1977) is a Russian operatic soprano. She was the 2009 winner of the BBC Cardiff Singer of the World competition. In April–May 2011 she appeared at La Scala, singing the role of Liù in ''Turandot''. Scherbachenko studied at the Moscow Conservatory until 2005. She joined the Stanislavski and Nemirovich-Danchenko Moscow Academic Music Theatre, and then the Bolshoi Theatre. Having sung the role of Lidochka in the French premiere of Shostakovich's '' Moscow, Cheryomushki'' at the Opéra de Lyon in 2004, she sang Lidochka again in 2006 in the first production at the Stanislavski complex after its long renovation. At the Stanislavski she also sang the role of Fiordiligi in ''Così fan tutte''. While at the Bolshoi, she sang the roles of Natasha in ''War and Peace'', Tatyana in ''Eugene Onegin'', Mimi in ''La bohème'', Liù in ''Turandot'', Micaëla in ''Carmen'' and the title role in ''Iolanta''. She also perf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
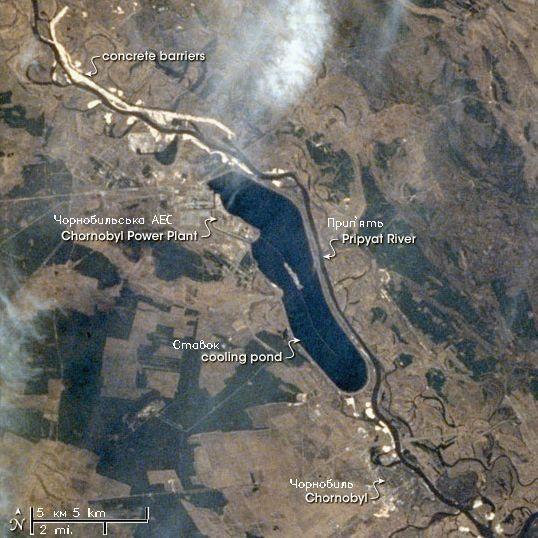
Chernobyl
Chernobyl, officially called Chornobyl, is a partially abandoned city in Vyshhorod Raion, Kyiv Oblast, Ukraine. It is located within the Chernobyl Exclusion Zone, to the north of Kyiv and to the southwest of Gomel in neighbouring Belarus. Prior to being evacuated in the aftermath of the Chernobyl disaster in 1986, it was home to approximately 14,000 residents—considerably less than adjacent Pripyat, which was completely abandoned following the incident. Since then, although living anywhere within the Chernobyl Exclusion Zone is technically illegal, Ukrainian authorities have tolerated those who have taken up living in some of the city's less irradiated areas; Chernobyl's 2020 population estimate was 150 people. First mentioned as a ducal hunting lodge in Kievan Rus' in 1193, the city has changed hands multiple times over the course of its history. In the 16th century, Jews began moving into Chernobyl, and at the end of the 18th century, it had become a major centre of Has ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eugene Onegin (opera)
''Eugene Onegin'' (, ), Op. 24, is an opera (designated as "lyrical scenes") in 3 acts (7 scenes), composed by Pyotr Ilyich Tchaikovsky. The libretto, organised by the composer himself, very closely follows certain passages in Alexander Pushkin's 1825–1832 novel in verse, retaining much of his poetry. Tchaikovsky's friend Konstantin Shilovsky contributed M. Triquet's verses in Act 2, Scene 1, while Tchaikovsky himself arranged the text for Lensky's arioso in Act 1, Scene 1, and almost all of Prince Gremin's aria in Act 3, Scene 1. ''Eugene Onegin'' is a well-known example of lyric opera, to which Tchaikovsky added music of a dramatic nature. The story concerns a selfish hero who lives to regret his blasé rejection of a young woman's love and his careless incitement of a fatal duel with his best friend. The opera was first performed in Moscow in 1879. There are several recordings of it, and it is regularly performed. The work's title refers to the protagonist. Composition ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
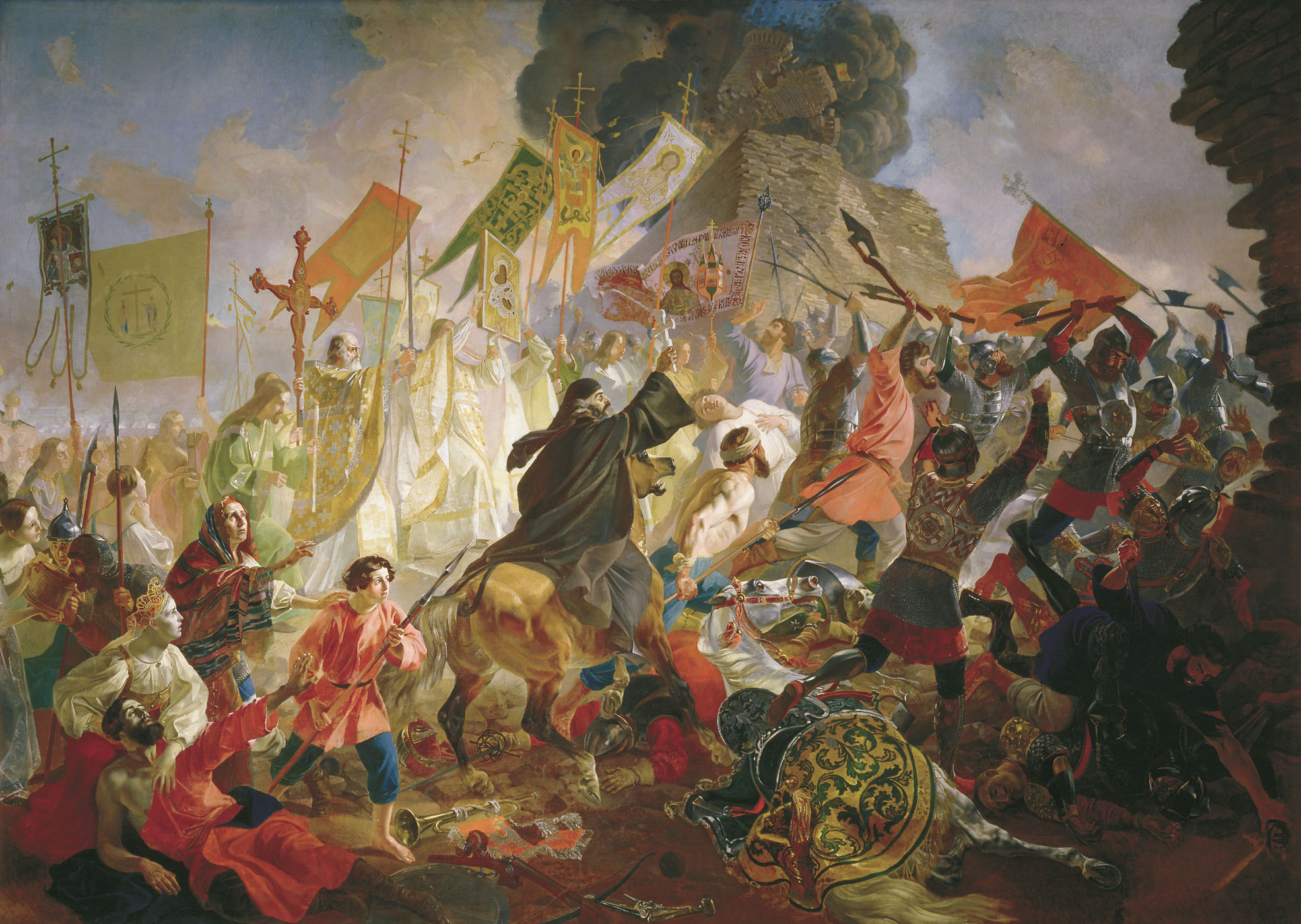
The Maid Of Pskov
''The Maid of Pskov'' ( ), also known as ''Ivan the Terrible'', is an 1872 opera originally in three acts (six scenes) by Nikolai Rimsky-Korsakov. The libretto is by the composer, after the play by Lev Mei. The storyline is fictitious, but set against the background of the campaign by Ivan IV Vasilyevich to subject the cities of Pskov and Novgorod to his will. Pskovityanka was Rimsky-Korsakov's first opera, and he revised it twice; once in 1876-7, when he added a prologue, and again in 1891-2, without the prologue (which was subsequently rewritten and became in 1898 the one act opera '' Boyarïnya Vera Sheloga''). The third version was made famous by Feodor Chaliapin in the role of the Tsar. The opera was introduced to Paris in 1909, also with Chaliapin, by Diaghilev, under the title ''Ivan the Terrible''. Composition history The first product of the composer's interest in this work was a lullaby composed in 1866. Rimsky-Korsakov then set to work in full earnest on an operati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pskov
Pskov ( rus, Псков, a=Ru-Псков.oga, p=psˈkof; see also Names of Pskov in different languages, names in other languages) is a types of inhabited localities in Russia, city in northwestern Russia and the administrative center of Pskov Oblast, located about east of the Estonian border, on the Velikaya, Velikaya River. Population: Pskov is one of the oldest cities in Russia. During the Middle Ages, it served as the capital of the Pskov Republic and was a trading post of the Hanseatic League before it was incorporated into the Grand Duchy of Moscow and became an important border fortress in the Tsardom of Russia. History Early history Pskov is one of the oldest cities in Russia. The name of the city, originally Pleskov (historic Russian spelling , ), may be loosely translated as "[the town] of :wikt:purling, purling waters". It was historically known in English as Plescow. Its earliest mention comes in 903, which records that Igor of Kiev married a local lady, Olga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semperoper
The Semperoper () is the opera house of the Sächsische Staatsoper Dresden (Saxon State Opera) and the concert hall of the Staatskapelle Dresden (Saxon State Orchestra). It is also home to the Semperoper Ballett. The building is located on the Theaterplatz (Dresden), Theaterplatz near the Elbe River in the historic centre of Dresden, Germany. The opera house was originally built by the architect Gottfried Semper in 1841. After a devastating fire in 1869, the opera house was rebuilt, partly again by Semper, and completed in 1878. The opera house has a long history of premieres, including major works by Richard Wagner and Richard Strauss. History The first opera house at the location of today's Semperoper was built by the architect Gottfried Semper. It opened on 13 April 1841 with an opera by Carl Maria von Weber. The building style itself is debated among many, as it has features that appear in three styles: early Renaissance and Baroque, with Corinthian style pillars typical o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wales Music
Wales ( ) is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is bordered by the Irish Sea to the north and west, England to the England–Wales border, east, the Bristol Channel to the south, and the Celtic Sea to the south-west. , it had a population of 3.2 million. It has a total area of and over of Coastline of Wales, coastline. It is largely mountainous with its higher peaks in the north and central areas, including Snowdon (), its highest summit. The country lies within the Temperate climate, north temperate zone and has a changeable, Oceanic climate, maritime climate. Its capital and largest city is Cardiff. A distinct Culture of Wales, Welsh culture emerged among the Celtic Britons after the End of Roman rule in Britain, Roman withdrawal from Britain in the 5th century, and Wales was briefly united under Gruffudd ap Llywelyn in 1055. After over 200 years of war, the Conquest of Wales by Edward I, conquest of Wales by King Edward I o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beijing
Beijing, Chinese postal romanization, previously romanized as Peking, is the capital city of China. With more than 22 million residents, it is the world's List of national capitals by population, most populous national capital city as well as China's List of cities in China by population, second largest city by urban area after Shanghai. It is located in North China, Northern China, and is governed as a Direct-administered municipalities of China, municipality under the direct administration of the Government of the People's Republic of China, State Council with List of administrative divisions of Beijing, 16 urban, suburban, and rural districts.Figures based on 2006 statistics published in 2007 National Statistical Yearbook of China and available online at archive. Retrieved 21 April 2009. Beijing is mostly surrounded by Hebei Province and neighbors Tianjin to the southeast; together, the three divisions form the Jing-Jin-Ji, Jing-Jin-Ji cluster. Beijing is a global city and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Centre For The Performing Arts (China)
The National Centre for the Performing Arts (NCPA) (), colloquially described as The Giant Egg (巨蛋), is an arts centre containing an opera house in Xicheng District, Xicheng, Beijing, China. Designed by French architect Paul Andreu, the NCPA opened in 2007 and is the largest theatre complex in Asia. The NCPA is semi-spherical in appearance, with a long axis length of 212.20 meters in the east-west direction, a short axis length of 143.64 meters in the north-south direction, a height of 46.285 meters, an area of 119,900 square meters, and a total construction area of approximately 165,000 square meters, including 105,000 square meters of main buildings and 60,000 square meters of underground, auxiliary facilities, with a total cost of 3.067 billion yuan. The centre contains an opera hall, music hall, theater and art exhibition halls, restaurants, audio shops, and other supporting facilities. Architecture Construction The exterior of the NCPA is a steel structural shell. It ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glagolitic Mass
The ''Glagolitic Mass'' (, '; also called ''Missa Glagolitica'' or ''Slavonic Mass'') is a composition for soloists (soprano, contralto, tenor, bass), double chorus, organ and orchestra by Leoš Janáček. Janáček completed the work in 1926. It received its premiere by the Brno Arts Society, conducted by Jaroslav Kvapil, in Brno on 5 December 1927. Janáček revised the mass the next year. The Glagolitic alphabet was an early Slavic alphabet, the predecessor of the modern Cyrillic alphabet. In Croatia, the Catholic Church gave permission for the Roman Rite liturgical Mass to be celebrated in Old Church Slavonic at a time when such liturgies were typically only permitted to be in Latin, resulting in the Glagolitic Use Mass. Background The text is in Old Church Slavonic, with five vocal movements that correspond to the Catholic Ordinary of the Mass, omitting "Dona nobis pacem" in the ''Agnus Dei''. The musical origins of the work can be traced to Janáček's Latin setting of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Bells (symphony)
''The Bells'' (, ''Kolokola''), Op. 35, is a choral symphony by Sergei Rachmaninoff, written in 1913 and premiered in St Petersburg on 30 November that year under the composer's baton. The words are from the poem ''The Bells (poem), The Bells'' by Edgar Allan Poe, very freely translated into Russian language, Russian by the Symbolism (movement), symbolist poet Konstantin Balmont. The traditional Gregorian melody ''Dies Irae'' is used frequently throughout the work. It was one of Rachmaninoff's two favorite compositions, along with his ''All-Night Vigil (Rachmaninoff), All-Night Vigil'', and is considered by some to be his secular choral masterpiece. Rachmaninoff called the work both a choral symphony and (unofficially) his Third Symphony shortly after writing it; however, he would later write a purely instrumental Symphony No. 3 (Rachmaninoff), Third Symphony at his new villa in Switzerland. Rachmaninoff dedicated ''The Bells'' to Netherlands, Dutch conductor Willem Mengelberg and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
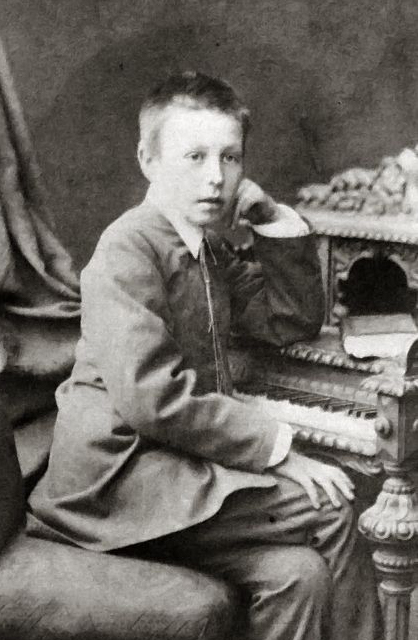
Rachmaninoff
Sergei Vasilyevich Rachmaninoff; in Russian pre-revolutionary script. (28 March 1943) was a Russian composer, virtuoso pianist, and conductor. Rachmaninoff is widely considered one of the finest pianists of his day and, as a composer, one of the last great representatives of Romanticism in Russian classical music. Early influences of Tchaikovsky, Rimsky-Korsakov, and other Russian composers gave way to a thoroughly personal idiom notable for its song-like melodicism, expressiveness, dense contrapuntal textures, and rich orchestral colours. The piano is featured prominently in Rachmaninoff's compositional output and he used his skills as a performer to fully explore the expressive and technical possibilities of the instrument. Born into a musical family, Rachmaninoff began learning the piano at the age of four. He studied piano and composition at the Moscow Conservatory, from which he graduated in 1892, having already written several compositions. In 1897, following the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |