|
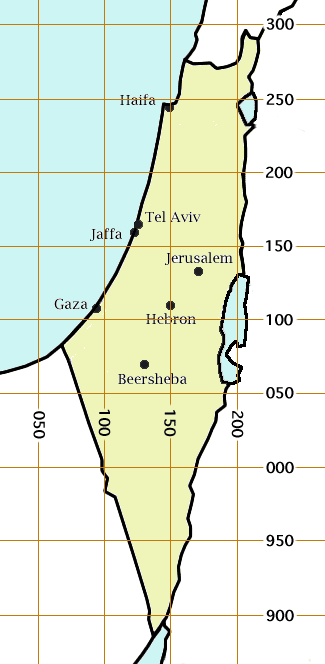
Ein Gedi
Ein Gedi (, ), also spelled En Gedi, meaning "Spring (hydrology), spring of the goat, kid", is an oasis, an Archaeological site, archeological site and a nature reserve in Israel, located west of the Dead Sea, near Masada and the Qumran Caves. Ein Gedi (kibbutz), Ein Gedi, a kibbutz, was established nearby in 1954. Ein Gedi is a popular tourist attraction and was listed in 2016 as one of the most popular nature sites in Israel. The site attracts about one million visitors a year. Etymology The name ''Ein Gedi'' is composed of two words (In both Arabic and Hebrew language, Hebrew): ''ein'' means spring or a fountain and ''gǝdi'' means goat-kid. Ein Gedi thus means "kid spring" or "fountain of the kid". The Hebrew name is also transliterated as 'En Gedi, En-gedi, Eggadi, Engaddi, and Engedi; the Arabic name as 'Ain Jidi and 'Ein Jidi.En Gedi at bibleplaces.com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Judean Desert
The Judaean Desert or Judean Desert (, ) is a desert in the West Bank and Israel that stretches east of the ridge of the Judaean Mountains and in their rain shadow, so east of Jerusalem, and descends to the Dead Sea. Under the name El-Bariyah, it has been nominated to the Tentative List of World Heritage Sites in the West Bank and Israel, particularly for its monastic ruins. Etymology The term originates in the Hebrew Bible, and it is mentioned in Judges and Psalms. It is sometimes known as ''Yeshimon'', meaning ''desert'' or ''wildland'', or yet ''Wilderness of Judah'' or ''Wilderness of Judaea'', among others. Similarly, the Arabic name برية الخليل, ''Bariyat El-Khalil'' (sometimes stylized 'El-Bariyah') means ''Wilderness of Hebron.'' Geography The Judaean Desert lies east of Jerusalem and descends to the Dead Sea. The Judaean Desert stretches from the northeastern Negev to the east of Beit El, and is marked by natural terraces with escarpments. It e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hebrew Language
Hebrew (; ''ʿÎbrit'') is a Northwest Semitic language within the Afroasiatic language family. A regional dialect of the Canaanite languages, it was natively spoken by the Israelites and remained in regular use as a first language until after 200 CE and as the liturgical language of Judaism (since the Second Temple period) and Samaritanism. The language was revived as a spoken language in the 19th century, and is the only successful large-scale example of linguistic revival. It is the only Canaanite language, as well as one of only two Northwest Semitic languages, with the other being Aramaic, still spoken today. The earliest examples of written Paleo-Hebrew date back to the 10th century BCE. Nearly all of the Hebrew Bible is written in Biblical Hebrew, with much of its present form in the dialect that scholars believe flourished around the 6th century BCE, during the time of the Babylonian captivity. For this reason, Hebrew has been referred to by Jews as '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
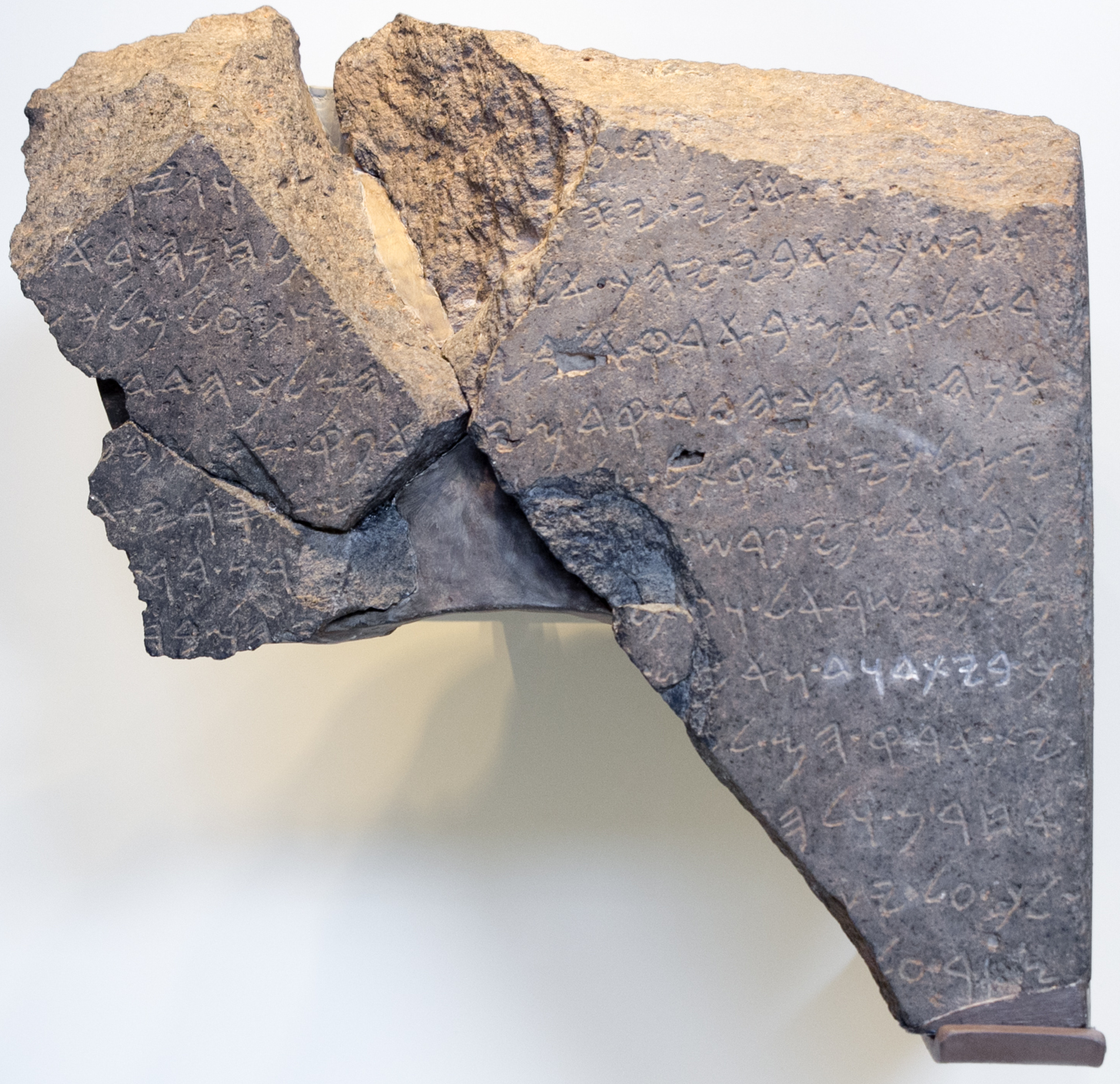
Kingdom Of Judah
The Kingdom of Judah was an Israelites, Israelite kingdom of the Southern Levant during the Iron Age. Centered in the highlands to the west of the Dead Sea, the kingdom's capital was Jerusalem. It was ruled by the Davidic line for four centuries. Jews are named after Judah, and primarily descend from people who lived in the region. The Hebrew Bible depicts the Kingdom of Judah as one of the two successor states of the Kingdom of Israel (united monarchy), United Kingdom of Israel, a term denoting the united monarchy under biblical kings Saul, David, and Solomon and covering the territory of Judah and Kingdom of Israel (Samaria), Israel. However, during the 1980s, Biblical minimalism, some biblical scholars began to argue that the archaeological evidence for an extensive kingdom before the late 8th century BCE is too weak, and that the methodology used to obtain the evidence is flawed. In the 10th and early 9th centuries BCE, the territory of Judah might have been limited ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hebrew
Hebrew (; ''ʿÎbrit'') is a Northwest Semitic languages, Northwest Semitic language within the Afroasiatic languages, Afroasiatic language family. A regional dialect of the Canaanite languages, it was natively spoken by the Israelites and remained in regular use as a first language until after 200 CE and as the Sacred language, liturgical language of Judaism (since the Second Temple period) and Samaritanism. The language was Revival of the Hebrew language, revived as a spoken language in the 19th century, and is the only successful large-scale example of Language revitalization, linguistic revival. It is the only Canaanite language, as well as one of only two Northwest Semitic languages, with the other being Aramaic, still spoken today. The earliest examples of written Paleo-Hebrew alphabet, Paleo-Hebrew date back to the 10th century BCE. Nearly all of the Hebrew Bible is written in Biblical Hebrew, with much of its present form in the dialect that scholars believe flourish ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palestine Grid
The Palestine grid was the geographic coordinate system used by the Survey Department of Palestine. The system was chosen by the Survey Department of the Government of Palestine in 1922. The projection used was the Cassini projection, Cassini-Soldner projection. The central Meridian (geography), meridian (the line of longitude along which there is no local distortion) was chosen as that passing through a marker on the hill of Mar Elias Monastery south of Jerusalem. The false origin (zero point) of the grid was placed 100 km to the south and west of the Ali el-Muntar hill that overlooks Gaza City, Gaza city. The unit length for the grid was the kilometre; the British units were not even considered. At the time the grid was established, there was no intention of mapping the lower reaches of the Negev Desert, but this did not remain true. Those southern regions having a negative Easting and northing, northing coordinate then became a source of confusion, which was solved by ad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
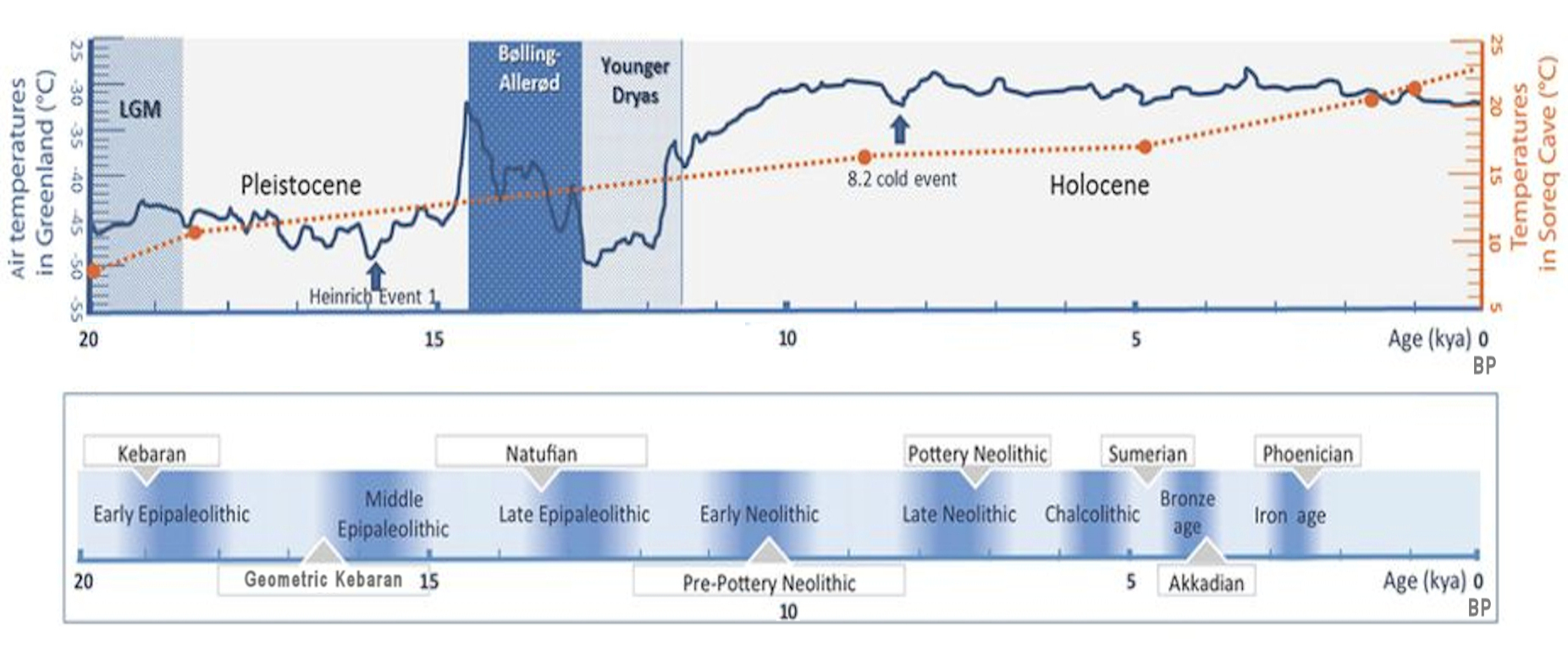
Ghassulian
Ghassulian refers to a culture and an archaeological stage dating to the Middle and Late Chalcolithic Period in the Southern Levant (c. 4400 – c. 3500 BC). Its type-site, Teleilat el-Ghassul, is located in the eastern Jordan Valley near the northern edge of the Dead Sea, in modern Jordan. It was excavated in 1929-1938 and in 1959–1960, by the Jesuits. Basil Hennessy dug at the site in 1967 and in 1975–1977, and Stephen Bourke in 1994–1999. The Ghassulian stage was characterized by small hamlet settlements of mixed farming peoples, who had emigrated from the north and settled in the southern Levant: today's Jordan, Israel and Palestinian territories. People of the Beersheba culture (a Ghassulian subculture) lived in underground dwellings, a unique phenomenon in the archaeological history of the region, or in trapezoidal houses of mud-brick. Those were often built partially underground (on top of collapsed underground dwellings) and were covered with remarkable po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flint Tool
Stone tools have been used throughout human history but are most closely associated with prehistoric cultures and in particular those of the Stone Age. Stone tools may be made of either ground stone or knapped stone, the latter fashioned by a craftsman called a flintknapper. Stone has been used to make a wide variety of tools throughout history, including arrowheads, spearheads, hand axes, and querns. Knapped stone tools are nearly ubiquitous in pre-metal-using societies because they are easily manufactured, the tool stone raw material is usually plentiful, and they are easy to transport and sharpen. The study of stone tools is a cornerstone of prehistoric archaeology because they are essentially indestructible and therefore a ubiquitous component of the archaeological record. Ethnoarchaeology is used to further the understanding and cultural implications of stone tool use and manufacture. Knapped stone tools are made from cryptocrystalline materials such as chert, flint, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pre-Pottery Neolithic A
Pre-Pottery Neolithic A (PPNA) denotes the first stage of the Pre-Pottery Neolithic, in early Levantine and Anatolian Neolithic culture, dating to years ago, that is, 10,000–8800 BCE. Archaeological remains are located in the Levantine and Upper Mesopotamian region of the Fertile Crescent. The time period is characterized by tiny circular mud-brick dwellings, the cultivation of crops, the hunting of wild game, and unique burial customs in which bodies were buried below the floors of dwellings. The Pre-Pottery Neolithic A and the following Pre-Pottery Neolithic B (PPNB) were originally defined by Kathleen Kenyon in the type site of Jericho, State of Palestine. During this time, pottery was not yet in use. They precede the ceramic Neolithic Yarmukian culture. PPNA succeeds the Natufian culture of the Epipalaeolithic Near East. Settlements PPNA archaeological sites are much larger than those of the preceding Natufian hunter-gatherer culture, and contain traces of commun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NKJV
The New King James Version (NKJV) is a translation of the Bible in contemporary English, working as a revision of the King James Version. Published by Thomas Nelson, the complete NKJV was released in 1982. With regard to its textual basis, the NKJV relies on a modern critical edition (the '' Biblia Hebraica Stuttgartensia'') for the Old Testament, while opting to use the ''Textus Receptus'' for the New Testament. The NKJV is described by Thomas Nelson as being "scrupulously faithful to the original ing James Version yet truly updated to enhance its clarity and readability." History The text of the New Testament was published in 1979; the Psalms in 1980; and the full Bible in 1982. The project took seven years in total to complete. A minor revision was completed in 1984. Translation philosophy The Executive Editor of the NKJV, Arthur L. Farstad, addressed textual concerns in a book explaining the NKJV translation philosophy.Arthur L. Farstad, "The New King James Version ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Complete Jewish Bible
Messianic Bible translations are translations, or editions of translations, in English of the Christian Bible, some of which are widely used in the Messianic Judaism and Hebrew Roots communities. They are not the same as Jewish English Bible translations. They are often not standard straight English translations of the Christian Bible, but are translations which specifically incorporate elements for a Messianic audience. These elements include, but are not limited to, the use of the Hebrew names for all books, the Hebrew Bible (Tanakh) ordering for the books of the Old Testament, both testaments being named their Hebrew names (''Tanakh'' and ''Brit Chadasha''). This approach also includes the New Testament being translated with the preference of spelling names (people, concepts and place names) in transliterated Hebrew rather than directly translated from Greek into English. Some Sacred Name Bibles, such as the ''Hallelujah Scriptures'', conform to these elements and therefore m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Common English Bible
The Common English Bible (CEB) is an English translation of the Bible whose language is intended to be at a comfortable reading level for the majority of English readers. The translation, sponsored by an alliance of American mainline Protestant denomination publishers, was begun in late 2008 and was finished in 2011. It generally uses gender-inclusive language in references to humans and some editions sold include the books of the Apocrypha which are used by the Catholic Church, Orthodox Church, and in some Anglican congregations. History The Common English Bible is sponsored by an alliance of several denominational publishers in the United States operating under an umbrella group called the Christian Resources Development Corporation (CRDC), incorporated in 2009 and based in Nashville, Tennessee. The publishing houses participating are Chalice Press (Disciples of Christ), Westminster John Knox Press ( Presbyterian Church U.S.A.), Church Publishing Inc ( Episcopal Church), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NRSV
The New Revised Standard Version (NRSV) is a translation of the Bible in American English. It was first published in 1989 by the National Council of Churches, the NRSV was created by an ecumenical committee of scholars "comprising about thirty members". The NRSV is considered a revision of the Revised Standard Version, and relies on recently published critical editions of the original Hebrew, Aramaic, and Greek texts. It is thus a revision in a series of English translations that has been identified as beginning with the King James Version. A major revision of the NRSV, the New Revised Standard Version Updated Edition (NRSVue), was released in 2021. Used broadly among biblical scholars, the NRSV was intended as a translation to serve the devotional, liturgical, and scholarly needs of the broadest possible range of Christian religious adherents. The full 84 book translation includes the Protestant enumeration of the Old Testament, the Apocrypha, and the New Testament; another ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |