|
Eilbek
(former Eilbeck) is a quarter of the German city of Hamburg and part of the Wandsbek borough. It originated as a small village on the outskirts of Hamburg and was eventually incorporated when the city expanded. In 2020 the population was 22,235. Etymology The village was named after the small Wandse river, here named Eilbek. This is usually regarded as derived from the old German for "rushing stream", ''eile'' meaning to hurry or rush and ''Beck'' meaning river or stream. However other sources interpret the first element, ''Ylen'' or ''Ilen'', as leech (German ''Egel''), because in northern Germany the language is Low German. History Eilbek first appears in 1247 as Ylenbeke. During the Great Fire of Hamburg from May 5 to May 8, 1842, the center of Hamburg was destroyed. Some of the people from Hamburg-Altstadt settled in Ylenbeke. In the Second World War Eilbek was almost completely destroyed by the heavy air raids in July 1943 (codenamed Operation Gomorrah). With the r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wandse
(in sections also called Eilbek) is a river flowing through Schleswig-Holstein and Hamburg, Germany. The Wandse rises west of the village of Siek in Kreis Stormarn in Schleswig-Holstein and ends in the center of Hamburg in the Alster. Along the banks of the Wandse there were many water mills. The river passes through the settlements of Siek, Braak, Stapelfeld, and Hamburg. The Hamburg district of Wandsbek takes its name from the river as it winds its way westwards via the , a public urban park. After passing through the Mühlenteich pond, the river continues as Eilbek (later Eilbekkanal), eponymous to the Eilbek district. The canal joins the Alster in the heart of Hamburg at Außenalster. Meander restoration The River Wandse is a site of interest for river management and conservation due to a pioneering project carried out in 1982 to restore the original meanders to an engineered section of the river flowing through the national park. See also *List of rivers of Schlesw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wandsbek
Wandsbek () is the second-largest of seven Boroughs and quarters of Hamburg#Boroughs, boroughs that make up the city and state of Hamburg, Germany. The name of the district is derived from the river Wandse which passes through here. Hamburg-Wandsbek, Wandsbek, which was formerly an independent city, is urban and, along with Hamburg-Eilbek, Eilbek and Marienthal, part of the city's economic and cultural core. In 2020 the population was 442,702, making it the most populous borough in Hamburg. History Wandsbek was the place of residence of the poet Johann Heinrich Voss and of Matthias Claudius, who here issued (1771–1775) the newspaper (The Wandsbeck Messenger). There is a monument to Claudius in the town. During World War II from May 2, 1944 until May 3, 1945 a subcamp of the Nazi concentration camp of Neuengamme concentration camp, Neuengamme was located in Wandsbek, listed as no. 565 Hamburg-Wandsbek in the official German list. On January 1, 2007 the ''Ortsämter'' (Precincts ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hamburg
Hamburg (, ; ), officially the Free and Hanseatic City of Hamburg,. is the List of cities in Germany by population, second-largest city in Germany after Berlin and List of cities in the European Union by population within city limits, 7th-largest in the European Union with a population of over 1.9 million. The Hamburg Metropolitan Region has a population of over 5.1 million and is the List of EU metropolitan areas by GDP, eighth-largest metropolitan region by GDP in the European Union. At the southern tip of the Jutland Peninsula, Hamburg stands on the branching River Elbe at the head of a estuary to the North Sea, on the mouth of the Alster and Bille (Elbe), Bille. Hamburg is one of Germany's three city-states alongside Berlin and Bremen (state), Bremen, and is surrounded by Schleswig-Holstein to the north and Lower Saxony to the south. The Port of Hamburg is Germany's largest and Europe's List of busiest ports in Europe, third-largest, after Port of Rotterdam, Rotterda ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
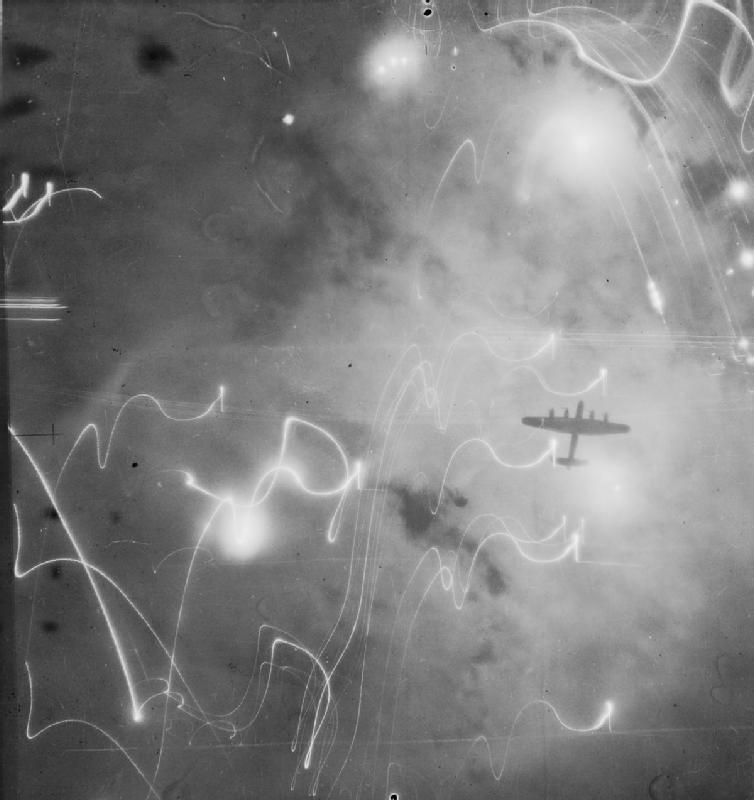
Bombing Of Hamburg In World War II
The Allied bombing of Hamburg during World War II included numerous attacks on civilians and civic infrastructure. As a large city and industrial centre, Hamburg's shipyards, U-boat pens, and the Hamburg-Harburg area oil refineries were attacked throughout the war. As part of a sustained campaign of strategic bombing during World War II, the attack during the last week of July 1943, code named Operation Gomorrah, created one of the largest firestorms raised by the Royal Air Force and United States Army Air Forces in World War II, killing an estimated 37,000 people in Hamburg, wounding 180,000 more, and destroying 60% of the city's houses. Hamburg was selected as a target because it was considered particularly susceptible to attack with incendiaries, which, from the experience of the Blitz, were known to inflict more damage than just high explosive bombs. Hamburg also contained a high number of targets supporting the German war effort and was relatively easy for navigators ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alliance '90/The Greens
Alliance 90/The Greens (, ), often simply referred to as Greens (, ), is a Green (politics), green political party in Germany. It was formed in 1993 by the merger of the Greens (formed in West Germany in 1980) and Alliance 90 (formed in East Germany in 1990). The Greens had itself merged with the East German Green Party after German reunification in 1990. Since November 2024, Franziska Brantner and Felix Banaszak have been co-leaders of the party. It currently holds 85 of the 630 seats in the Bundestag, having won 11% of first votes and 11.6% of second votes cast in the 2025 German federal election, 2025 federal election, putting it in fourth place of the seven political parties by number of seats. Its parliamentary co-leaders are Britta Haßelmann and Katharina Dröge. The Greens have been part of the federal government twice: first as a junior partner to the Social Democratic Party of Germany, Social Democrats (SPD) from 1998 to 2005, and then with the SPD and the Free Democrat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lower Saxony
Lower Saxony is a States of Germany, German state (') in Northern Germany, northwestern Germany. It is the second-largest state by land area, with , and fourth-largest in population (8 million in 2021) among the 16 ' of the Germany, Federal Republic of Germany. In rural areas, Northern Low Saxon and Saterland Frisian language, Saterland Frisian are still spoken, though by declining numbers of people. Lower Saxony borders on (from north and clockwise) the North Sea, the states of Schleswig-Holstein, Hamburg, , Brandenburg, Saxony-Anhalt, Thuringia, Hesse and North Rhine-Westphalia, and the Netherlands. Furthermore, the Bremen (state), state of Bremen forms two enclaves within Lower Saxony, one being the city of Bremen, the other its seaport, Bremerhaven (which is a semi-exclave, as it has a coastline). Lower Saxony thus borders more neighbours than any other single '. The state's largest cities are the state capital Hanover, Braunschweig (Brunswick), Oldenburg (city), Oldenburg, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Delmenhorst
Delmenhorst (; Northern Low Saxon: ''Demost'') is an urban district (''List of German urban districts, Kreisfreie Stadt'') in Lower Saxony, Germany. It has a population of 74,500 and is located west of downtown Bremen (city), Bremen with which it forms a contiguous urban area, whereas the city of Oldenburg (city), Oldenburg is to the northwest. The city has a total area of ; and a population density of approx. 1200 inhabitants per km². Since 2021 the mayor has been Petra Gerlach (Christian Democratic Union of Germany, CDU). History Delmenhorst was first mentioned in a charter in 1254, after the Count of Duchy of Oldenburg, Oldenburg, Otto I, bought the place near the river Delme in 1234. A castle to protect the newly founded settlement was established in about 1247. The following count, Otto II, made the castle his residency; Delmenhorst was declared an independent town on 15 July 1371 under Bremen's law. After a short period under the governance of the bishop of Bremen fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lübeck
Lübeck (; or ; Latin: ), officially the Hanseatic League, Hanseatic City of Lübeck (), is a city in Northern Germany. With around 220,000 inhabitants, it is the second-largest city on the German Baltic Sea, Baltic coast and the second-largest city in the state of Schleswig-Holstein, after its capital of Kiel. It is the List of cities in Germany by population, 36th-largest city in Germany. The city lies in the Holsatian part of Schleswig-Holstein, on the mouth of the Trave, which flows into the Bay of Lübeck in the borough of Travemünde, and on the Trave's tributary Wakenitz. The island with the historic old town and the districts north of the Trave are also located in the historical region of Wagria. Lübeck is the southwesternmost city on the Baltic Sea, and the closest point of access to the Baltic from Hamburg. The city lies in the Northern Low Saxon, Holsatian dialect area of Low German. The name ''Lübeck'' ultimately stems from the Slavic languages, Slavic root (' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bundesstraße 75
The Bundesstraße 75 (or B 75) is a German federal highway running in a northeast to southwest direction from the Lübeck borough of Travemünde to Delmenhorst near Bremen. The highway goes through the Herren Tunnel under the Trave river just shy of its northeastern terminus. It formerly crossed a drawbridge that the tunnel replaced. See also * Transport in Hamburg Transport in Hamburg comprises an extensive, Rail transport, rail system, rapid transit, subway system, airports and Waterway, maritime services for the more than 1.8 million inhabitants of the city of Hamburg and 5.3 million people in the Hamburg ... External links 075 B075 B075 B075 B 075 {{Germany-road-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Free Democratic Party (Germany)
The Free Democratic Party (, FDP, ) is a liberalism, liberal political party in Germany. The FDP was founded in 1948 by members of former liberal political parties in Germany before World War II, namely the German Democratic Party and the German People's Party. For most of the second half of the 20th century, particularly from 1961 to 1982, the FDP held the Balance of power (parliament), balance of power in the Bundestag. It has been a junior coalition partner to both the CDU/CSU (1949–1956, 1961–1966, 1982–1998, and 2009–2013) and Social Democratic Party of Germany, Social Democratic Party (SPD; 1969–1982 and 2021–2024). In the 2013 German federal election, 2013 federal election, the FDP failed to win any directly elected seats in the Bundestag and came up short of the Electoral threshold#Germany, 5 percent threshold to qualify for list representation, being left without representation in the Bundestag for the first time in its history. In the 2017 German federal el ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alternative For Germany
Alternative for Germany (, AfD, ) is a Far-right politics in Germany (1945–present), far-right,Far-right: * * * * * * * * * * * * * * Right-wing populism, right-wing populist and National conservatism, national-conservative political party in Germany. The Federal Office for the Protection of the Constitution (BfV), Germany's domestic intelligence agency, had classified the party as a "confirmed right-wing extremist endeavour". This classification was temporarily suspended by the BfV a week after its announcement in May 2025. The report that led to the classification was later leaked to the public. The federal branch of the AfD has been under surveillance since a court ruling in 2022 after it was classified by the domestic intelligence as a "suspected extremist party" in 2021. This classification of a party represented in the federal parliament was a first in the history of Germany. Its name reflects its resistance to the mainstream policies of Angela Merkel a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christian Democratic Union Of Germany
The Christian Democratic Union of Germany ( , CDU ) is a Christian democratic and conservative political party in Germany. It is the major party of the centre-right in German politics. Friedrich Merz has been federal chairman of the CDU since 31 January 2022, and has served as the Chancellor of Germany since 6 May 2025. The CDU is the largest party in the Bundestag, the German federal legislature, with 208 out of 630 seats, having won 28.5% of votes in the 2025 German federal election, 2025 federal election. It forms the CDU/CSU Bundestag faction, also known as the Union, with its Bavarian counterpart, the Christian Social Union in Bavaria (CSU). The group's parliamentary leader is also Friedrich Merz. Founded in 1945 as an interdenominational Christian party, the CDU effectively succeeded the pre-war Catholic Centre Party (Germany), Centre Party, with many former members joining the party, including its first leader Konrad Adenauer. The party also included politicians of other ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |