 |
Eigenvalue
In linear algebra, an eigenvector ( ) or characteristic vector is a vector that has its direction unchanged (or reversed) by a given linear transformation. More precisely, an eigenvector \mathbf v of a linear transformation T is scaled by a constant factor \lambda when the linear transformation is applied to it: T\mathbf v=\lambda \mathbf v. The corresponding eigenvalue, characteristic value, or characteristic root is the multiplying factor \lambda (possibly a negative or complex number). Geometrically, vectors are multi-dimensional quantities with magnitude and direction, often pictured as arrows. A linear transformation rotates, stretches, or shears the vectors upon which it acts. A linear transformation's eigenvectors are those vectors that are only stretched or shrunk, with neither rotation nor shear. The corresponding eigenvalue is the factor by which an eigenvector is stretched or shrunk. If the eigenvalue is negative, the eigenvector's direction is reversed. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Stability Theory
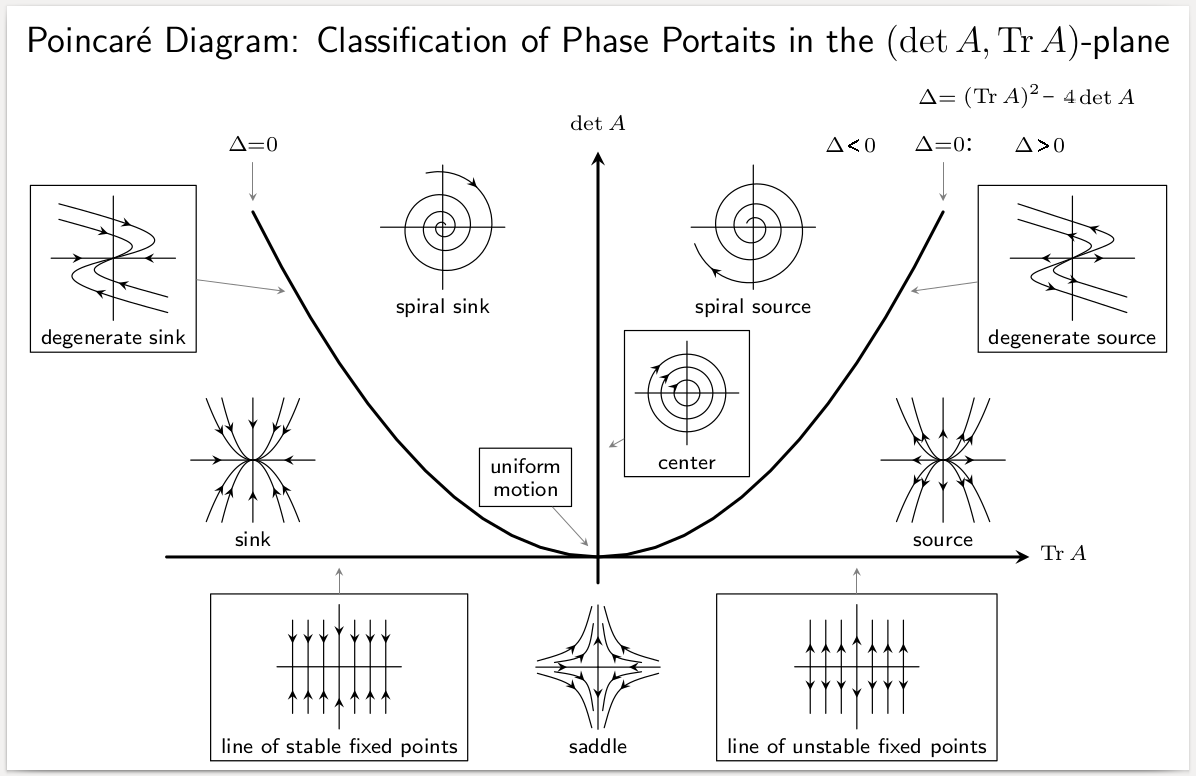
In mathematics, stability theory addresses the stability of solutions of differential equations and of trajectories of dynamical systems under small perturbations of initial conditions. The heat equation, for example, is a stable partial differential equation because small perturbations of initial data lead to small variations in temperature at a later time as a result of the maximum principle. In partial differential equations one may measure the distances between functions using Lp space, Lp norms or the sup norm, while in differential geometry one may measure the distance between spaces using the Gromov–Hausdorff convergence, Gromov–Hausdorff distance. In dynamical systems, an orbit (dynamics), orbit is called ''Lyapunov stability, Lyapunov stable'' if the forward orbit of any point is in a small enough neighborhood or it stays in a small (but perhaps, larger) neighborhood. Various criteria have been developed to prove stability or instability of an orbit. Under favorable ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Matrix (mathematics)
In mathematics, a matrix (: matrices) is a rectangle, rectangular array or table of numbers, symbol (formal), symbols, or expression (mathematics), expressions, with elements or entries arranged in rows and columns, which is used to represent a mathematical object or property of such an object. For example, \begin1 & 9 & -13 \\20 & 5 & -6 \end is a matrix with two rows and three columns. This is often referred to as a "two-by-three matrix", a " matrix", or a matrix of dimension . Matrices are commonly used in linear algebra, where they represent linear maps. In geometry, matrices are widely used for specifying and representing geometric transformations (for example rotation (mathematics), rotations) and coordinate changes. In numerical analysis, many computational problems are solved by reducing them to a matrix computation, and this often involves computing with matrices of huge dimensions. Matrices are used in most areas of mathematics and scientific fields, either directly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Eigenface
An eigenface ( ) is the name given to a set of eigenvectors when used in the computer vision problem of human face recognition. The approach of using eigenfaces for recognition was developed by Sirovich and Kirby and used by Matthew Turk and Alex Pentland in face classification. The eigenvectors are derived from the covariance matrix of the probability distribution over the high-dimensional vector space of face images. The eigenfaces themselves form a basis set of all images used to construct the covariance matrix. This produces dimension reduction by allowing the smaller set of basis images to represent the original training images. Classification can be achieved by comparing how faces are represented by the basis set. History The eigenface approach began with a search for a low-dimensional representation of face images. Sirovich and Kirby showed that principal component analysis could be used on a collection of face images to form a set of basis features. These basis ima ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Vibration Analysis
Vibration () is a mechanical phenomenon whereby oscillations occur about an equilibrium point. Vibration may be deterministic if the oscillations can be characterised precisely (e.g. the periodic motion of a pendulum), or random if the oscillations can only be analysed statistically (e.g. the movement of a tire on a gravel road). Vibration can be desirable: for example, the motion of a tuning fork, the reed in a woodwind instrument or harmonica, a mobile phone, or the cone of a loudspeaker. In many cases, however, vibration is undesirable, wasting energy and creating unwanted sound. For example, the vibrational motions of engines, electric motors, or any mechanical device in operation are typically unwanted. Such vibrations could be caused by imbalances in the rotating parts, uneven friction, or the meshing of gear teeth. Careful designs usually minimize unwanted vibrations. The studies of sound and vibration are closely related (both fall under acoustics). Sound, o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Linear Algebra
Linear algebra is the branch of mathematics concerning linear equations such as :a_1x_1+\cdots +a_nx_n=b, linear maps such as :(x_1, \ldots, x_n) \mapsto a_1x_1+\cdots +a_nx_n, and their representations in vector spaces and through matrix (mathematics), matrices. Linear algebra is central to almost all areas of mathematics. For instance, linear algebra is fundamental in modern presentations of geometry, including for defining basic objects such as line (geometry), lines, plane (geometry), planes and rotation (mathematics), rotations. Also, functional analysis, a branch of mathematical analysis, may be viewed as the application of linear algebra to Space of functions, function spaces. Linear algebra is also used in most sciences and fields of engineering because it allows mathematical model, modeling many natural phenomena, and computing efficiently with such models. For nonlinear systems, which cannot be modeled with linear algebra, it is often used for dealing with first-order a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Square Matrix
In mathematics, a square matrix is a Matrix (mathematics), matrix with the same number of rows and columns. An ''n''-by-''n'' matrix is known as a square matrix of order Any two square matrices of the same order can be added and multiplied. Square matrices are often used to represent simple linear transformations, such as Shear mapping, shearing or Rotation (mathematics), rotation. For example, if R is a square matrix representing a rotation (rotation matrix) and \mathbf is a column vector describing the Position (vector), position of a point in space, the product R\mathbf yields another column vector describing the position of that point after that rotation. If \mathbf is a row vector, the same transformation can be obtained using where R^ is the transpose of Main diagonal The entries a_ () form the main diagonal of a square matrix. They lie on the imaginary line which runs from the top left corner to the bottom right corner of the matrix. For instance, the main diagonal of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Quantum Mechanics
Quantum mechanics is the fundamental physical Scientific theory, theory that describes the behavior of matter and of light; its unusual characteristics typically occur at and below the scale of atoms. Reprinted, Addison-Wesley, 1989, It is the foundation of all quantum physics, which includes quantum chemistry, quantum field theory, quantum technology, and quantum information science. Quantum mechanics can describe many systems that classical physics cannot. Classical physics can describe many aspects of nature at an ordinary (macroscopic and Microscopic scale, (optical) microscopic) scale, but is not sufficient for describing them at very small submicroscopic (atomic and subatomic) scales. Classical mechanics can be derived from quantum mechanics as an approximation that is valid at ordinary scales. Quantum systems have Bound state, bound states that are Quantization (physics), quantized to Discrete mathematics, discrete values of energy, momentum, angular momentum, and ot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Complex Number
In mathematics, a complex number is an element of a number system that extends the real numbers with a specific element denoted , called the imaginary unit and satisfying the equation i^= -1; every complex number can be expressed in the form a + bi, where and are real numbers. Because no real number satisfies the above equation, was called an imaginary number by René Descartes. For the complex number is called the , and is called the . The set of complex numbers is denoted by either of the symbols \mathbb C or . Despite the historical nomenclature, "imaginary" complex numbers have a mathematical existence as firm as that of the real numbers, and they are fundamental tools in the scientific description of the natural world. Complex numbers allow solutions to all polynomial equations, even those that have no solutions in real numbers. More precisely, the fundamental theorem of algebra asserts that every non-constant polynomial equation with real or complex coefficie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Shear Mapping
In plane geometry, a shear mapping is an affine transformation that displaces each point in a fixed direction by an amount proportional to its signed distance function, signed distance from a given straight line, line parallel (geometry), parallel to that direction. This type of mapping is also called shear transformation, transvection, or just shearing. The transformations can be applied with a shear matrix or transvection, an elementary matrix that represents the Elementary row operations#Row-addition transformations, addition of a multiple of one row or column to another. Such a matrix (mathematics), matrix may be derived by taking the identity matrix and replacing one of the zero elements with a non-zero value. An example is the linear map that takes any point with Cartesian coordinates, coordinates (x,y) to the point (x + 2y,y). In this case, the displacement is horizontal by a factor of 2 where the fixed line is the -axis, and the signed distance is the -coordinate. Not ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Scaling (geometry)
In affine geometry, uniform scaling (or isotropic scaling) is a linear transformation that enlarges (increases) or shrinks (diminishes) objects by a '' scale factor'' that is the same in all directions ( isotropically). The result of uniform scaling is similar (in the geometric sense) to the original. A scale factor of 1 is normally allowed, so that congruent shapes are also classed as similar. Uniform scaling happens, for example, when enlarging or reducing a photograph, or when creating a scale model of a building, car, airplane, etc. More general is scaling with a separate scale factor for each axis direction. Non-uniform scaling (anisotropic scaling) is obtained when at least one of the scaling factors is different from the others; a special case is directional scaling or stretching (in one direction). Non-uniform scaling changes the shape of the object; e.g. a square may change into a rectangle, or into a parallelogram if the sides of the square are not parallel to th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Atomic Orbital
In quantum mechanics, an atomic orbital () is a Function (mathematics), function describing the location and Matter wave, wave-like behavior of an electron in an atom. This function describes an electron's Charge density, charge distribution around the Atomic nucleus, atom's nucleus, and can be used to calculate the probability of finding an electron in a specific region around the nucleus. Each orbital in an atom is characterized by a set of values of three quantum numbers , , and , which respectively correspond to electron's energy, its angular momentum, orbital angular momentum, and its orbital angular momentum projected along a chosen axis (magnetic quantum number). The orbitals with a well-defined magnetic quantum number are generally complex-valued. Real-valued orbitals can be formed as linear combinations of and orbitals, and are often labeled using associated Spherical harmonics#Harmonic polynomial representation, harmonic polynomials (e.g., ''xy'', ) which describe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Eigen
Eigen may refer to: People with the given name *, Japanese sport shooter *, Japanese professional wrestler * Frauke Eigen (born 1969) German photographer, photojournalist and artist * Manfred Eigen (1927–2019), German biophysicist * Michael Eigen (born 1936) American psychologist and psychoanalyst * Karl Eigen (1927–2016) German farmer and politician * Saint Eigen, female Christian saint * Peter Eigen, (born 1938) German lawyer, development economist and civil society leader Places * Eigen, Schwyz, settlement in the municipality of Alpthal in the canton of Schwyz, Switzerland * Eigen, Thurgau, locality in the municipality of Lengwil in the canton of Thurgau, Switzerland * Eigen-ji, Buddhist temple Others * Eigen (C++ library), computer programming library for matrix and linear algebra operations * Eigen Wereld, is Opgezwolle's third album * Eigen Kweek, was a 2013-2019 Belgian crime comedy television series See also * Eigenvalue, eigenvector and eigenspace in mat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |