|
Egyptian Frigate Rasheed
USS ''Moinester'' (FF-1097) was a . The ship was named for Lieutenant (navy), LTJG Robert W. Moinester who was killed in action during the Battle of Huế on 31 January 1968 and was posthumously awarded the Silver Star. ''Moinester'' was christened by Mrs. Gertrude Mahoney Moinester, the mother of the ship's namesake and ship sponsor. Design and description The ''Knox''-class design was derived from the modified to extend range and without a long-range missile system. The ships had an length overall, overall length of , a beam (nautical), beam of and a draft (ship), draft of . They Displacement (ship), displaced at full load. Their crew consisted of 13 officers and 211 enlisted men. The ships were equipped with one Westinghouse Combustion Turbine Systems Division, Westinghouse geared steam turbine that drove the single propeller shaft. The turbine was designed to produce , using steam provided by 2 Combustion Engineering, C-E boilers, to reach the designed speed of . The ''Kn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Avondale Shipyard
Avondale Shipyard was an independent shipbuilding company, acquired by Litton Industries, in turn acquired by Northrop Grumman Corporation. In 2011, along with the former Ingalls Shipbuilding, the yard was part of Huntington Ingalls Industries. It closed in October 2014. The yard was located on the west bank of the Mississippi River in an area called Bridge City, about upriver from New Orleans near Westwego, Louisiana. It was the site of the modernization of the battleship in the early 1980s and also constructed some of the lighter aboard ships (LASH). At one time, it was the largest employer in Louisiana, with about 26,000 employees. History Avondale Shipyards was founded in 1938 as Avondale Marine Ways by James Grinstead Viavant, Harry Koch, and Perry N. Ellis.University of New ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ship Sponsor
A ship sponsor, by tradition, is a female civilian who is invited to "sponsor" a vessel, presumably to bestow good luck and divine protection over the seagoing vessel and all that sail aboard.Eyers, Jonathan (2011). ''Don't Shoot the Albatross!: Nautical Myths and Superstitions''. A&C Black, London, UK. . In the United States Navy and the United States Coast Guard, the sponsor is technically considered a permanent member of the ship's crew and is expected to give a part of her personality to the ship, as well as advocate for its continued service and well-being. For passenger ships the sponsor is called a godmother if the sponsor is female, or a godfather if the sponsor is male. See also * Ceremonial ship launching Ceremonial ship launching involves the performing of ceremonies associated with the process of transferring a vessel to the water. It is a nautical tradition in many cultures, dating back millennia, to accompany the physical process with ... (christening) R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mark 32 Surface Vessel Torpedo Tubes
Mark 32 surface vessel torpedo tubes (Mk 32 SVTT) is a torpedo launching system designed for the United States Navy. History The Mark 32 has been the standard anti-submarine torpedo launching system aboard United States Navy surface vessels since its introduction in 1960, and is in use aboard the warships of several other navies. During the FRAM Program, , and destroyers were modernized and fitted with two Mark 32 torpedo tubes on each side of their midship. The torpedo tubes' service extended to multiple other countries such as Mexico, South Korea, Taiwan, Turkey, Egypt and many more due to the fact that decommissioned American ships were bought or transferred over to them throughout the years, notably s. Japan uses the HOS-301 torpedo tubes which are redesignated version of the Mark 32. Design Most versions (referred to as modifications or mods) are triple-tube sets that can be rotated or trained to face a target. The exception is the Mod 9 sets, which only have two ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bridge (nautical)
A bridge (also known as a command deck), or wheelhouse (also known as a pilothouse), is a room or platform of a ship, submarine, airship, or spacecraft, spaceship from which the ship can be commanded. When a ship is under way, the bridge is manned by an Watchstanding, officer of the watch aided usually by an Able Seaman (occupation), able seaman acting as a lookout. During critical maneuvers the Captain (naval), captain will be on the bridge, often supported by an officer of the watch, an able seaman on the wheel and sometimes a Maritime pilot, pilot, if required. File:Bridge of Cargo Ship in Port Everglades.jpg, Navigational bridge of a cargo ship docked in Port Everglades, Florida File:Bridge of the RV Sikuliaq.jpg, The interior of the bridge of the Research Vessel ''RV Sikuliaq, Sikuliaq'', docked in Ketchikan, Alaska File:Wheelhouse of Leao Dos Mares.jpg, Wheelhouse on a tugboat, topped with a flying bridge File:Bridge of a Modern Cruise Ship.jpg, Appearance of a bridge on a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
3-inch/50-caliber Gun
The 3-inch/50-caliber gun (spoken "three-inch fifty-caliber") in United States naval gun terminology indicates the gun fired a projectile in diameter, and the barrel was 50 calibers long (barrel length is 3 in × 50 = ). Different guns (identified by Mark numbers) of this caliber were used by the U.S. Navy and U.S. Coast Guard from 1900 through to 1990 on a variety of combatant and transport ship classes. The gun is still in use with the Spanish Navy on ''Serviola''-class patrol boats. Early low-angle guns The US Navy's first 3 inch /50-caliber gun (Mark 2) was an early model with a projectile velocity of per second. Low-angle (single-purpose/non-anti-aircraft) mountings for this gun had a range of 7000 yards at the maximum elevation of 15 degrees. The gun entered service around 1900 with the s, and was also fitted to s. By World War II these guns were found only on a few Coast Guard cutters and Defensively Equipped Merchant Ships. Low-angle 3 inch/50-caliber guns ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boiler
A boiler is a closed vessel in which fluid (generally water) is heated. The fluid does not necessarily boil. The heated or vaporized fluid exits the boiler for use in various processes or heating applications, including water heating, central heating, boiler-based power generation, cooking, and sanitation. Heat sources In a fossil fuel power plant using a steam cycle for power generation, the primary heat source will be combustion of coal, oil, or natural gas. In some cases byproduct fuel such as the carbon monoxide rich offgasses of a coke battery can be burned to heat a boiler; biofuels such as bagasse, where economically available, can also be used. In a nuclear power plant, boilers called steam generators are heated by the heat produced by nuclear fission. Where a large volume of hot gas is available from some process, a heat recovery steam generator or recovery boiler can use the heat to produce steam, with little or no extra fuel consumed; such a configuration is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Combustion Engineering
Combustion Engineering (C-E) was a multi-national American-based engineering firm that developed nuclear steam supply power systems in the United States. Originally headquartered in New York City, C-E moved its corporate offices to Stamford, Connecticut, in 1973. C-E owned over three dozen other companies including Lummus Company, National Tank Company and the Morgan Door Company. The company was acquired by Asea Brown Boveri in early 1990. The boiler and fossil fuel businesses were purchased by Alstom in 2000, and the nuclear business was purchased by Westinghouse Electric Company also in 2000. History Founding Combustion Engineering was organized in 1912 through the merger of the Grieve Grate Company and the American Stoker Company, two well-known manufacturers of fuel burning equipment. The company was originally headquartered on Bowling Green Offices Building, 11 Broadway and at 43 ''-'' 5 ''-'' 7 Broad Street (Manhattan), both in Lower Manhattan. The city block was leased ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Propeller Shaft
A drive shaft, driveshaft, driving shaft, tailshaft (Australian English), propeller shaft (prop shaft), or Cardan shaft (after Girolamo Cardano) is a component for transmitting mechanical power, torque, and rotation, usually used to connect other components of a drivetrain that cannot be connected directly because of distance or the need to allow for relative movement between them. As torque carriers, drive shafts are subject to torsion and shear stress, equivalent to the difference between the input torque and the load. They must therefore be strong enough to bear the stress, while avoiding too much additional weight as that would in turn increase their inertia. To allow for variations in the alignment and distance between the driving and driven components, drive shafts frequently incorporate one or more universal joints, jaw couplings, or rag joints, and sometimes a splined joint or prismatic joint. History The term ''driveshaft'' first appeared during the mid-19th cen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Steam Turbine
A steam turbine or steam turbine engine is a machine or heat engine that extracts thermal energy from pressurized steam and uses it to do mechanical work utilising a rotating output shaft. Its modern manifestation was invented by Sir Charles Parsons in 1884. It revolutionized marine propulsion and navigation to a significant extent. Fabrication of a modern steam turbine involves advanced metalwork to form high-grade steel alloys into precision parts using technologies that first became available in the 20th century; continued advances in durability and efficiency of steam turbines remains central to the energy economics of the 21st century. The largest steam turbine ever built is the 1,770 MW Arabelle steam turbine built by Arabelle Solutions (previously GE Steam Power), two units of which will be installed at Hinkley Point C Nuclear Power Station, England. The steam turbine is a form of heat engine that derives much of its improvement in thermodynamic efficiency from the u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Westinghouse Combustion Turbine Systems Division
The Westinghouse Combustion Turbine Systems Division (CTSD), part of Westinghouse Electric (1886), Westinghouse Electric Corporation's Westinghouse Power Generation group, was originally located, along with the Steam Turbine Division (STD), in a major industrial manufacturing complex, referred to as the South Philadelphia Works, in Lester, Pennsylvania near to the Philadelphia International Airport. Before first being called "CTSD" in 1978, the Westinghouse industrial and electric utility gas turbine business operation progressed through several other names starting with Small Steam & Gas Turbine Division (SSGT) in the 1950s through 1971, then Gas Turbine Systems Division (GTSD) and Generation Systems Division (GSD) through the mid-late 1970s. The name CTSD came with the passage of energy legislation by the US government in 1978 which prohibited electric utilities from building new base load power plants that burned natural gas. Some participants in the industry decided to use the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
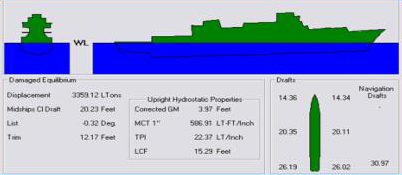
Displacement (ship)
The displacement or displacement tonnage of a ship is its weight. As the term indicates, it is measured indirectly, using Archimedes' principle, by first calculating the volume of water displaced by the ship, then converting that value into weight. Traditionally, various measurement rules have been in use, giving various measures in long tons. Today, tonnes are more commonly used. Ship displacement varies by a vessel's degree of load, from its empty weight as designed (known as "lightweight tonnage") to its maximum load. Numerous specific terms are used to describe varying levels of load and trim, detailed below. Ship displacement should not be confused with measurements of volume or capacity typically used for commercial vessels and measured by tonnage: net tonnage and gross tonnage. Calculation The process of determining a vessel's displacement begins with measuring its draft.George, 2005. p. 5. This is accomplished by means of its "draft marks". A merchant vessel has t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Draft (ship)
The draft or draught of a ship is a determined depth of the vessel below the waterline, measured vertically to its hull's lowest—its propellers, or keel, or other reference point. Draft varies according to the loaded condition of the ship. A deeper draft means the ship will have greater vertical depth below the waterline. Draft is used in under keel clearance calculations, where the draft is calculated with the available depth of water (from Electronic navigational charts) to ensure the ship can navigate safely, without grounding. Navigators can determine their draught by calculation or by visual observation (of the ship's painted load lines). Related terminology A ship's draft/draught is the "depth of the vessel below the waterline measured vertically to the lowest part of the hull, propellers, or other reference point". That is, the draft or draught is the maximum depth of any part of the vessel, including appendages such as rudders, propellers and drop keels if depl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |