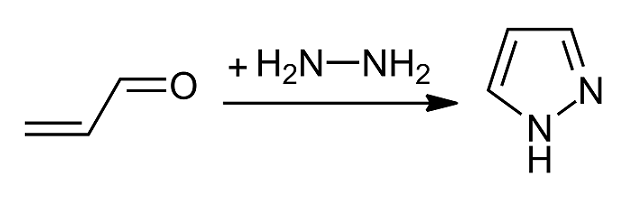|
Eganelisib
Eganelisib (USAN), codenamed IPI-549, is an experimental drug being investigated as a possible treatment for cancer. It is a highly selective phosphoinositide 3-kinase inhibitor, and thus works by inhibiting the enzyme PIK3CG, disrupting the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway which plays important roles in the development of cancer. Eganelisib is being developed by Infinity Pharmaceuticals. Early clinical trial results were published in September 2016. On September 29, 2020, it was granted Fast Track designation by the United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) as a treatment for inoperable, locally advanced, or metastatic triple-negative breast cancer, combined with a checkpoint inhibitor and chemotherapy. , five phase I/II clinical trials were ongoing in the United States, and one in Europe. Eganelisib has also been explored for its potential use in the treatment of COVID-19 and MRSA. Early, pre-clinical in vitro studies published in 2024 suggested eganelisib's ability to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphoinositide 3-kinase Inhibitor
Phosphoinositide 3-kinase inhibitors (PI3K inhibitors) are a class of medical drugs that are mainly used to treat advanced cancers. They function by inhibiting one or more of the phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K) enzymes, which are part of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway. This signal pathway regulates cellular functions such as growth and survival. It is strictly regulated in healthy cells, but is always active in many cancer cells, allowing the cancer cells to better survive and multiply. PI3K inhibitors block the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway and thus slow down cancer growth. They are examples of a targeted therapy. While PI3K inhibitors are an effective treatment, they can have very severe side effects and are therefore only used if other treatments have failed or are not suitable. After PI3K inhibitors had been under investigation as anti-cancer drugs for several years, the first one to be approved for treatment in clinical practice was idelalisib in 2014. Several others followed, and even ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
3C-like Protease
The 3C-like protease (3CLpro) or main protease (Mpro), formally known as C30 endopeptidase or 3-chymotrypsin-like protease, is the main protease found in coronaviruses. It cleaves the coronavirus polyprotein at eleven conserved sites. It is a cysteine protease and a member of the PA clan of proteases. It has a cysteine-histidine catalytic dyad at its active site and cleaves a Gln–( Ser/ Ala/ Gly) peptide bond. The Enzyme Commission refers to this family as SARS coronavirus main proteinase (Mpro; ). The 3CL protease corresponds to coronavirus nonstructural protein 5 (nsp5). The "3C" in the common name refers to the 3C protease (3Cpro) which is a homologous protease found in picornaviruses. Function The 3C-like protease is able to catalytically cleave a peptide bond between a glutamine at position P1 and a small amino acid (serine, alanine, or glycine) at position P1'. The SARS coronavirus 3CLpro can for instance self-cleave the following peptides: The protease is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Adopted Name
A United States Adopted Name (USAN) is a unique nonproprietary name assigned to a medication marketed in the United States. Each name is assigned by the USAN Council, which is co-sponsored by the American Medical Association (AMA), the United States Pharmacopeial Convention (USP), and the American Pharmacists Association (APhA). The USAN Program states that its goal is to select simple, informative, and unique nonproprietary names (also called generic names) for drugs by establishing logical nomenclature classifications based on pharmacological or chemical relationships. In addition to drugs, the USAN Council names agents for gene therapy and cell therapy, contact lens polymers, surgical materials, diagnostics, carriers, and substances used as an excipient. The USAN Council works in conjunction with the World Health Organization (WHO) international nonproprietary name (INN) Expert Committee and national nomenclature groups to standardize drug nomenclature and establish rule ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
COVID-19
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is a contagious disease caused by the coronavirus SARS-CoV-2. In January 2020, the disease spread worldwide, resulting in the COVID-19 pandemic. The symptoms of COVID‑19 can vary but often include fever, fatigue, cough, breathing difficulties, anosmia, loss of smell, and ageusia, loss of taste. Symptoms may begin one to fourteen days incubation period, after exposure to the virus. At least a third of people who are infected asymptomatic, do not develop noticeable symptoms. Of those who develop symptoms noticeable enough to be classified as patients, most (81%) develop mild to moderate symptoms (up to mild pneumonia), while 14% develop severe symptoms (dyspnea, hypoxia (medical), hypoxia, or more than 50% lung involvement on imaging), and 5% develop critical symptoms (respiratory failure, shock (circulatory), shock, or organ dysfunction, multiorgan dysfunction). Older people have a higher risk of developing severe symptoms. Some complicati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amines
In chemistry, amines (, ) are organic compounds that contain carbon-nitrogen bonds. Amines are formed when one or more hydrogen atoms in ammonia are replaced by alkyl or aryl groups. The nitrogen atom in an amine possesses a lone pair of electrons. Amines can also exist as hetero cyclic compounds. Aniline is the simplest aromatic amine, consisting of a benzene ring bonded to an amino group. Amines are classified into three types: primary (1°), secondary (2°), and tertiary (3°) amines. Primary amines (1°) contain one alkyl or aryl substituent and have the general formula RNH2. Secondary amines (2°) have two alkyl or aryl groups attached to the nitrogen atom, with the general formula R2NH. Tertiary amines (3°) contain three substituent groups bonded to the nitrogen atom, and are represented by the formula R3N. The functional group present in primary amines is called the amino group. Classification of amines Amines can be classified according to the nature and number o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyrazoles
Pyrazole is an organic compound with the formula . It is a heterocycle characterized as an azole with a 5-membered ring of three carbon atoms and two adjacent nitrogen atoms, which are in ortho-substitution. Pyrazoles are also a class of compounds that have the ring C3N2 with adjacent nitrogen atoms. Pyrazole itself has few applications but many substituted pyrazoles are of commercial interest. Notable drugs containing a pyrazole ring are celecoxib (celebrex) and the anabolic steroid stanozolol. Properties Pyrazole is a weak base, with p''K''b 11.5 (p''K''a of the conjugate acid 2.49 at 25 °C). According to X-ray crystallography, the compound is planar. The two C-N distances are similar, both near 1.33 Å History The term pyrazole was given to this class of compounds by German Chemist Ludwig Knorr in 1883. In a classical method developed by German chemist Hans von Pechmann in 1898, pyrazole was synthesized from acetylene and diazomethane. Preparation Pyrazoles are syn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphoinositide 3-kinase Inhibitors
Phosphatidylinositol or inositol phospholipid is a biomolecule. It was initially called "inosite" when it was discovered by Léon Maquenne and Johann Joseph von Scherer in the late 19th century. It was discovered in bacteria but later also found in eukaryotes, and was found to be a signaling molecule. The biomolecule can exist in 9 different isomers. It is a lipid which contains a phosphate group, two fatty acid chains, and one inositol sugar molecule. Typically, the phosphate group has a negative charge (at physiological pH values). As a result, the molecule is amphiphilic. The production of the molecule is limited to the endoplasmic reticulum. History of phospatidylinositol Phosphatidylinositol (PI) and its derivatives have a rich history dating back to their discovery by Johann Joseph von Scherer and Léon Maquenne in the late 19th century. Initially known as "inosite" based on its sweet taste, the isolation and characterization of inositol laid the groundwork for unders ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Experimental Drugs
An experiment is a procedure carried out to support or refute a hypothesis, or determine the efficacy or likelihood of something previously untried. Experiments provide insight into cause-and-effect by demonstrating what outcome occurs when a particular factor is manipulated. Experiments vary greatly in goal and scale but always rely on repeatable procedure and logical analysis of the results. There also exist natural experimental studies. A child may carry out basic experiments to understand how things fall to the ground, while teams of scientists may take years of systematic investigation to advance their understanding of a phenomenon. Experiments and other types of hands-on activities are very important to student learning in the science classroom. Experiments can raise test scores and help a student become more engaged and interested in the material they are learning, especially when used over time. Experiments can vary from personal and informal natural comparisons ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antineoplastic Drugs
Chemotherapy (often abbreviated chemo, sometimes CTX and CTx) is the type of cancer treatment that uses one or more anti-cancer drugs ( chemotherapeutic agents or alkylating agents) in a standard regimen A regimen is a plan, or course of action such as a Diet (nutrition), diet, exercise or medical treatment. A salt#Health effects, low-salt diet is a regimen. A course of penicillin is a regimen, and there are many chemotherapy regimens in the trea .... Chemotherapy may be given with a curative intent (which almost always involves combinations of drugs), or it may aim only to prolong life or to Palliative care, reduce symptoms (Palliative care, palliative chemotherapy). Chemotherapy is one of the major categories of the medical discipline specifically devoted to pharmacotherapy for cancer, which is called ''oncology#Specialties, medical oncology''. The term ''chemotherapy'' now means the non-specific use of intracellular poisons to inhibit mitosis (cell division) or to indu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SARS-CoV-2
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS‑CoV‑2) is a strain of coronavirus that causes COVID-19, the respiratory illness responsible for the COVID-19 pandemic. The virus previously had the Novel coronavirus, provisional name 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV), and has also been called human coronavirus 2019 (HCoV-19 or hCoV-19). First identified in the city of Wuhan, Hubei, China, the World Health Organization designated the outbreak a public health emergency of international concern from January 30, 2020, to May 5, 2023. SARS‑CoV‑2 is a positive-sense single-stranded RNA virus that is Contagious disease, contagious in humans. SARS‑CoV‑2 is a strain of the species ''Betacoronavirus pandemicum'' (SARSr-CoV), as is SARS-CoV-1, the virus that caused the 2002–2004 SARS outbreak. There are animal-borne coronavirus strains more closely related to SARS-CoV-2, the most closely known relative being the BANAL-52 bat coronavirus. SARS-CoV-2 is of Zoonosis, z ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cytokine Storm
A cytokine storm, also called hypercytokinemia, is a pathological reaction in humans and other animals in which the innate immune system causes an uncontrolled and excessive release of pro-inflammatory signaling molecules called cytokines. Cytokines are a normal part of the body's immune response to infection, but their sudden release in large quantities may cause multisystem organ failure and death. Cytokine storms may be caused by infectious or non-infectious etiologies, especially viral respiratory infections such as H1N1 influenza, H5N1 influenza, SARS-CoV-1, SARS-CoV-2, Influenza B, and parainfluenza virus. Other causative agents include the Epstein-Barr virus, cytomegalovirus, group A streptococcus, and non-infectious conditions such as graft-versus-host disease. The viruses can invade lung epithelial cells and alveolar macrophages to produce viral nucleic acid, which stimulates the infected cells to release cytokines and chemokines, activating macrophages, dendrit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myeloid Cell
Myeloid tissue, in the bone marrow sense of the word ''wikt:myeloid#Adjective, myeloid'' (''wikt:myelo-#Prefix, myelo-'' + ''wikt:-oid#Suffix, -oid''), is tissue (biology), tissue of bone marrow, of bone marrow cell lineage, or resembling bone marrow, and myelogenous tissue (''myelo-'' + ''wikt:-geny#Suffix, -genous'') is any tissue of, or arising from, bone marrow; in these senses the terms are usually used synonymously, as for example with chronic myelogenous leukemia, chronic myeloid/myelogenous leukemia. In haematopoiesis, hematopoiesis, myeloid cells, or myelogenous cells are blood cells that arise from a progenitor cell for granulocytes, monocytes, erythrocytes, or platelets (the CFU-GEMM, common myeloid progenitor, that is, CMP or CFU-GEMM), or in a narrower sense also often used, specifically from the lineage of the myeloblast (the myelocytes, monocytes, and their daughter types). Thus, although all blood cells, even lymphocytes, are normally born in the bone marrow in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |