|
Edward Rooper
Edward Rooper (25 January 1818 Wick Hall, Furze Hill, Brighton - 11 or 15 November 1854 Inkerman, Crimea) was an English soldier, landscape painter, and botanical collector and illustrator. He was the fourth son of the Rev. Thomas Richard Rooper (1782-1865) and Persis Standly (1783-1871), with siblings William Henry Rooper, Marianne Rooper, George Rooper, Henrietta Persis Rooper and John Rooper. He was the grandson of John Rooper of Berkhamsted Castle. He received a commission as 2nd Lieutenant in the Rifle Brigade on 2 September 1834 and was promoted to Captain on 2 September 1842, and to brevet Major on 26 September 1854. He served in South Africa with the Rifle Brigade after landing at Algoa Bay on 20 November 1846 and was promptly posted to the Kei where he took part in the Seventh Xhosa War, mainly in the Amatola Mountains. At the end of hostilities he was appointed Resident Magistrate of East London on 1 January 1849, a post which he held until June 1850 when he returne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
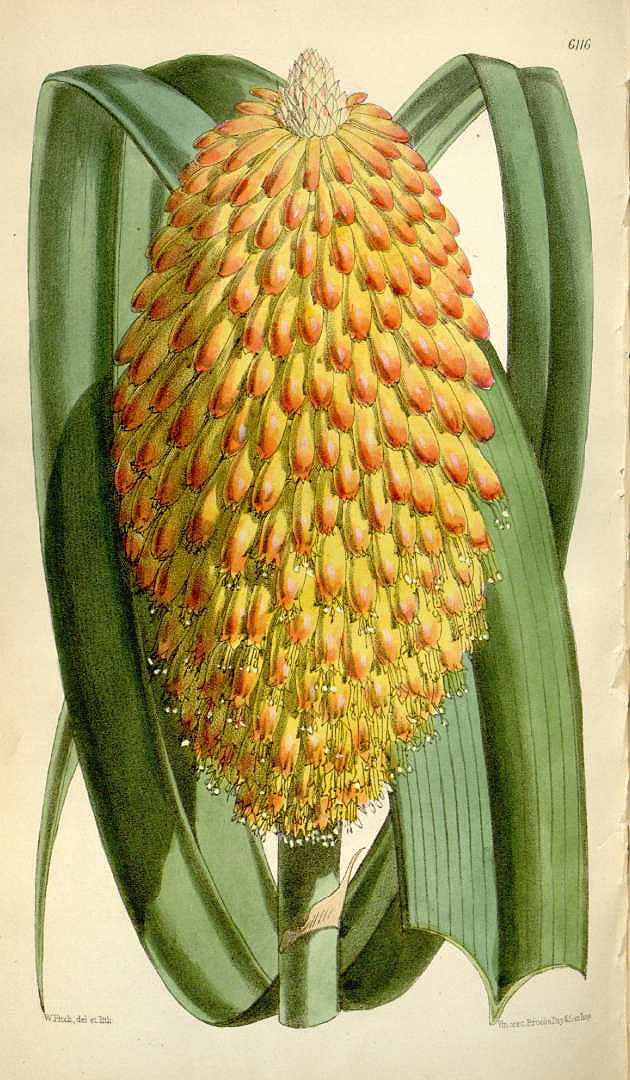
Kniphofia Rooperi01
''Kniphofia'' is a genus of perennial flowering plants in the family Asphodelaceae, first described as a genus in 1794. Species are native to Africa. Common names include tritoma, red hot poker, torch lily and poker plant. Description Herbaceous species and hybrids have narrow, grass-like leaves long, while evergreen species have broader, strap-shaped foliage up to long. All plants produce spikes of upright, brightly coloured flowers well above the foliage, in shades of red, orange and yellow, often bicoloured. The flowers produce copious nectar while blooming and are attractive to bees and sunbirds. In the New World, they may attract nectarivores such as hummingbirds and New World orioles. Etymology The genus ''Kniphofia'' is named after Johann Hieronymus Kniphof, an 18th-century German physician and botanist. Species There are about 73 described species, including two hybrids. # ''Kniphofia acraea'' Codd - Cape Provinces of South Africa # ''Kniphofia albescens'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
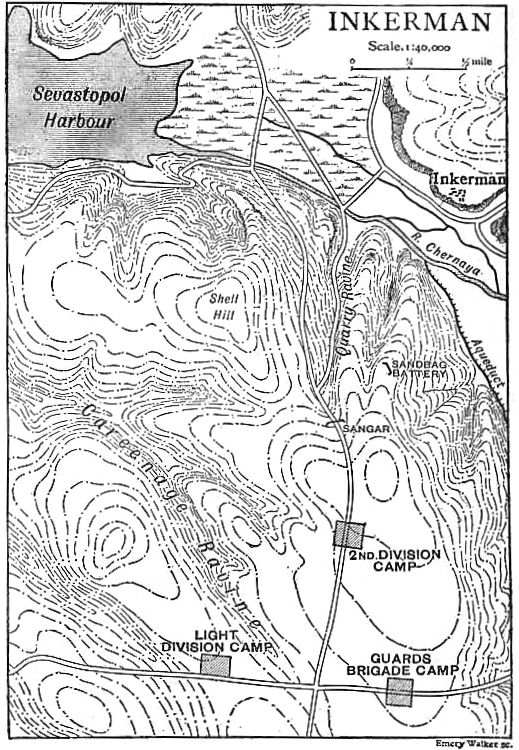
Battle Of Inkerman
The Battle of Inkerman was fought during the Crimean War on 5 November 1854 between the allied armies of Britain and France against the Imperial Russian Army. The battle broke the will of the Russian Army to defeat the allies in the field, and was followed by the siege of Sevastopol. The role of troops fighting mostly on their own initiative due to the foggy conditions during the battle has earned the engagement the name "The Soldier's Battle." Prelude to the battle The allied armies of Britain, France, Sardinia, and the Ottoman Empire had landed on the west coast of Crimea on 14 September 1854, intending to capture the Russian naval base at Sevastopol. The allied armies fought off and defeated the Russian Army at the Battle of Alma, forcing them to retreat in some confusion toward the River Kacha. While the allies could have taken this opportunity to attack Sevastopol before Sevastopol could be put into a proper state of defence, the allied commanders, British general FitzR ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Botanical Illustrators
British may refer to: Peoples, culture, and language * British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories, and Crown Dependencies. ** Britishness, the British identity and common culture * British English, the English language as spoken and written in the United Kingdom or, more broadly, throughout the British Isles * Celtic Britons, an ancient ethno-linguistic group * Brittonic languages, a branch of the Insular Celtic language family (formerly called British) ** Common Brittonic, an ancient language Other uses *''Brit(ish)'', a 2018 memoir by Afua Hirsch *People or things associated with: ** Great Britain, an island ** United Kingdom, a sovereign state ** Kingdom of Great Britain (1707–1800) ** United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland (1801–1922) See also * Terminology of the British Isles * Alternative names for the British * English (other) * Britannic (other) * British Isles * Brit (other) * Bri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
19th-century English Artists
The 19th (nineteenth) century began on 1 January 1801 ( MDCCCI), and ended on 31 December 1900 ( MCM). The 19th century was the ninth century of the 2nd millennium. The 19th century was characterized by vast social upheaval. Slavery was abolished in much of Europe and the Americas. The First Industrial Revolution, though it began in the late 18th century, expanding beyond its British homeland for the first time during this century, particularly remaking the economies and societies of the Low Countries, the Rhineland, Northern Italy, and the Northeastern United States. A few decades later, the Second Industrial Revolution led to ever more massive urbanization and much higher levels of productivity, profit, and prosperity, a pattern that continued into the 20th century. The Islamic gunpowder empires fell into decline and European imperialism brought much of South Asia, Southeast Asia, and almost all of Africa under colonial rule. It was also marked by the collapse of the lar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1854 Deaths
Events January–March * January 4 – The McDonald Islands are discovered by Captain William McDonald aboard the ''Samarang''. * January 6 – The fictional detective Sherlock Holmes is perhaps born. * January 9 – The Teutonia Männerchor in Pittsburgh, U.S.A. is founded to promote German culture. * January 20 – The North Carolina General Assembly in the United States charters the Atlantic and North Carolina Railroad, to run from Goldsboro through New Bern, to the newly created seaport of Morehead City, near Beaufort. * January 21 – The iron clipper runs aground off the east coast of Ireland, on her maiden voyage out of Liverpool, bound for Australia, with the loss of at least 300 out of 650 on board. * February 11 – Major streets are lit by coal gas for the first time by the San Francisco Gas Company; 86 such lamps are turned on this evening in San Francisco, California. * February 13 – Mexican troops force William Walker ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1818 Births
Events January–March * January 1 ** Battle of Koregaon: Troops of the British East India Company score a decisive victory over the Maratha Empire. ** Mary Shelley's ''Frankenstein'' is published anonymously in London. * January 2 – The British Institution of Civil Engineers is founded. * January 3 (21:52 UTC) – Venus occults Jupiter. It is the last occultation of one planet by another before November 22, 2065. * January 6 – The Treaty of Mandeswar brings an end to the Third Anglo-Maratha War, ending the dominance of Marathas, and enhancing the power of the British East India Company, which controls territory occupied by 180 million Indians. * January 11 – Percy Bysshe Shelley's '' Ozymandias'' is published pseudonymously in London. * January 12 – The Dandy horse (''Laufmaschine'' bicycle) is invented by Karl Drais in Mannheim. * February 3 – Jeremiah Chubb is granted a British patent for the Chubb detector lock. * February 5 – Upon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hove
Hove is a seaside resort and one of the two main parts of the city of Brighton and Hove, along with Brighton in East Sussex, England. Originally a "small but ancient fishing village" surrounded by open farmland, it grew rapidly in the 19th century in response to the development of its eastern neighbour Brighton, and by the Victorian era it was a fully developed town with borough status. Neighbouring parishes such as Aldrington and Hangleton were annexed in the late 19th and early 20th centuries. The neighbouring urban district of Portslade was merged with Hove in 1974. In 1997, as part of local government reform, the borough merged with Brighton to form the Borough of Brighton and Hove, and this unitary authority was granted city status in 2000. Name and etymology Old spellings of Hove include Hou (Domesday Book, 1086), la Houue (1288), Huua (13th century), Houve (13th and 14th centuries), Huve (14th and 15th centuries), Hova (16th century) and Hoova (1675). The etymo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
St Andrew's Church, Church Road, Hove
St Andrew's Church is an Anglican church in Church Road, Hove, in the English city of Brighton and Hove. It is usually referred to as St Andrew (Old Church) to distinguish it from another St Andrew's Church in Waterloo Street, elsewhere in Hove. It served as Hove's parish church for several centuries until 1892, although the building was in a state of near-ruin until Hove began to grow from an isolated village to a popular residential area in the early 19th century. History Hove developed independently of, and separately from, neighbouring Brighton, beginning as a linear village along a single street, now known as Hove Street, running from north to south. A church was established in mediaeval times, possibly around the 12th century, at an isolated location in fields to the northeast of the village; access was only possible from the west. The original building was replaced with a simple Norman-style church with an aisled nave and a tower. By the 13th century a chancel ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kniphofia Rooperi
''Kniphofia rooperi'', Rooper’s red-hot poker, is a species of flowering plant in the family Asphodelaceae, native to the Eastern Cape of South Africa. Growing to tall, it is a robust evergreen perennial with strap-shaped leaves produced at an angle from the main stem. In autumn the stout central stems bear flattened oval flowerheads consisting of many tubular florets packed closely together. Green in bud, the flowers open to bright red and fade from the base to yellow and brown, thus giving the appearance of a red-hot poker. ''K. rooperi'' is valued in horticulture for its architectural qualities and late season flowering, and is equally at home in the mixed flower border and in more naturalistic plantings. It is hardy down to . It requires a situation in full sun, which is reliably moist but well-drained. Excessive dryness may prevent flowerheads from forming, while bad drainage can cause the crown to rot. The evergreen foliage may become untidy during the winter months. It ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypoxis Rooperi
''Hypoxis hemerocallidea'', the African star grass or African potato, is a medicinal plant in the Hypoxidaceae family. It is native to southern Africa from South Africa as far north as Mozambique and Zimbabwe. This plant is the best known member of this genus. Medicinal uses ''Hypoxis'' is promoted as an alternative medicine treatment for benign prostatic hyperplasia, but research has found no evidence of beneficial effect. Additionally, one study suggests ''Hypoxis'' alters the activity of cytochrome P450, suggesting that it may interfere with the effectiveness of other drugs or supplements, such as antiretroviral drug The management of HIV/AIDS normally includes the use of multiple antiretroviral drugs as a strategy to control HIV infection. There are several classes of antiretroviral agents that act on different stages of the HIV life-cycle. The use of multip ...s. References External links * Hypoxis hemerocallidea research University Kwazulu-Nata* Hypoxis hemerocallid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
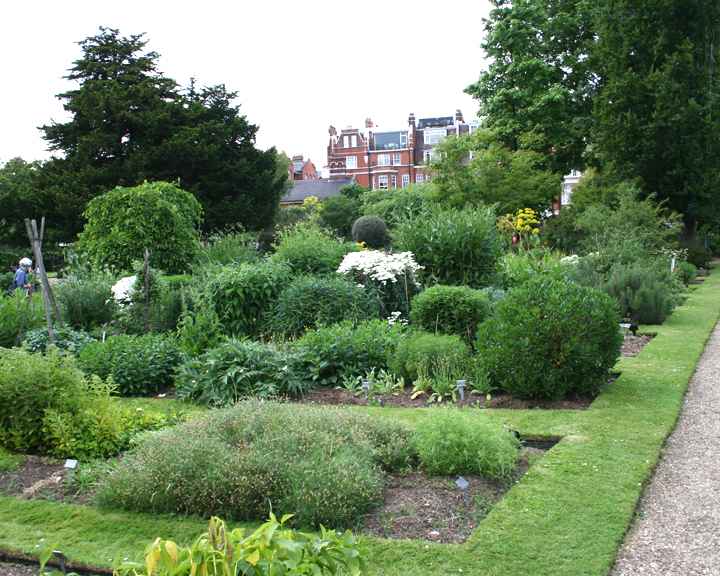
Chelsea Physic Garden
The Chelsea Physic Garden was established as the Apothecaries' Garden in London, England, in 1673 by the Worshipful Society of Apothecaries to grow plants to be used as medicines. This four acre physic garden, the term here referring to the science of healing, is among the oldest botanical gardens in Britain, after the University of Oxford Botanic Garden. Its rock garden is the oldest in Europe devoted to alpine plants and Mediterranean plants. The largest fruiting olive tree in Britain is there, protected by the garden's heat-trapping high brick walls, along with what is doubtless the world's northernmost grapefruit growing outdoors. Jealously guarded during the tenure of the Worshipful Society of Apothecaries, the garden became a registered charity in 1983 and was opened to the general public for the first time. The garden is a member of the London Museums of Health & Medicine. It is also Grade I listed in the Register of Historic Parks and Gardens of Special Historic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomas Moore (botanist)
Thomas Moore (21 May 1821 – 1 January 1887) was a British gardener and botanist. An expert on ferns and fern allies from the British Isles, he served as Curator of the Society of Apothecaries Garden from 1848 to 1887. In 1855 he authored '' The Ferns of Great Britain and Ireland.'' Life He was born at Stoke, near Guildford, Surrey, on 21 May 1821. He was brought up as a gardener, and was employed at Fraser's Lee Bridge Nursery, and subsequently, under Robert Marnock, in the laying out of the Regent's Park gardens. In 1848, by the influence of Dr. John Lindley, he was appointed curator of the Apothecaries' Company's Garden at Chelsea, in succession to Robert Fortune, an appointment which gave him leisure for other work. Under Moore's tenure during the period of so-called "pteridomania", the garden increased the number of fern species cultivated there by fifty percent and was renamed the Chelsea Physic Garden in 1875. The Thomas Moore Fernery was built in 1907 on the site ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |