|
Edward McGeachy
Edward McGeachy (died c. 1851) was the Crown Surveyor for the county of Surrey in Jamaica. He trained Thomas Harrison, the first Government Surveyor of Jamaica. He owned Bull Park plantation and Brighton Pen in Saint David Parish and in 1837 received compensation for the loss of eight slaves following the abolition of slavery in the British Empire in 1833. Early life and family McGeachy's place and date of birth are unknown, but he described himself as a "colonist" of Jamaica and as having learned surveying "at school". He served a five-year apprenticeship with Francis Ramsay. He married Margaret and they had daughters Rosa, Emma, Ada, and Margaret, and a son Charles Edward Alleyne McGeachy, indicating a family connection to the Alleynes of Barbados. Career After the completion of his apprenticeship, McGeachy was in partnership with Francis Ramsay before working on his own from 1824. He was with McGeachy, Dadley & Smith from 1826 to 1828 in partnership with former apprentices ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plan Of Albion Estate By Edward McGeachy, 1842
A plan is typically any diagram or list of steps with details of timing and resources, used to achieve an Goal, objective to do something. It is commonly understood as a modal logic, temporal set (mathematics), set of intended actions through which one expects to achieve a goal. For space, spatial or Plane (geometry), planar topology, topologic or topography, topographic sets see map. Plans can be formal or informal: * Structured and formal plans, used by multiple people, are more likely to occur in projects, diplomacy, careers, economic development, military campaigns, combat, sports, games, or in the conduct of other business. In most cases, the absence of a well-laid plan can have adverse effects: for example, a non-robust project plan can cost the organization time and money. * Informal or ad hoc plans are created by individuals in all of their pursuits. The most popular ways to describe plans are by their breadth, time frame, and specificity; however, these planning clas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
House Of Assembly Of Jamaica
The House of Assembly was the legislature of the British colony of Jamaica. It held its first meeting on 20 January 1664 at Spanish Town. Cundall, Frank. (1915''Historic Jamaica''.London: Institute of Jamaica. p. 15. As a result of the Morant Bay Rebellion, the Assembly voted to abolish self-governance in 1865. Jamaica then became a direct-ruled crown colony. Originally there were twelve districts represented. For many years, a high property qualification ensured that the House of Assembly was dominated by the White Jamaican planter class. However, to elect these representatives, the bar was lower for "freeholders", who just had to be white men with a house, pen or plantation, and owned black slaves.Christer Petley, ''White Fury'' (Oxford: Oxford University Press, 2018), p. 42. A law passed in 1840 allowed some blacks and mixed-race men to vote in elections to the Assembly, though they had to own property, so the white planters continued to dominate it. See also * Jamaica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Emigrants To The British West Indies
British may refer to: Peoples, culture, and language * British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories, and Crown Dependencies. ** Britishness, the British identity and common culture * British English, the English language as spoken and written in the United Kingdom or, more broadly, throughout the British Isles * Celtic Britons, an ancient ethno-linguistic group * Brittonic languages, a branch of the Insular Celtic language family (formerly called British) ** Common Brittonic, an ancient language Other uses *'' Brit(ish)'', a 2018 memoir by Afua Hirsch *People or things associated with: ** Great Britain, an island ** United Kingdom, a sovereign state ** Kingdom of Great Britain (1707–1800) ** United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland (1801–1922) See also * Terminology of the British Isles * Alternative names for the British * English (other) * Britannic (other) * British Isles * Brit (other) * Briton ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
19th-century British People
The 19th (nineteenth) century began on 1 January 1801 ( MDCCCI), and ended on 31 December 1900 ( MCM). The 19th century was the ninth century of the 2nd millennium. The 19th century was characterized by vast social upheaval. Slavery was abolished in much of Europe and the Americas. The First Industrial Revolution, though it began in the late 18th century, expanding beyond its British homeland for the first time during this century, particularly remaking the economies and societies of the Low Countries, the Rhineland, Northern Italy, and the Northeastern United States. A few decades later, the Second Industrial Revolution led to ever more massive urbanization and much higher levels of productivity, profit, and prosperity, a pattern that continued into the 20th century. The Islamic gunpowder empires fell into decline and European imperialism brought much of South Asia, Southeast Asia, and almost all of Africa under colonial rule. It was also marked by the collapse of the la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jamaican Planters
Jamaican may refer to: * Something or someone of, from, or related to the country of Jamaica * Jamaicans, people from Jamaica * Jamaican English, a variety of English spoken in Jamaica * Jamaican Patois, an English-based creole language * Culture of Jamaica * Jamaican cuisine See also * *Demographics of Jamaica *List of Jamaicans *Languages of Jamaica This is a demography of the population of Jamaica including population density Population density (in agriculture: Stock (other), standing stock or plant density) is a measurement of population per unit land area. It is mostly applied ... {{disambiguation Language and nationality disambiguation pages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Surveyors
British may refer to: Peoples, culture, and language * British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories, and Crown Dependencies. ** Britishness, the British identity and common culture * British English, the English language as spoken and written in the United Kingdom or, more broadly, throughout the British Isles * Celtic Britons, an ancient ethno-linguistic group * Brittonic languages, a branch of the Insular Celtic language family (formerly called British) ** Common Brittonic, an ancient language Other uses *''Brit(ish)'', a 2018 memoir by Afua Hirsch *People or things associated with: ** Great Britain, an island ** United Kingdom, a sovereign state ** Kingdom of Great Britain (1707–1800) ** United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland (1801–1922) See also * Terminology of the British Isles * Alternative names for the British * English (other) * Britannic (other) * British Isles * Brit (other) * Briton (d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saint Thomas Parish, Jamaica
Saint Thomas, once known as ''Saint Thomas in the East'', is a suburban parish situated at the south eastern end of Jamaica, within the county of Surrey. It is the birthplace of the Right Honourable Paul Bogle, designated in 1969 as one of Jamaica's seven National Heroes. Morant Bay, its chief town and capital, is the site of the Morant Bay Rebellion in 1865, of which Bogle was a leader. Representative George William Gordon, a wealthy mixed race businessman and politician from this district, was tried and executed in 1865 under martial law on suspicion of directing the rebellion. Governor Eyre was forced to resign due to the controversy over his execution of Gordon and violent suppression of the rebellion. Gordon was designated in 1969 as a National Hero. Brief history Saint Thomas was densely populated by the Taíno/Arawak when Christopher Columbus first came to the island in 1494. The Spaniards established cattle ranches at Morant Bay and Yallahs. In 1655, when the En ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abolition Of Slavery In The British Empire
The Slavery Abolition Act 1833 (3 & 4 Will. IV c. 73) was an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom which provided for the gradual abolition of slavery in most parts of the British Empire. It was passed by Earl Grey's reforming administration and expanded the jurisdiction of the Slave Trade Act 1807 and made the purchase or ownership of slaves illegal within the British Empire, with the exception of "the Territories in the Possession of the East India Company", Ceylon (now Sri Lanka), and Saint Helena. The Act was repealed in 1998 as a part of wider rationalisation of English statute law; however, later anti-slavery legislation remains in force. Background It is important to note the long history of efforts to end or limit the practice of slavery. In 1080, William the Conqueror banned the slave trade between Bristol and Ireland upon the urging of Bishop Wulfstan of Worcester. In 1102, the ecclesiastical Council of London condemned the slave trade within England, decreeing � ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jamaica Journal
The ''Jamaica Journal'' is a peer-reviewed academic journal published by the Institute of Jamaica. It publishes scholarly articles on the history, natural history, art, literature, music, and culture of Jamaica. Its predecessor was the ''Journal of the Institute of Jamaica'', established in 1896. In 1967, the ''Jamaica Journal'' was established as a quarterly journal, "to reflect the Institute's interest in the development and promotion of Jamaica's history, literature, science and arts". In 2002, the journal temporarily ceased publication; it was relaunched in 2004 under a new editor-in-chief, Kim Robinson-Walcott. Abstracting and indexing The journal is abstracted and indexed in America: History and Life, Historical Abstracts, International Bibliography of the Social Sciences, and the Modern Language Association Database. References External links *Institute of Jamaica [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
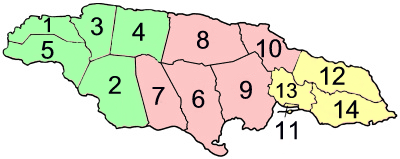
Surrey County, Jamaica
Surrey (also Surry) is the easternmost and the smallest by area of the three historic counties into which Jamaica is divided. It was created in 1758, and is divided into four parishes. History Jamaica's three counties (Surrey, Middlesex and Cornwall) were established in 1758 to facilitate the holding of courts along the lines of the British county court system. Surrey was named after the English county in which Kingston upon Thames Kingston upon Thames (hyphenated until 1965, colloquially known as Kingston) is a town in the Royal Borough of Kingston upon Thames, southwest London, England. It is situated on the River Thames and southwest of Charing Cross. It is notable a ... is found. Kingston was its county town. Parish (1) Kingston Parish and Saint Andrew Parish together form ''Kingston and St Andrew Corporation''. (2) Kingston Parish does not encompass all of Kingston. References {{Authority control Counties of Jamaica 1758 establishments in the Britis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Crown
The Crown is the state (polity), state in all its aspects within the jurisprudence of the Commonwealth realms and their subdivisions (such as the Crown Dependencies, British Overseas Territories, overseas territories, Provinces and territories of Canada#Provinces, provinces, or states and territories of Australia, states). Legally ill-defined, the term has different meanings depending on context. It is used to designate the monarch in either a personal capacity, as Head of the Commonwealth, or as the king or queen of their realms (whereas the monarchy of the United Kingdom and the monarchy of Canada, for example, are distinct although they are in personal union). It can also refer to the rule of law; however, in common parlance 'The Crown' refers to the functions of executive (government), government and the civil service. Thus, in the United Kingdom (one of the Commonwealth realms), the government of the United Kingdom can be distinguished from the Crown and the state, in prec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)