|
Education Index
The Education Index is a component of the Human Development Index (HDI) published every year by the United Nations Development Programme. Alongside the economical indicators (GDP) and Life Expectancy Index, it helps measure the educational attainment. List of countries by GNI (PPP) per capita, GNI (PPP) per capita and life expectancy are also used with the education index to get the HDI of each country. Since 2010, the education index has been measured by combining average adult years of schooling with expected years of schooling for students under the age of 25, each receiving 50% weighting. Before 2010, the education index was measured by the adult literacy rate (with two-thirds weighting) and the combined primary, secondary, and tertiary gross enrollment ratio (with one-third weighting). Education is a major component of quality of life, well-being and is used in the measure of economic development and quality of life, which is a key factor determining whether a country is a D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
UNDP Education Index (1990 - 2019)
The United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) is a United Nations agency tasked with helping countries eliminate poverty and achieve sustainable economic growth and human development. The UNDP emphasizes on developing local capacity towards long-term self-sufficiency and prosperity. Based at the headquarters of the United Nations in New York City, it is the largest UN development aid agency, with offices in 177 countries. The UNDP is funded entirely by voluntary contributions from UN member states. Founding The UNDP was founded on 22 November 1965 through the merger of the Expanded Programme of Technical Assistance (EPTA) and the Special Fund in 1958. The rationale was to "avoid duplication of heiractivities". The EPTA was set up in 1949 to support the economic and political aspects of underdeveloped countries while the Special Fund was to enlarge the scope of UN technical assistance. The Special Fund arose from the idea of a Special United Nations Fund for Economic Dev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Education
Education is the transmission of knowledge and skills and the development of character traits. Formal education occurs within a structured institutional framework, such as public schools, following a curriculum. Non-formal education also follows a structured approach but occurs outside the formal schooling system, while informal education involves unstructured learning through daily experiences. Formal and non-formal education are categorized into levels, including early childhood education, primary education, secondary education, and tertiary education. Other classifications focus on teaching methods, such as teacher-centered and student-centered education, and on subjects, such as science education, language education, and physical education. Additionally, the term "education" can denote the mental states and qualities of educated individuals and the academic field studying educational phenomena. The precise definition of education is disputed, and there are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Countries By Literacy Rate
This is a list of countries by literacy rate. The global literacy rate for all people aged 15 and above is 86.3%. The global literacy rate for all males is 90.0%, and the rate for all females is 82.7%. The rate varies throughout the world, with developed nations having a rate of 99.2% (2013), South and West Asia having 70.2% (2015), and sub-Saharan Africa at 64.0% (2015). Over 75% of the world's 781 million illiterate adults are found in South Asia, West Asia, and sub-Saharan Africa, and women represent almost two-thirds of all illiterate adults globally. List of UN member states by age group and gender disparity Data published by UNESCO using the following definitions: ''"*"'' ''indicates "Literacy in country or territory" or "Education in country or territory" links.'' List of UN member and observer states by adult literacy rate ''"*"'' ''indicates "Literacy in country or territory" or "Education in country or territory" links.'' List of other states and territories ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Least Developed Country
The least developed countries (LDCs) are developing countries listed by the United Nations that exhibit the lowest indicators of socioeconomic development. The concept of LDCs originated in the late 1960s and the first group of LDCs was listed by the UN in its resolution 2768 (XXVI) on 18 November 1971. A country is classified among the Least Developed Countries if it meets three criteria:UN-OHRLLS . * Poverty – adjustable criterion based on Gross national income (GNI) per capita averaged over three years. , a country must have GNI per capita less than US$1,025 to be included on the list, and over $1,230 to graduate from it. * Human resource weakness (based on indicators of nutrition, health, education and adult literacy). * Economic vulnerability (based on instability of agricultural production, instability of exports of goods and services, economic importance of non-traditional activities, merchandise export concentration, handicap of economic smallness, and the percentage o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Developing Country
A developing country is a sovereign state with a less-developed industrial base and a lower Human Development Index (HDI) relative to developed countries. However, this definition is not universally agreed upon. There is also no clear agreement on which countries fit this category. The terms low-and middle-income country (LMIC) and newly emerging economy (NEE) are often used interchangeably but they refer only to the economy of the countries. The World Bank classifies the world's economies into four groups, based on gross national income per capita: high-, upper-middle-, lower-middle-, and low-income countries. Least developed countries, landlocked developing countries, and small island developing states are all sub-groupings of developing countries. Countries on the other end of the spectrum are usually referred to as high-income countries or developed countries. There are controversies over the terms' use, as some feel that it perpetuates an outdated concept of "us" and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Developed Country
A developed country, or advanced country, is a sovereign state that has a high quality of life, developed economy, and advanced technological infrastructure relative to other less industrialized nations. Most commonly, the criteria for evaluating the degree of economic development are the gross domestic product (GDP), gross national product (GNP), the per capita income, level of industrialization, amount of widespread infrastructure and general standard of living. Which criteria are to be used and which countries can be classified as being developed are subjects of debate. Different definitions of developed countries are provided by the International Monetary Fund and the World Bank; moreover, HDI ranking is used to reflect the composite index of life expectancy, education, and income per capita. In 2025, 40 countries fit all three criteria, while an additional 21 countries fit two out of three. Developed countries have generally more advanced post-industrial economies, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Economic Development
In economics, economic development (or economic and social development) is the process by which the economic well-being and quality of life of a nation, region, local community, or an individual are improved according to targeted goals and objectives. The term has been used frequently in the 20th and 21st centuries, but the concept has existed in the West for far longer. "Modernization", "Westernization", and especially "industrialization" are other terms often used while discussing economic development. Historically, economic development policies focused on industrialization and infrastructure; since the 1960s, it has increasingly focused on poverty reduction. Whereas economic development is a Public policy, policy intervention aiming to improve the well-being of people, economic growth is a phenomenon of market productivity and increases in GDP; economist Amartya Sen describes economic growth as but "one aspect of the process of economic development". Definition and terminolo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quality Of Life
Quality of life (QOL) is defined by the World Health Organization as "an individual's perception of their position in life in the context of the culture and value systems in which they live and in relation to their goals, expectations, standards and concerns". Standard indicators of the quality of life include wealth, employment, the environment, physical and mental health, education, recreation and leisure time, social belonging, religious beliefs, safety, security and freedom. QOL has a wide range of contexts, including the fields of international development, healthcare, politics and employment. Health related QOL (HRQOL) is an evaluation of QOL and its relationship with health. Engaged theory One approach, called the engaged theory, outlined in the journal of ''Applied Research in the Quality of Life'', posits four domains in assessing quality of life: ecology, economics, politics and culture. In the domain of culture, for example, it includes the following subd ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gross Enrollment Ratio
Gross enrolment ratio (GER) or gross enrolment index (GEI) is a statistical measure used in the education sector, and formerly by the UN in its Education Index, to determine the number of students enrolled in school at several different grade levels (like elementary, middle school and high school), and use it to show the ratio of the number of students who live in that country to those who qualify for the particular grade level. The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO), describes "Gross Enrolment Ratio" as the total enrolment within a country "in a specific level of education, regardless of age, expressed as a percentage of the population in the official age group corresponding to this level of education". The GER can be over 100% as it includes students who may be older or younger than the official age group. This is because the GER includes students who are repeating a grade, those who enrolled late and are older than their classmates, or tho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Development Index
The Human Development Index (HDI) is a statistical composite index of life expectancy, Education Index, education (mean years of schooling completed and expected years of schooling upon entering the education system), and per capita income indicators, which is used to rank countries into four tiers of Human development (humanity), human development. A country scores a higher level of HDI when the life expectancy at birth, lifespan is higher, the education level is higher, and the gross national income GNI (PPP) per capita is higher. It was developed by Pakistani economist Mahbub ul-Haq and was further used to measure a country's development by the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP)'s Human Development Report Office. The 2010 Human Development Report introduced an List of countries by inequality-adjusted Human Development Index, inequality-adjusted Human Development Index (IHDI). While the simple HDI remains useful, it stated that "the IHDI is the actual level of huma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Literacy
Literacy is the ability to read and write, while illiteracy refers to an inability to read and write. Some researchers suggest that the study of "literacy" as a concept can be divided into two periods: the period before 1950, when literacy was understood solely as alphabetical literacy (word and letter recognition); and the period after 1950, when literacy slowly began to be considered as a wider concept and process, including the social and cultural aspects of reading, writing, and functional literacy. Definition The range of definitions of literacy used by Non-governmental organization, NGOs, think tanks, and advocacy groups since the 1990s suggests that this shift in understanding from "discrete skill" to "social practice" is both ongoing and uneven. Some definitions remain fairly closely aligned with the traditional "ability to read and write" connotation, whereas others take a broader view: * The 2003 National Assessment of Adult Literacy (USA) included "quantitativ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
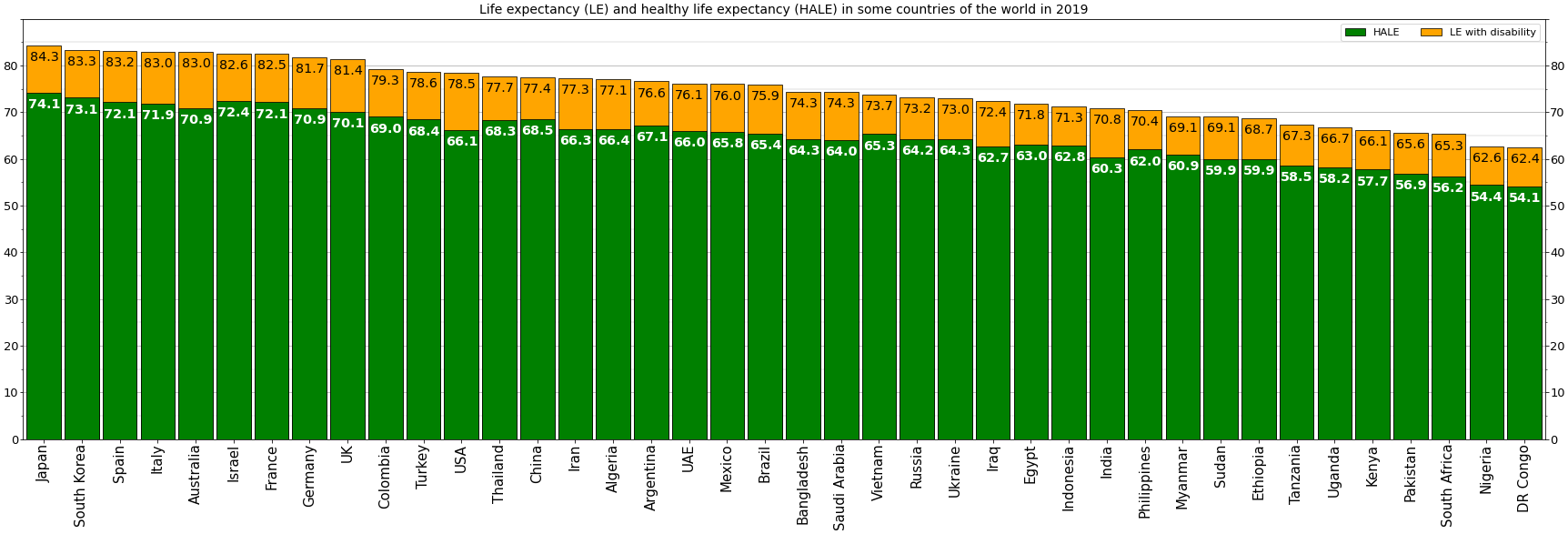
Life Expectancy
Human life expectancy is a statistical measure of the estimate of the average remaining years of life at a given age. The most commonly used measure is ''life expectancy at birth'' (LEB, or in demographic notation ''e''0, where ''e''x denotes the average life remaining at age ''x''). This can be defined in two ways. ''Cohort'' LEB is the mean length of life of a birth Cohort (statistics), cohort (in this case, all individuals born in a given year) and can be computed only for cohorts born so long ago that all their members have died. ''Period'' LEB is the mean length of life of a hypothetical cohort assumed to be exposed, from birth through death, to the mortality rates observed at a given year. National LEB figures reported by national agencies and international organizations for human populations are estimates of ''period'' LEB. Human remains from the early Bronze Age indicate an LEB of 24. In 2019, world LEB was 73.3. A combination of high infant mortality and d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |