|
Edge Side Includes
Edge Side Includes (ESI) is a small markup language for edge level dynamic web content assembly. The purpose of ESI is to tackle the problem of web infrastructure scaling. It is an application of edge computing. It is fairly common for websites to have generated content. It could be because of changing content like catalogs or forums, or because of personalization. This creates a problem for caching systems. To overcome this problem a group of companies ( Akamai, Art Technology Group, BEA Systems, Circadence Corporation, Digital Island, Inc., Interwoven, Inc., Open Market, whose ESI-related technology is now owned by FatWire Software, Oracle Corporation and Vignette Corporation) developed the ESI specification and submitted it to the W3C for approval. The proposal editor was Mark Nottingham. ESI Language Specification 1.0 was submitted to the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) for approval in August 2001. The W3C has acknowledged receipt, but has not accepted the proposal. ESI ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Markup Language
A markup language is a Encoding, text-encoding system which specifies the structure and formatting of a document and potentially the relationships among its parts. Markup can control the display of a document or enrich its content to facilitate automated processing. A markup language is a set of rules governing what markup information may be included in a document and how it is combined with the content of the document in a way to facilitate use by humans and computer programs. The idea and terminology evolved from the "marking up" of paper manuscripts (e.g., with revision instructions by editors), traditionally written with a red pen or blue pencil (editing), blue pencil on authors' manuscripts. Older markup languages, which typically focus on typography and presentation, include Troff, TeX, and LaTeX. Scribe (markup language), Scribe and most modern markup languages, such as Extensible Markup Language, XML, identify document components (for example headings, paragraphs, and tabl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Varnish (software)
Varnish is a Reverse proxy, reverse caching proxy used as HTTP accelerator for content-heavy dynamic web sites as well as APIs. In contrast to other web accelerators, such as Squid (software), Squid, which began life as a client-side cache, or Apache HTTP Server, Apache and nginx, which are primarily Upstream server, origin servers, Varnish was designed as an HTTP accelerator. Varnish is focused exclusively on HTTP, unlike other proxy servers that often support FTP, SMTP, and other network protocols. History The project was initiated by the online branch of the Norwegian tabloid newspaper ''Verdens Gang''. The architect and lead developer is Danish independent consultant Poul-Henning Kamp (a well-known FreeBSD developer), with management, infrastructure and additional development originally provided by the Norwegian Linux consulting company Linpro. The support, management and development of Varnish was later spun off into a separate company, Varnish Software. Varnish is free and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Web Components
Web Components are a set of features that provide a standard component model for the web allowing for encapsulation and interoperability of individual HTML elements. Web Components are a popular approach when building microfrontends. Primary technologies used to create Web Components include: ; Custom Elements : APIs to define new HTML elements ; Shadow DOM : encapsulated DOM and styling, with composition ; HTML Templates : HTML fragments that are not rendered, but stored until instantiated via JavaScript Features Custom Elements There are two parts to Custom Elements: autonomous custom elements and customized built-in elements. Autonomous custom elements are HTML elements that are entirely separated from native HTML elements; they are essentially built from the bottom up using the Custom Elements API. Customized built-in elements are elements that are built upon native HTML elements to reuse their functionality. Shadow DOM The Shadow DOM is a functionality that allows ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
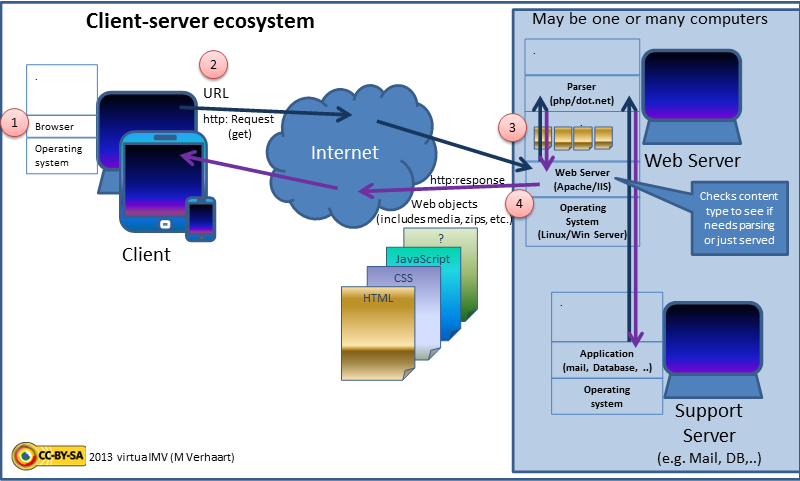
Web Browser
A web browser, often shortened to browser, is an application for accessing websites. When a user requests a web page from a particular website, the browser retrieves its files from a web server and then displays the page on the user's screen. Browsers can also display content stored locally on the user's device. Browsers are used on a range of devices, including desktops, laptops, tablets, smartphones, smartwatches and consoles. As of 2024, the most used browsers worldwide are Google Chrome (~66% market share), Safari (~16%), Edge (~6%), Firefox (~3%), Samsung Internet (~2%), and Opera (~2%). As of 2023, an estimated 5.4 billion people had used a browser. Function The purpose of a web browser is to fetch content and display it on the user's device. This process begins when the user inputs a Uniform Resource Locator (URL), such as ''https://en.wikipedia.org/'', into the browser's address bar. Virtually all URLs on the Web start with either ''http:'' or ''h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dynamic Web Page
A dynamic web page is a web page constructed at runtime (during software execution), as opposed to a ''static web page'', delivered as it is stored. A server-side dynamic web page is a web page whose construction is controlled by an application server processing server-side scripts. In server-side scripting, Parameter (computer programming), parameters determine how the assembly of every new web page proceeds, and including the setting up of more client-side processing. A client-side dynamic web page processes the web page using JavaScript running in the browser as it loads. JavaScript can interact with the page via Document Object Model (DOM), to query page state and modify it. Even though a web page can be dynamic on the client-side, it can still be hosted on a static Web hosting service, hosting service such as GitHub Pages or Amazon S3 as long as there is not any server-side code included. A dynamic web page is then reloaded by the user or by a computer program to change som ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ajax (programming)
Ajax (also AJAX ; short for "asynchronous I/O, asynchronous JavaScript and XML") is a set of web development techniques that uses various web technologies on the client-side to create asynchronous web applications. With Ajax, web applications can send and retrieve data from a Web server, server asynchronously (in the background) without interfering with the display and behaviour of the existing page. By decoupling the data exchange, data interchange layer from the presentation layer, Ajax allows web pages and, by extension, web applications, to change content dynamically without the need to reload the entire page. In practice, modern implementations commonly utilize JSON instead of XML. Ajax is not a technology, but rather a programming pattern. Hypertext Markup Language, HTML and Cascading Style Sheets, CSS can be used in combination to mark up and style information. The webpage can be modified by JavaScript to dynamically display (and allow the user to interact with) the new i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Client-side Scripting
A dynamic web page is a web page constructed at runtime (during software execution), as opposed to a ''static web page'', delivered as it is stored. A server-side dynamic web page is a web page whose construction is controlled by an application server processing server-side scripts. In server-side scripting, parameters determine how the assembly of every new web page proceeds, and including the setting up of more client-side processing. A client-side dynamic web page processes the web page using JavaScript running in the browser as it loads. JavaScript can interact with the page via Document Object Model (DOM), to query page state and modify it. Even though a web page can be dynamic on the client-side, it can still be hosted on a static hosting service such as GitHub Pages or Amazon S3 as long as there is not any server-side code included. A dynamic web page is then reloaded by the user or by a computer program to change some variable content. The updating information could ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Server-side Scripting
Server-side scripting is a technique used in web development which involves employing scripts on a web server which produces a response customized for each user's (client's) request to the website. Scripts can be written in any of a number of server-side scripting languages that are available. Server-side scripting is distinguished from client-side scripting where embedded scripts, such as JavaScript, are run client-side in a web browser, but both techniques are often used together. The alternative to either or both types of scripting is for the web server itself to deliver a static web page. Server-side scripting is often used to provide a customized interface for the user. These scripts may assemble client characteristics for use in customizing the response based on those characteristics, the user's requirements, access rights, etc. Server-side scripting also enables the website owner to hide the source code that generates the interface, whereas, with client-side scripting, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Server Side Includes
Server Side Includes (SSI) is a simple interpreted server-side scripting language used almost exclusively for the World Wide Web. It is most useful for including the contents of one or more files into a web page on a web server (see below), using its #include directive. This could commonly be a common piece of code throughout a site, such as a page header, a page footer and a navigation menu. SSI also contains control directives for conditional features and directives for calling external programs. It is supported by Apache, LiteSpeed, nginx, IIS as well as W3C's Jigsaw. It has its roots in NCSA HTTPd. In order for a web server to recognize an SSI-enabled HTML file and therefore carry out these instructions, either the filename should end with a special extension, by default .shtml, .stm, .shtm, or, if the server is configured to allow this, set the execution bit of the file. Design As a simple programming language, SSI supports only one type: text. Its control flow is rath ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Web Server
A web server is computer software and underlying Computer hardware, hardware that accepts requests via Hypertext Transfer Protocol, HTTP (the network protocol created to distribute web content) or its secure variant HTTPS. A user agent, commonly a web browser or web crawler, initiates communication by making a request for a web page or other Web Resource, resource using HTTP, and the server (computing), server responds with the content of that resource or an List of HTTP status codes, error message. A web server can also accept and store resources sent from the user agent if configured to do so. The hardware used to run a web server can vary according to the volume of requests that it needs to handle. At the low end of the range are embedded systems, such as a router (computing), router that runs a small web server as its configuration interface. A high-traffic Internet website might handle requests with hundreds of servers that run on racks of high-speed computers. A reso ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Failover
Failover is switching to a redundant or standby computer server, system, hardware component or network upon the failure or abnormal termination of the previously active application, server, system, hardware component, or network in a computer network. Failover and switchover are essentially the same operation, except that failover is automatic and usually operates without warning, while switchover requires human intervention. History The term "failover", although probably in use by engineers much earlier, can be found in a 1962 declassified NASA report. The term "switchover" can be found in the 1950s when describing '"Hot" and "Cold" Standby Systems', with the current meaning of immediate switchover to a running system (hot) and delayed switchover to a system that needs starting (cold). A conference proceedings from 1957 describes computer systems with both Emergency Switchover (i.e. failover) and Scheduled Failover (for maintenance). Failover Systems designers usually pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HTTP Header
HTTP header fields are a list of strings sent and received by both the client program and server on every HTTP request and response. These headers are usually invisible to the end-user and are only processed or logged by the server and client applications. They define how information sent/received through the connection are encoded (as in Content-Encoding), the session verification and identification of the client (as in browser cookies, IP address, user-agent) or their anonymity thereof (VPN or proxy masking, user-agent spoofing), how the server should handle data (as in Do-Not-Track or Global Privacy Control), the age (the time it has resided in a shared cache) of the document being downloaded, amongst others. General format In HTTP version 1.x, header fields are transmitted after the request line (in case of a request HTTP message) or the response line (in case of a response HTTP message), which is the first line of a message. Header fields are colon-separated key-val ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |