|
Ectrodactyly–ectodermal Dysplasia–cleft Syndrome
Ectrodactyly–ectodermal dysplasia– cleft syndrome, or EEC, and also referred to as EEC syndrome and split hand–split foot–ectodermal dysplasia–cleft syndromeFreedberg, et al. (2003). ''Fitzpatrick's Dermatology in General Medicine''. (6th ed.). McGraw-Hill. . is a rare form of ectodermal dysplasia, an autosomal dominant disorder inherited as a genetic trait.James, William; Berger, Timothy; Elston, Dirk (2005). ''Andrews' Diseases of the Skin: Clinical Dermatology''. (10th ed.). Saunders. . EEC is characterized by the triad of ectrodactyly, ectodermal dysplasia, and facial clefts. Other features noted in association with EEC include vesicoureteral reflux, recurrent urinary tract infections, obstruction of the nasolacrimal duct, decreased pigmentation of the hair and skin, missing or abnormal teeth, enamel hypoplasia, absent punctae in the lower eyelids, photophobia, occasional cognitive impairment and kidney anomalies, and conductive hearing loss. Presentation Ectrodacty ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ectrodactyly
Ectrodactyly, split hand, or cleft hand () involves the deficiency or absence of one or more central Digit (anatomy), digits of the hand or foot and is also known as split hand/split foot malformation (SHFM). The hands and feet of people with ectrodactyly (ectrodactyls) are often described as "claw-like" and may include only the thumb and one finger (usually either the little finger, ring finger, or a syndactyly of the two) with similar abnormalities of the feet. It is a substantial rare form of a congenital disorder in which the development of the hand is disturbed. It is a type I failure of formation – longitudinal arrest. The central ray of the hand is affected and usually appears without proximal deficiencies of nerves, vessels, tendons, muscles and bones in contrast to the radial and ulnar deficiencies. The cleft hand appears as a V-shaped cleft situated in the centre of the hand. The digits at the borders of the cleft might be syndactilyzed, and one or more digits can be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photophobia
Photophobia is a medical symptom of abnormal intolerance to visual perception of light. As a medical symptom, photophobia is not a morbid fear or phobia, but an experience of discomfort or pain to the eyes due to light exposure or by presence of actual physical sensitivity of the eyes, though the term is sometimes additionally applied to abnormal or irrational fear of light, such as heliophobia. The term ''photophobia'' comes . Causes Patients may develop photophobia as a result of several different medical conditions, related to the human eye, eye, the nervous system, genetic, or other causes. Photophobia may manifest itself in an increased response to light starting at any step in the visual system, such as: * Too much light entering the eye. Too much light can enter the eye if it is damaged, such as with corneal abrasion and retinal damage, or if its pupil is unable to normally constrict (seen with damage to the oculomotor nerve). * Due to albinism, the lack of pigment in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phonation
The term phonation has slightly different meanings depending on the subfield of phonetics. Among some phoneticians, ''phonation'' is the process by which the vocal folds produce certain sounds through quasi-periodic vibration. This is the definition used among those who study laryngeal anatomy and physiology and speech production in general. Phoneticians in other subfields, such as linguistic phonetics, call this process '' voicing'', and use the term ''phonation'' to refer to any oscillatory state of any part of the larynx that modifies the airstream, of which voicing is just one example. Voiceless and supra-glottal phonations are included under this definition. Voicing The phonatory process, or voicing, occurs when air is expelled from the lungs through the glottis, creating a pressure drop across the larynx. When this drop becomes sufficiently large, the vocal folds start to oscillate. The minimum pressure drop required to achieve phonation is called the phonation thres ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endothelial Cells
The endothelium (: endothelia) is a single layer of squamous endothelial cells that line the interior surface of blood vessels and lymphatic vessels. The endothelium forms an interface between circulating blood or lymph in the lumen and the rest of the vessel wall. Endothelial cells in direct contact with blood are called vascular endothelial cells whereas those in direct contact with lymph are known as lymphatic endothelial cells. Vascular endothelial cells line the entire circulatory system, from the heart to the smallest capillaries. These cells have unique functions that include fluid filtration, such as in the glomerulus of the kidney, blood vessel tone, hemostasis, neutrophil recruitment, and hormone trafficking. Endothelium of the interior surfaces of the heart chambers is called endocardium. An impaired function can lead to serious health issues throughout the body. Structure The endothelium is a thin layer of single flat (squamous) cells that line the interior s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dentin
Dentin ( ) (American English) or dentine ( or ) (British English) () is a calcified tissue (biology), tissue of the body and, along with tooth enamel, enamel, cementum, and pulp (tooth), pulp, is one of the four major components of teeth. It is usually covered by enamel on the crown and cementum on the root and surrounds the entire pulp. By volume, 45% of dentin consists of the mineral hydroxyapatite, 33% is organic material, and 22% is water. Yellow in appearance, it greatly affects the color of a tooth due to the translucency of enamel. Dentin, which is less mineralized and less brittle than enamel, is necessary for the support of enamel. Dentin rates approximately 3 on the Mohs scale of mineral hardness. There are two main characteristics which distinguish dentin from enamel: firstly, dentin forms throughout life; secondly, dentin is sensitive and can become hypersensitive to changes in temperature due to the sensory function of odontoblasts, especially when enamel recedes an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypodermis
The subcutaneous tissue (), also called the hypodermis, hypoderm (), subcutis, or superficial fascia, is the lowermost layer of the integumentary system in vertebrates. The types of cells found in the layer are fibroblasts, adipose cells, and macrophages. The subcutaneous tissue is derived from the mesoderm, but unlike the dermis, it is not derived from the mesoderm's dermatome region. It consists primarily of loose connective tissue and contains larger blood vessels and nerves than those found in the dermis. It is a major site of fat storage in the body. In arthropods, a hypodermis can refer to an epidermal layer of cells that secretes the chitinous cuticle. The term also refers to a layer of cells lying immediately below the epidermis of plants. Structure * Fibrous bands anchoring the skin to the deep fascia * Collagen and elastin fibers attaching it to the dermis * Fat is absent from the eyelids, clitoris, penis, much of pinna, and scrotum * Blood vessels on route to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dermis
The dermis or corium is a layer of skin between the epidermis (skin), epidermis (with which it makes up the cutis (anatomy), cutis) and subcutaneous tissues, that primarily consists of dense irregular connective tissue and cushions the body from stress and strain. It is divided into two layers, the superficial area adjacent to the epidermis called the papillary region and a deep thicker area known as the reticular dermis.James, William; Berger, Timothy; Elston, Dirk (2005). ''Andrews' Diseases of the Skin: Clinical Dermatology'' (10th ed.). Saunders. Pages 1, 11–12. . The dermis is tightly connected to the epidermis through a basement membrane. Structural components of the dermis are collagen, elastic fibers, and Ground substance, extrafibrillar matrix.Marks, James G; Miller, Jeffery (2006). ''Lookingbill and Marks' Principles of Dermatology'' (4th ed.). Elsevier Inc. Page 8–9. . It also contains mechanoreceptors that provide the sense of touch and thermoreceptors that provide ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Internal Ear
The inner ear (internal ear, auris interna) is the innermost part of the vertebrate ear. In vertebrates, the inner ear is mainly responsible for sound detection and balance. In mammals, it consists of the bony labyrinth, a hollow cavity in the temporal bone of the skull with a system of passages comprising two main functional parts: * The cochlea, dedicated to hearing; converting sound pressure patterns from the outer ear into electrochemical impulses which are passed on to the brain via the auditory nerve. * The vestibular system, dedicated to balance. The inner ear is found in all vertebrates, with substantial variations in form and function. The inner ear is innervated by the eighth cranial nerve in all vertebrates. Structure The labyrinth can be divided by layer or by region. Bony and membranous labyrinths The bony labyrinth, or osseous labyrinth, is the network of passages with bony walls lined with periosteum. The three major parts of the bony labyrinth are the vesti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pituitary
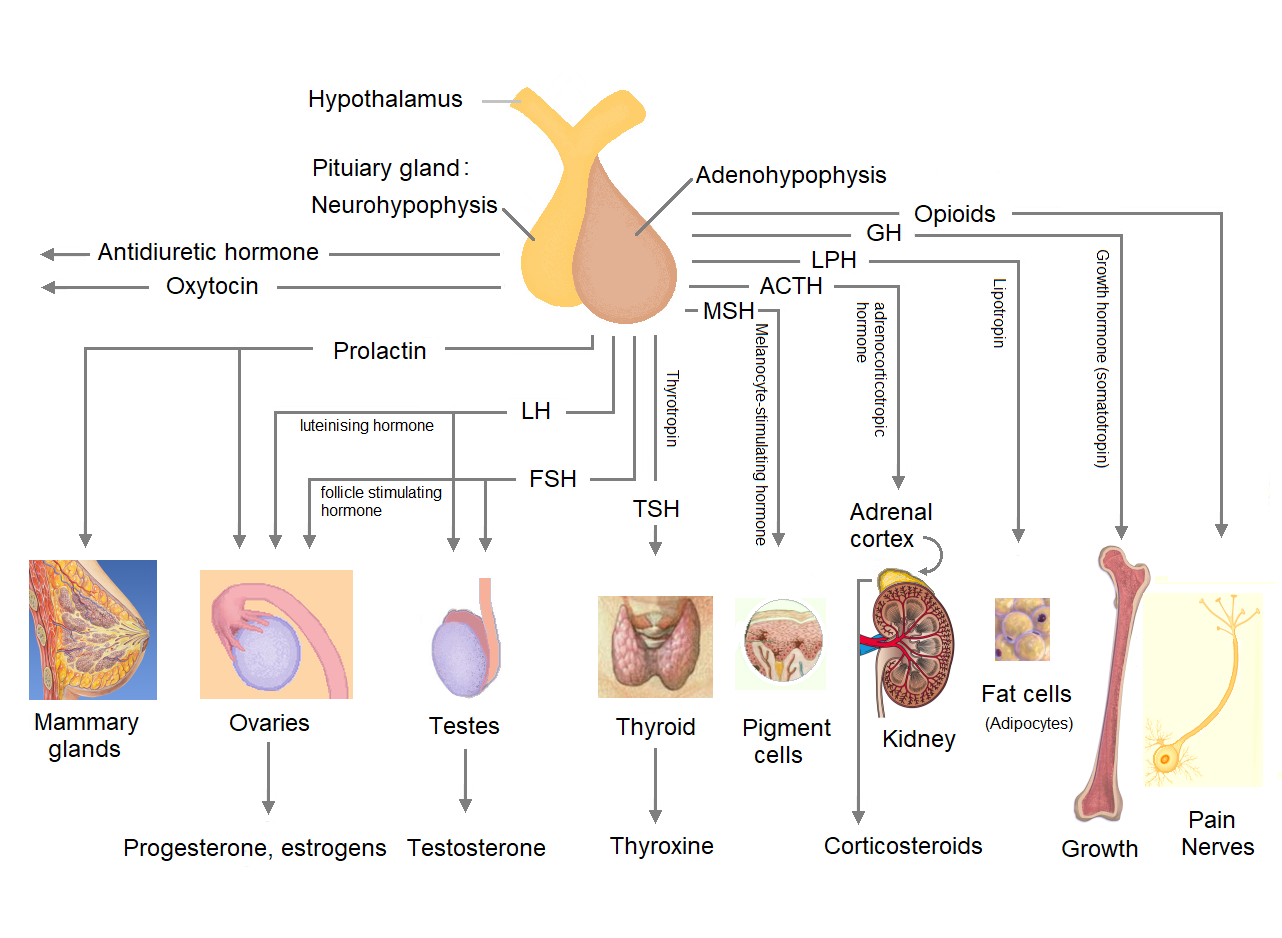
The pituitary gland or hypophysis is an endocrine gland in vertebrates. In humans, the pituitary gland is located at the base of the brain, protruding off the bottom of the hypothalamus. The pituitary gland and the hypothalamus control much of the body's endocrine system. It is seated in part of the sella turcica a depression in the sphenoid bone, known as the hypophyseal fossa. The human pituitary gland is oval shaped, about 1 cm in diameter, in weight on average, and about the size of a kidney bean. Digital version. There are two main lobes of the pituitary, an anterior lobe, and a posterior lobe joined and separated by a small intermediate lobe. The anterior lobe (adenohypophysis) is the glandular part that produces and secretes several hormones. The posterior lobe (neurohypophysis) secretes neurohypophysial hormones produced in the hypothalamus. Both lobes have different origins and they are both controlled by the hypothalamus. Hormones secreted from the pituitary g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epidermis (skin)
The epidermis is the outermost of the three layers that comprise the skin, the inner layers being the dermis and hypodermis. The epidermal layer provides a barrier to infection from environmental pathogens and regulates the amount of water released from the body into the atmosphere through transepidermal water loss. The epidermis is composed of multiple layers of flattened cells that overlie a base layer ( stratum basale) composed of columnar cells arranged perpendicularly. The layers of cells develop from stem cells in the basal layer. The thickness of the epidermis varies from 31.2μm for the penis to 596.6μm for the sole of the foot with most being roughly 90μm. Thickness does not vary between the sexes but becomes thinner with age. The human epidermis is an example of epithelium, particularly a stratified squamous epithelium. The word epidermis is derived through Latin , itself and . Something related to or part of the epidermis is termed epidermal. Structure ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nail (anatomy)
A nail is a protective plate characteristically found at the tip of the digit (anatomy), digits (fingers and toes) of all primates, corresponding to the claws in other tetrapod animals. Fingernails and toenails are made of a tough rigid protein called alpha-keratin, a polymer also found in the claws, hooves, and horn (anatomy), horns of vertebrates. Structure The nail consists of the nail plate, the nail matrix and the nail bed below it, and the grooves surrounding it. Parts of the nail The nail matrix is the active Tissue (biology), tissue (or Germ layer, germinal Matrix (biology), matrix) that generates cells. The cells harden as they move outward from the nail root to the nail plate. The nail matrix is also known as the ''matrix unguis'', keratogenous membrane, or onychostroma. It is the part of the nail bed that is beneath the nail and contains nerves, lymph, and blood vessels. The matrix produces cells that become the nail plate. The width and thickness of the nail p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sweat Glands
Sweat glands, also known as sudoriferous or sudoriparous glands, , are small tubular structures of the skin that produce sweat. Sweat glands are a type of exocrine gland, which are glands that produce and secrete substances onto an epithelial surface by way of a duct (anatomy), duct. There are two main types of sweat glands that differ in their structure, function, secretory product, mechanism of excretion, anatomic distribution, and distribution across species: * Eccrine sweat glands are distributed almost all over the human body, in varying densities, with the highest density in palms and soles, then on the head, but much less on the trunk and the extremities. Their water-based secretion represents a primary form of thermoregulation, cooling in humans. * Apocrine sweat glands are mostly limited to the axilla, axillae (armpits) and perineum, perineal area in humans. They are not significant for cooling in humans, but are the sole effective sweat glands in hoofed animals, such as t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |