|
Ectomy
The surgical terminology suffix "-ectomy" was taken from Greek εκ-τομια = "act of cutting out". It means surgical removal of something, usually from inside the body. A *Adenectomy is the surgical removal of a gland. *Adenoidectomy is the surgical removal of the adenoids, also known as the pharyngeal tonsils. *Adrenalectomy is the removal of one or both adrenal glands. *Apicoectomy is the surgical removal of tooth's root tip. *Appendectomy is the surgical removal of the appendix; it is also known as an appendicectomy. * Arthrectomy is the removal of a joint of the body. *Auriculectomy is the removal of the ear B *Bullectomy is the surgical removal of bullae from the lung. *Bunionectomy is the removal of a bunion. *Bursectomy is the removal of a bursa, a small sac filled with synovial fluid. C *Cardiectomy is the removal of the cardia of the stomach. *Cecectomy is the removal of the cecum. * Cephalectomy is the surgical removal of the head ( decapitation). *Cervicectomy i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cholecystectomy
Cholecystectomy is the surgical removal of the gallbladder. Cholecystectomy is a common treatment of symptomatic gallstones and other gallbladder conditions. In 2011, cholecystectomy was the eighth most common operating room procedure performed in hospitals in the United States. Cholecystectomy can be performed either laparoscopically, or via an open surgical technique. The surgery is usually successful in relieving symptoms, but up to 10 percent of people may continue to experience similar symptoms after cholecystectomy, a condition called postcholecystectomy syndrome. Complications of cholecystectomy include bile duct injury, wound infection, bleeding, retained gallstones, abscess formation and stenosis (narrowing) of the bile duct. Medical use Pain and complications caused by gallstones are the most common reasons for removal of the gallbladder. The gallbladder can also be removed in order to treat biliary dyskinesia or gallbladder cancer. Gallstones are very common but ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Appendectomy
An appendectomy, also termed appendicectomy, is a surgical operation in which the vermiform appendix (a portion of the intestine) is removed. Appendectomy is normally performed as an urgent or emergency procedure to treat complicated acute appendicitis. Appendectomy may be performed laparoscopically (as minimally invasive surgery) or as an open operation. Over the 2010s, surgical practice has increasingly moved towards routinely offering laparoscopic appendicectomy; for example in the United Kingdom over 95% of adult appendicectomies are planned as laparoscopic procedures. Laparoscopy is often used if the diagnosis is in doubt, or in order to leave a less visible surgical scar. Recovery may be slightly faster after laparoscopic surgery, although the laparoscopic procedure itself is more expensive and resource-intensive than open surgery and generally takes longer. Advanced pelvic sepsis occasionally requires a lower midline laparotomy. Complicated (perforated) appendicitis should ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adenoidectomy
Adenoidectomy is the surgical removal of the adenoid for reasons which include impaired breathing through the nose, chronic infections, or recurrent earaches. The effectiveness of removing the adenoids in children to improve recurrent nasal symptoms and/or nasal obstruction has not been well studied. The surgery is less commonly performed in adults in whom the adenoid is much smaller and less active than it is in children. It is most often done on an outpatient basis under general anesthesia. Post-operative pain is generally minimal and reduced by icy or cold foods. The procedure is often combined with tonsillectomy (this combination is usually called an "adenotonsillectomy" or "T&A"), for which the recovery time is an estimated 10–14 days, sometimes longer, mostly dependent on age. Adenoidectomy is not often performed under one year of age as adenoid function is part of the body's immune system but its contribution to this decreases progressively beyond this age. Medical uses T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adrenalectomy
Adrenalectomy (Latin root Ad "near/at" + renal "related to the kidneys" + Greek '' ‑ectomy'' “out-cutting”; sometimes written as ADX for the procedure or resulting state) is the surgical removal of one (unilateral) or both (bilateral) adrenal glands. It is usually done to remove tumors of the adrenal glands that are producing excess hormones or is large in size (more than 2 inches or 4 to 5 centimeters). Adrenalectomy can also be done to remove a cancerous tumor of the adrenal glands, or cancer that has spread from another location, such as the kidney or lung. Adrenalectomy is not performed on those who have severe coagulopathy or whose heart and lungs are too weak to undergo surgery. The procedure can be performed using an open incision (laparotomy) or minimally invasive laparoscopic or robot-assisted techniques. Minimally invasive techniques are increasingly the gold standard of care due to shorter length of stay in the hospital, lower blood loss, and similar complication ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cervicectomy
In gynecologic oncology, trachelectomy, also called cervicectomy, is a surgical removal of the uterine cervix. As the uterine body is preserved, this type of surgery is a fertility preserving surgical alternative to a radical hysterectomy and applicable in selected younger women with early cervical cancer. Types Trachelectomies, broadly, can be divided into the ''simple'' and ''radical'' variants. Radical The formal name of this operation is ''radical vaginal trachelectomy (RVT)'' and also known as the ''Dargent operation'' and ''radical trachelectomy''. The word ''radical'' is used as, in addition to the cervix (like in radical hysterectomies), the parametria (tissue adjacent to the cervix) and vaginal cuff (the end of the vagina close to the cervix) are also excised as a part of the operation. It is usually done with a lymphadenectomy, to assess for tumour spread to the lymph nodes. This operation was pioneered by the renowned French Obstetrician-Gynecologist Surgeon, Daniel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clitoridectomy
Clitoridectomy or clitorectomy is the surgical removal, reduction, or partial removal of the clitoris. It is rarely used as a therapeutic medical procedure, such as when cancer has developed in or spread to the clitoris. It is often performed on intersex newborns. Commonly, non-medical removal of the clitoris is performed during female genital mutilation (FGM). Medical uses Malignancies A clitoridectomy is often done to remove malignancy or necrosis of the clitoris. This is sometimes done along with a radical complete vulvectomy. Surgery may also become necessary due to therapeutic radiation treatments to the pelvic area. Removal of the clitoris may be due to malignancy or trauma. Intersexuality and other conditions Female infants born with a 46,XX genotype but have genitalia affected by congenital adrenal hyperplasia and are treated surgically with vaginoplasty that often reduces the size of the clitoris without its total removal. The atypical size of the clitoris is due t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
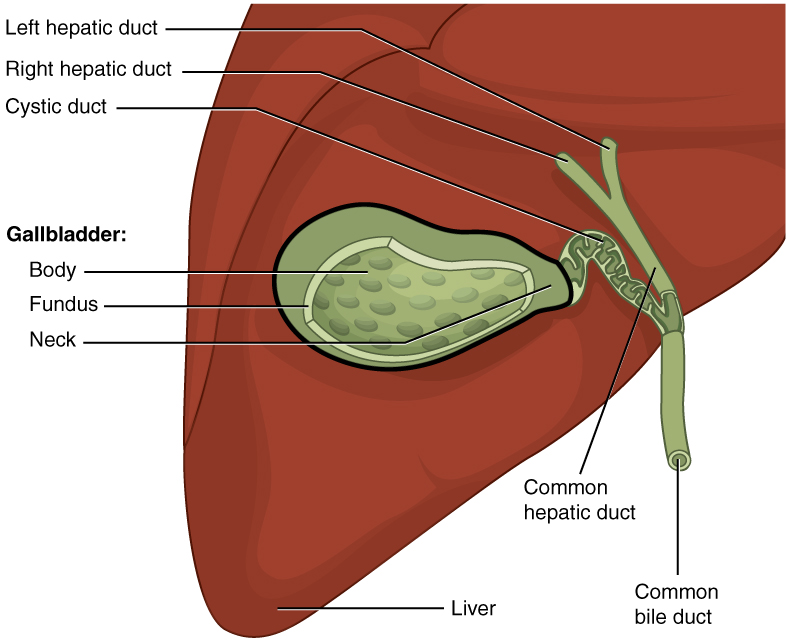
Gallbladder
In vertebrates, the gallbladder, also known as the cholecyst, is a small hollow organ where bile is stored and concentrated before it is released into the small intestine. In humans, the pear-shaped gallbladder lies beneath the liver, although the structure and position of the gallbladder can vary significantly among animal species. It receives and stores bile, produced by the liver, via the common hepatic duct, and releases it via the common bile duct into the duodenum, where the bile helps in the digestion of fats. The gallbladder can be affected by gallstones, formed by material that cannot be dissolved – usually cholesterol or bilirubin, a product of haemoglobin breakdown. These may cause significant pain, particularly in the upper-right corner of the abdomen, and are often treated with removal of the gallbladder (called a cholecystectomy). Cholecystitis, inflammation of the gallbladder, has a wide range of causes, including result from the impaction of gallstone ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apicoectomy
A root end surgery, also known as apicoectomy ('' apico-'' + '' -ectomy''), apicectomy ('' apic-'' + '' -ectomy''), retrograde root canal treatment (''c.f.'' orthograde root canal treatment) or root-end filling, is an endodontic surgical procedure whereby a tooth's root tip is removed and a root end cavity is prepared and filled with a biocompatible material. It is an example of a periradicular surgery. An apicoectomy is necessary when conventional root canal therapy has failed and a re-treatment was already unsuccessful or is not advised. Removal of the root tip is indicated to remove the entire apical delta ensuring no uncleaned missed anatomy. The only alternative may be extraction followed by prosthetic replacement with a denture, dental bridge or dental implant. State-of-the-art procedures make use of microsurgical endodontic techniques, such as a dental operating microscope, micro instruments, ultrasonic preparation tips and calcium-silicate based filling materials. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bullectomy
Bullectomy is a surgical procedure in which dilated air-spaces or bullae in lung parenchyma are removed. Common causes of dilated air-spaces include chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and emphysema Emphysema, or pulmonary emphysema, is a lower respiratory tract disease, characterised by air-filled spaces ( pneumatoses) in the lungs, that can vary in size and may be very large. The spaces are caused by the breakdown of the walls of the alve .... Patients with giant bullae filling half the thoracic volume and compressing relatively normal adjacent parenchyma are recommended for bullectomy. It is also indicated in severe dyspnea, repeated respiratory infections and spontaneous pneumothorax. The size of dilated air-spaces or bullae volume is the most important factor in relation to ventilator capacity post-bullectomy. In cases where the size of bullae are enlarged, bullectomy is indicated if the percentage of forced expiratory volume in one second(FEV1%) is greater than 40% ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cardiectomy
The stomach is a muscular, hollow organ in the gastrointestinal tract of humans and many other animals, including several invertebrates. The stomach has a dilated structure and functions as a vital organ in the digestive system. The stomach is involved in the gastric phase of digestion, following chewing. It performs a chemical breakdown by means of enzymes and hydrochloric acid. In humans and many other animals, the stomach is located between the oesophagus and the small intestine. The stomach secretes digestive enzymes and gastric acid to aid in food digestion. The pyloric sphincter controls the passage of partially digested food (chyme) from the stomach into the duodenum, where peristalsis takes over to move this through the rest of intestines. Structure In the human digestive system, the stomach lies between the oesophagus and the duodenum (the first part of the small intestine). It is in the left upper quadrant of the abdominal cavity. The top of the stomach lies ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clitoris
The clitoris ( or ) is a female sex organ present in mammals, ostriches and a limited number of other animals. In humans, the visible portion – the glans – is at the front junction of the labia minora (inner lips), above the opening of the urethra. Unlike the penis, the male homologue (equivalent) to the clitoris, it usually does not contain the distal portion (or opening) of the urethra and is therefore not used for urination. In most species, the clitoris lacks any reproductive function. While few animals urinate through the clitoris or use it reproductively, the spotted hyena, which has an especially large clitoris, urinates, mates, and gives birth via the organ. Some other mammals, such as lemurs and spider monkeys, also have a large clitoris. The clitoris is the human female's most sensitive erogenous zone and generally the primary anatomical source of human female sexual pleasure. In humans and other mammals, it develops from an outgrowth in the em ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bursectomy
A bursectomy is the removal of a bursa, which is a small sac filled with synovial fluid that cushions adjacent bone structures and reduces friction in joint movement. This procedure is usually carried out to relieve chronic inflammation ( bursitis) or infection, when conservative management has failed to improve patient outcomes. See also * List of surgeries by type Many surgical procedure names can be broken into parts to indicate the meaning. For example, in gastrectomy, "ectomy" is a suffix meaning the removal of a part of the body. "Gastro-" means stomach. Thus, ''gastrectomy'' refers to the surgical re ... References Further reading * * * Orthopedic surgical procedures Synovial bursae {{Treatment-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.png)