|
Economy Act
The Economy Act of 1933, officially titled the Act of March 20, 1933 (ch. 3, , is an Act of Congress that cut the salaries of federal workers and reduced benefit payments to veterans, moves intended to reduce the federal deficit in the United States.Olson, James Stuart. ''Historical Dictionary of the Great Depression, 1929-1940.'' Santa Barbara, calif.: Greenwood Publishing Group, 2001. The Economy Act of 1933 is sometimes confused with the '' Economy Act of 1932'', which was signed in the final days of the Hoover administration in February 1933.Lee, Mordecai. ''Institutionalizing Congress and the Presidency: The U.S. Bureau of Efficiency, 1916-1933.'' College Station, Tex.: Texas A&M University Press, 2006. This Hoover-sponsored bill established the purchasing authority of the federal government. Title VI of this earlier act authorized heads of executive departments, establishments, bureaus, and offices to place orders with any other such Federal agency unless the requisition ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Act Of Congress
An act of Congress is a statute enacted by the United States Congress. Acts may apply only to individual entities (called Public and private bills, private laws), or to the general public (Public and private bills, public laws). For a Bill (law), bill to become an act, the text must pass through both houses with a majority, then be either signed into law by the president of the United States, be left unsigned for ten days (excluding Sundays) while Congress remains in session, or, if vetoed by the president, receive a congressional override from of both houses. Public law, private law, designation In the United States, acts of Congress are designated as either public laws, relating to the general public, or private laws, relating to specific institutions or individuals. Since 1957, all Acts of Congress have been designated as "Public Law X–Y" or "Private Law X–Y", where X is the number of the Congress and Y refers to the sequential order of the bill (when it was enacted). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
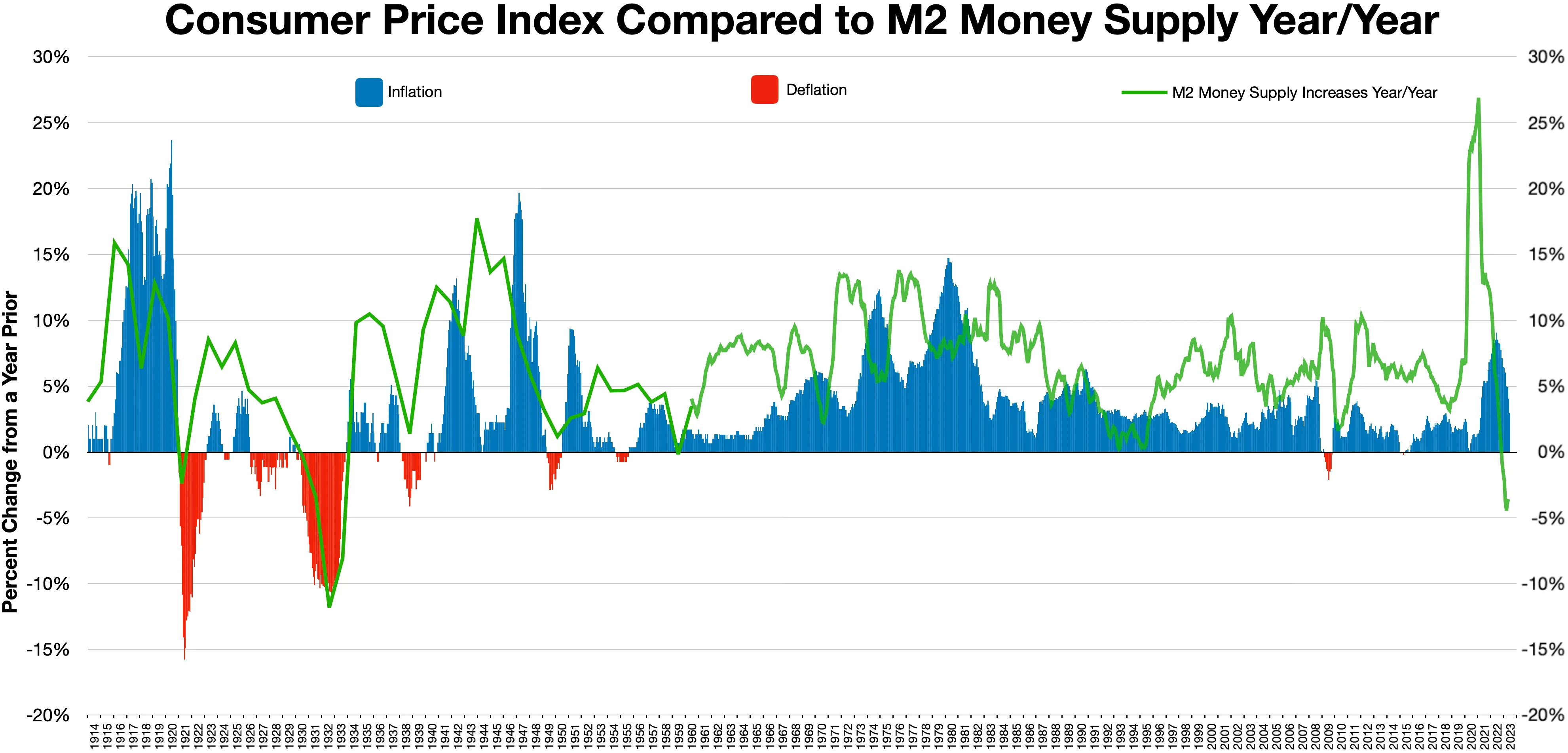
Deflation
In economics, deflation is a decrease in the general price level of goods and services. Deflation occurs when the inflation rate falls below 0% and becomes negative. While inflation reduces the value of currency over time, deflation increases it. This allows more goods and services to be bought than before with the same amount of currency. Deflation is distinct from '' disinflation'', a slowdown in the inflation rate; i.e., when inflation declines to a lower rate but is still positive. Economists generally believe that a sudden deflationary shock is a problem in a modern economy because it increases the real value of debt, especially if the deflation is unexpected. Deflation may also aggravate recessions and lead to a deflationary spiral . Some economists argue that prolonged deflationary periods are related to the underlying technological progress in an economy, because as productivity increases ( TFP), the cost of goods decreases. Deflation usually happens when supply is hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
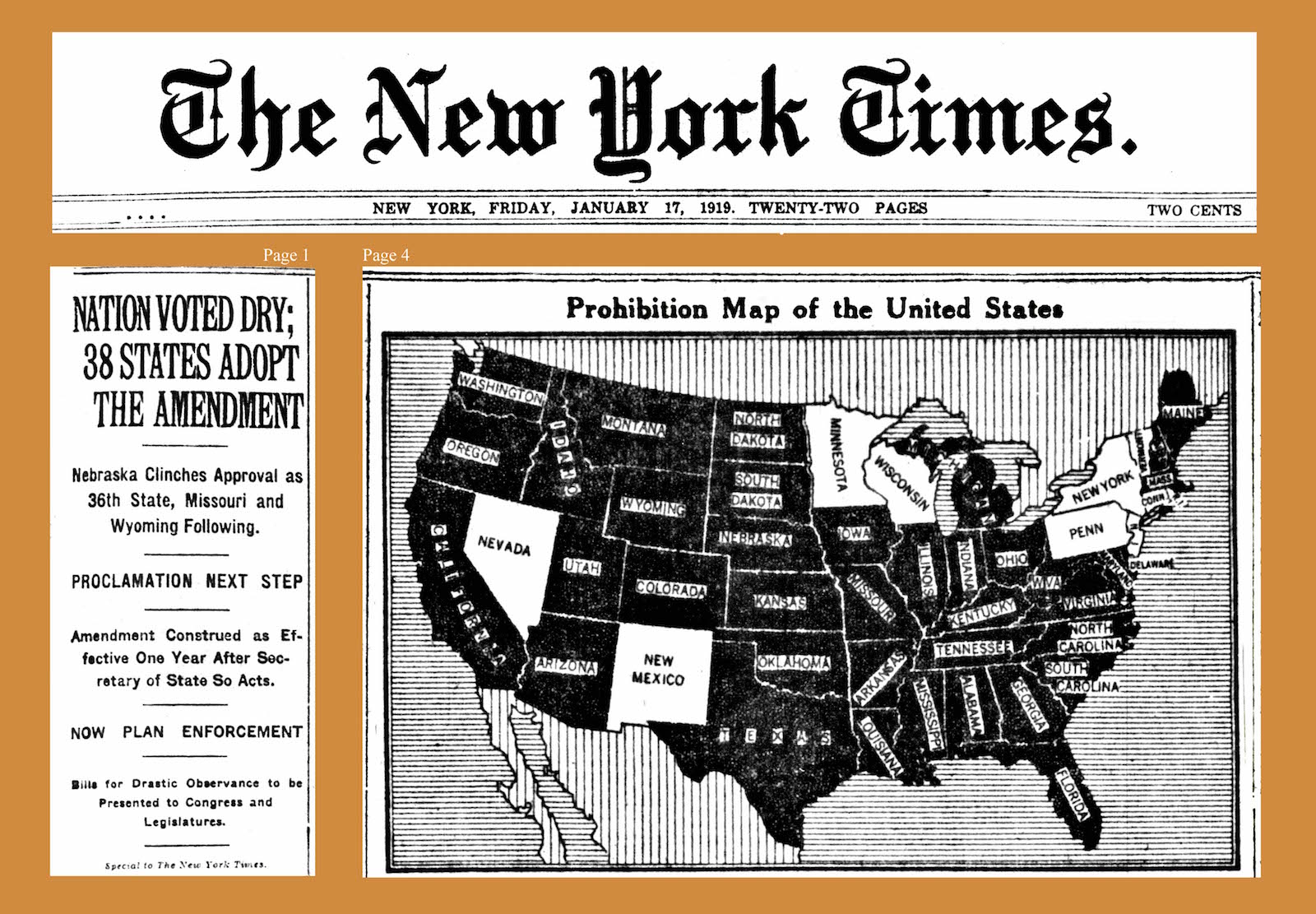
Volstead Act
The National Prohibition Act, known informally as the Volstead Act, was an act of the 66th United States Congress designed to execute the 18th Amendment (ratified January 1919) which established the prohibition of alcoholic drinks. The Anti-Saloon League's Wayne Wheeler conceived and drafted the bill, which was named after Andrew Volstead, chairman of the House Judiciary Committee, who managed the legislation. Historical context The Volstead Act had a number of contributing factors that led to its ratification in 1919. For example, the formation of the Anti-Saloon League in 1893. The league used the after effects of World War I to push for national prohibition because there was a lot of prejudice and suspicion of foreigners following the war. Many reformers used the war to get measures passed and a major example of this was national prohibition. The league was successful in getting many states to ban alcohol prior to 1917 by claiming that to drink was to be pro-German an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Democratic Caucus Of The United States Senate
The Democratic Caucus of the United States Senate, sometimes referred to as the Democratic Conference, is the formal organization of all senators who are part of the Democratic Party in the United States Senate. For the makeup of the 119th Congress, the caucus additionally includes two independent senators (Bernie Sanders of Vermont, and Angus King of Maine) who caucus with the Democrats, bringing the current total to 47 members. The central organizational front for Democrats in the Senate, its primary function is communicating the party's message to all of its members under a single banner. The present chair of the Senate Democratic Caucus is Chuck Schumer of New York. Current leadership Effective with the start of the 119th Congress, the conference leadership is as follows: * Democratic Leader Chuck Schumer * Democratic Whip Dick Durbin * Chair of Steering and Policy Committee Amy Klobuchar * Chair of Strategic Communications Committee Cory Booker * Vice Chair of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Senate
The United States Senate is a chamber of the Bicameralism, bicameral United States Congress; it is the upper house, with the United States House of Representatives, U.S. House of Representatives being the lower house. Together, the Senate and House have the authority under Article One of the United States Constitution, Article One of the Constitution of the United States, U.S. Constitution to pass or defeat federal legislation. The Senate also has exclusive power to confirm President of the United States, U.S. presidential appointments, to approve or reject treaties, and to convict or exonerate Impeachment in the United States, impeachment cases brought by the House. The Senate and the House provide a Separation of powers under the United States Constitution, check and balance on the powers of the Federal government of the United States#Executive branch, executive and Federal judiciary of the United States, judicial branches of government. The composition and powers of the Se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Republican Party (United States)
The Republican Party, also known as the Grand Old Party (GOP), is a Right-wing politics, right-wing political parties in the United States, political party in the United States. One of the Two-party system, two major parties, it emerged as the main rival of the then-dominant Democratic Party (United States), Democratic Party in the 1850s, and the two parties have dominated American politics since then. The Republican Party was founded in 1854 by anti-slavery activists opposing the Kansas–Nebraska Act and the expansion of slavery in the United States, slavery into U.S. territories. It rapidly gained support in the Northern United States, North, drawing in former Whig Party (United States), Whigs and Free Soil Party, Free Soilers. Abraham Lincoln's 1860 United States presidential election, election in 1860 led to the secession of Southern states and the outbreak of the American Civil War. Under Lincoln and a Republican-controlled Congress, the party led efforts to preserve th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States House Of Representatives
The United States House of Representatives is a chamber of the Bicameralism, bicameral United States Congress; it is the lower house, with the U.S. Senate being the upper house. Together, the House and Senate have the authority under Article One of the United States Constitution, Article One of the Constitution of the United States, U.S. Constitution to pass or defeat federal legislation, known as Bill (United States Congress), bills. Those that are also passed by the Senate are sent to President of the United States, the president for signature or veto. The House's exclusive powers include initiating all revenue bills, Impeachment in the United States, impeaching federal officers, and Contingent election, electing the president if no candidate receives a majority of votes in the United States Electoral College, Electoral College. Members of the House serve a Fixed-term election, fixed term of two years, with each seat up for election before the start of the next Congress. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Democratic Party (United States)
The Democratic Party is a Centre-left politics, center-left political parties in the United States, political party in the United States. One of the Major party, major parties of the U.S., it was founded in 1828, making it the world's oldest active political party. Its main rival since the 1850s has been the Republican Party (United States), Republican Party, and the two have since dominated American politics. The Democratic Party was founded in 1828 from remnants of the Democratic-Republican Party. Senator Martin Van Buren played the central role in building the coalition of state organizations which formed the new party as a vehicle to help elect Andrew Jackson as president that year. It initially supported Jacksonian democracy, agrarianism, and Manifest destiny, geographical expansionism, while opposing Bank War, a national bank and high Tariff, tariffs. Democrats won six of the eight presidential elections from 1828 to 1856, losing twice to the Whig Party (United States) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Democratic Caucus Of The United States House Of Representatives
The House Democratic Caucus is a congressional caucus composed of all Democratic representatives in the United States House of Representatives, voting and non-voting, and is responsible for nominating and electing the Democratic Party leadership in the chamber. In its roles as a party conference, the caucus writes and enforces rules of conduct and discipline for its members, approves committee assignments, and serves as the primary forum for development of party policy and legislative priorities. It hosts weekly meetings for these purposes and to communicate the party's message to members. When the caucus holds the majority of seats, it is usually led by the speaker of the U.S. House of Representatives who is assisted on the floor by the House majority leader and the party's chief whip. When in the minority, it is led by the House minority leader, assisted by the chief whip. The caucus has a Caucus chairman and Caucus vice-chair (formerly called the secretary). For the 119th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Capitol
The United States Capitol, often called the Capitol or the Capitol Building, is the Seat of government, seat of the United States Congress, the United States Congress, legislative branch of the Federal government of the United States, federal government. It is located on Capitol Hill at the eastern end of the National Mall in Washington, D.C. Although no longer at the geographic center of the Geography of Washington, D.C., national capital, the U.S. Capitol forms the origin point for the street-numbering system of the district as well as Quadrants of Washington, D.C., its four quadrants. Like the principal buildings of the Federal government of the United States#Executive branch, executive and Federal judiciary of the United States, judicial branches, the Capitol is built in a neoclassical architecture, neoclassical style and has a white exterior. Central sections of the present building were completed in 1800. These were partly destroyed in the Burning of Washington, 1814 Burni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George S
George may refer to: Names * George (given name) * George (surname) People * George (singer), American-Canadian singer George Nozuka, known by the mononym George * George Papagheorghe, also known as Jorge / GEØRGE * George, stage name of Giorgio Moroder * George, son of Andrew I of Hungary Places South Africa * George, South Africa, a city ** George Airport United States * George, Iowa, a city * George, Missouri, a ghost town * George, Washington, a city * George County, Mississippi * George Air Force Base, a former U.S. Air Force base located in California Computing * George (algebraic compiler) also known as 'Laning and Zierler system', an algebraic compiler by Laning and Zierler in 1952 * GEORGE (computer), early computer built by Argonne National Laboratory in 1957 * GEORGE (operating system), a range of operating systems (George 1–4) for the ICT 1900 range of computers in the 1960s * GEORGE (programming language), an autocode system invented by Charles Le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |