|
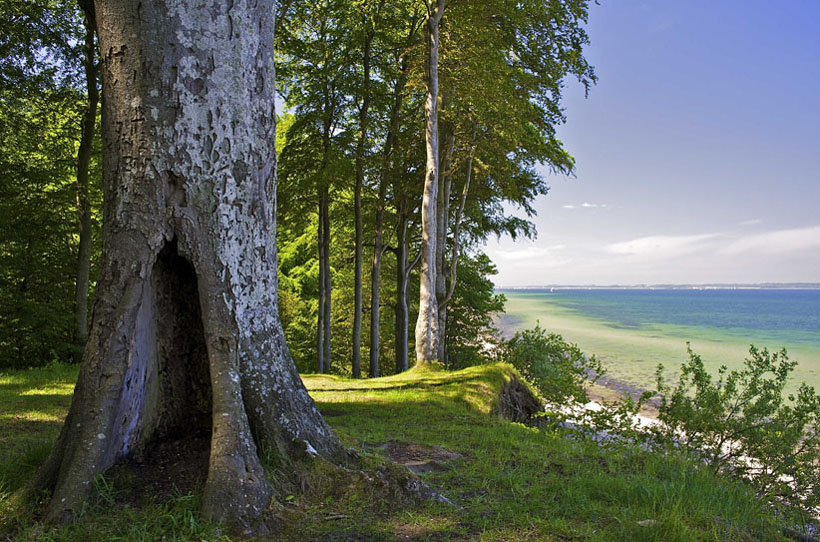
Eckernförde Bay
Eckernförde Bay (; ) is a firth and a branch of the Bay of Kiel between the Danish Wahld peninsula in the south and the Schwansen peninsula in the north in the Baltic Sea off the lands of Schleswig-Holstein, Germany. The bay extends around deep into the land and is wide at its entrance where ''Booknis-Eck'' (municipality of ''Waabs'') and ''Danish-Nienhof'' (municipality of ''Schwedeneck'') mark the endpoints. The bay is up to deep. The border to the Kiel Fjord lies at the Bülk Lighthouse. The once forested Danish Wahld peninsula between Kiel Fjord and Eckernförde Bay constituted the borderland between the Saxons and the Danes (Germanic tribe), Danes until the Middle Ages. At the inner end of the bay lies the town of Eckernförde. Geography The bay formed during the Last Glacial Period, last Ice Age between 120,000 and 10,000 years ago from a glacier. According to some geologists, the Bathymetry, depth contour of the Eckernförde Bay had already formed before the Ice Age a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schleswig-Holstein
Schleswig-Holstein (; ; ; ; ; occasionally in English ''Sleswick-Holsatia'') is the Northern Germany, northernmost of the 16 states of Germany, comprising most of the historical Duchy of Holstein and the southern part of the former Duchy of Schleswig. Its capital city is Kiel; other notable cities are Lübeck and Flensburg. It covers an area of , making it the 5th smallest German federal state by area (including the city-states). Historically, the name can also refer to a larger region, containing both present-day Schleswig-Holstein and the former South Jutland County (Northern Schleswig; now part of the Region of Southern Denmark) in Denmark. Schleswig, named South Jutland at the time, was under Danish control during the Viking Age, but in the 12th century it became a duchy within Denmark due to infighting in the Danish Royal House. It bordered Holstein, which was a part of the Holy Roman Empire. Beginning in 1460, the King of Denmark ruled both Schleswig and Holstein as the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Altenhof, Schleswig-Holstein
Altenhof (, ) is a municipality in the district of Rendsburg-Eckernförde, in Schleswig-Holstein, Germany Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It lies between the Baltic Sea and the North Sea to the north and the Alps to the south. Its sixteen States of Germany, constituent states have a total popu .... References Municipalities in Schleswig-Holstein Rendsburg-Eckernförde {{RendsburgEckernförde-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
EuroVelo
EuroVelo is a network of 17 long-distance cycling routes criss-crossing Europe, with 2 more in early construction across various stages of completion. When completed, the EuroVelo network's total length will be almost . more than were in place. EuroVelo is a project of the European Cyclists' Federation (ECF). The multinational project aims to connect 40 countries via the 19 unique routes across the European continent. EuroVelo routes can be used for bicycle touring across the continent, as well as by local people making short journeys. The routes are made of both existing national bike routes — such as the Dutch LF-Routes, the German D-Routes, the French véloroute "SN3V" and the British National Cycle Network — and existing general purpose roads, together with new stretches of cycle routes to connect them. History The idea of creating a network of international cycle routes spanning Europe started in 1995. It was initially coordinated by the ECF, ''De Frie Fugle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kiel–Flensburg Railway
The Kiel–Flensburg railway is a single-track railway in Schleswig-Holstein, Germany. The railway connects the city of Kiel on the Baltic Sea with Eckernförde and Flensburg. Travel time over the railway is around 75 minutes with a maximum speed of . Alignment The railway crosses three peninsulas: from Kiel, it crosses the Kiel Canal and then traverses the Dänischer Wohld to Eckernförde. From that town to the Schlei it crosses Schwansen. North of the Schlei, the line runs through the typical landscape of Angeln, the location of the station of Süderbrarup. At the end point, Flensburg, the original terminal was at the Kiel Station, directly in the harbour. Since the current Flensburg station was completed in 1927, the railway now terminates there, entering from the east. Important structures along the line are the Levensau High Bridge over the Kiel Canal and the Lindaunis Bridge crossing the Schlei, which is a combined road-rail bridge. Connecting lines Standard gauge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bundeswehr
The (, ''Federal Defence'') are the armed forces of the Germany, Federal Republic of Germany. The is divided into a military part (armed forces or ''Streitkräfte'') and a civil part, the military part consists of the four armed forces: German Army, German Navy, German Air Force and Cyber and Information Domain Service (Germany), Cyber and Information Domain Service, which are supported by the Bundeswehr Support Area. , the had a strength of 180,215 active-duty military personnel and 80,761 civilians, placing it among the 30 largest military forces in the world, and making it the second largest in the European Union behind French Armed Forces, France. In addition, the has approximately 34,600 reserve personnel (2024). With German military expenditures at $88.5 billion (2024), the is the fourth-highest-funded military in the world, though military expenditures have until recently remained low at an average at 1.5% of national GDP, well below the non-binding NATO targ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kiel Week
The Kiel Week () or Kiel Regatta is an annual sailing event in Kiel, the capital of Schleswig-Holstein, Germany. It is considered to be one of the largest sailing events globally, and also the largest summer festivals in Northern Europe, attracting millions of people every year from all over Germany and neighbouring countries. Together with the Trofeo Princesa Sofía, Semaine Olympique Française, and Allianz Regatta regattas, Kiel Week is part of the Sailing World Cup in the 2023 and 2024 seasons. Events Kiel Week is held annually in the last week in June, and opens officially on the preceding Saturday with the official ''Glaser'', followed by the ''Holstenbummel''. The "Soundcheck" is on the Friday before the official opening; it is a music festival across all the stages within the city. Kiel Week, ends with a large fireworks display at 11 p.m. on Sunday, fired from pontoons or the quays at the Howaldtswerke, visible all across the Bay of Kiel. There are also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1872 Baltic Sea Flood
The 1872 Baltic Sea flood (), often referred to as a storm flood, ravaged the Baltic Sea coast from Denmark to Pomerania, also affecting Sweden, during the night between 12 and 13 November 1872 and was, until then, the worst storm surge in the Baltic. The highest recorded peak water level was about 3.3 m above sea level (NN). Course In the days before the storm tide, a storm blew from the southwest across the Baltic that drove the sea towards Finland and '' Balticum''. The result was flooding there and extreme low water levels on the Danish-German coastlines. As a result, large quantities of water were able to flow into the western Baltic from the North Sea. The storm increased in strength, and changed direction. The winds now blew from the northeast, and drove the water masses back in a south-westerly direction. Because the water could only flow slowly back into the North Sea, huge waves caught coastal dwellers by surprise on the morning of 13 November 1872 and caused flo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frigate
A frigate () is a type of warship. In different eras, the roles and capabilities of ships classified as frigates have varied. The name frigate in the 17th to early 18th centuries was given to any full-rigged ship built for speed and maneuverability, intended to be used in scouting, escort and patrol roles. The term was applied loosely to ships varying greatly in design. In the second quarter of the 18th century, what is now generally regarded as the 'true frigate' was developed in France. This type of vessel was characterised by possessing only one armed deck, with an unarmed deck below it used for berthing the crew. Late in the 19th century (British and French prototypes were constructed in 1858), a type of powerful ironclad warships was developed, and because they had a single gun deck, the term 'frigate' was used to describe them. Later developments in ironclad ships rendered the 'frigate' designation obsolete and the term fell out of favour. During the Second World War ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ship Of The Line
A ship of the line was a type of naval warship constructed during the Age of Sail from the 17th century to the mid-19th century. The ship of the line was designed for the naval tactics in the Age of Sail, naval tactic known as the line of battle, which involved the two columns of opposing warships manoeuvering to volley fire with the naval cannon, cannons along their Broadside (naval), broadsides. In conflicts where opposing ships were both able to fire from their broadsides, the faction with more cannons firingand therefore more firepowertypically had an advantage. From the end of the 1840s, the introduction of steam engine, steam power brought less dependence on the wind in battle and led to the construction of propeller, screw-driven wooden-hulled ships of the line; a number of purely sail-powered ships were converted to this propulsion mechanism. However, the rise of the ironclad warship, ironclad frigate, starting in 1859, made steam-assisted ships of the line obsolete. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
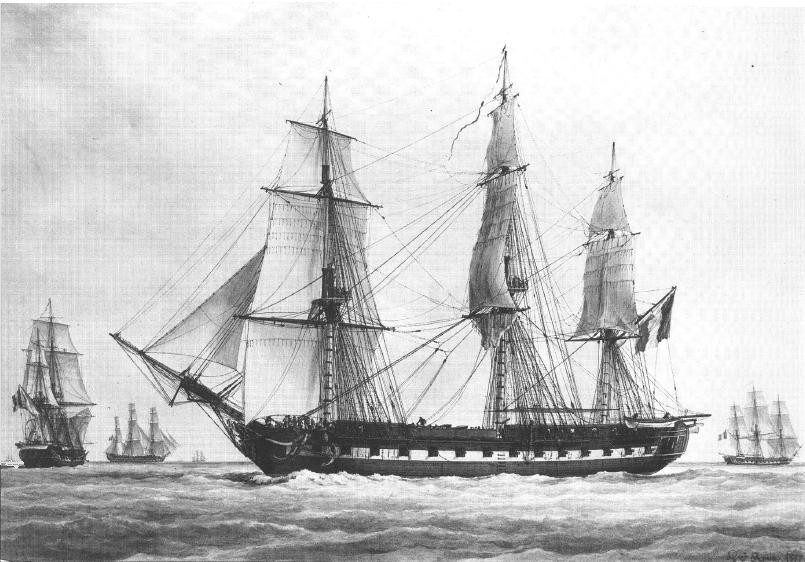
Battle Of Eckernförde
The Battle of Eckernförde was a Danish naval assault on Schleswig. The Danes were defeated and two of their ships were lost with the surviving crew being detained.Carsen Jensen: ''Vi, de druknede'' (oversatt av Mie Hidle), Forlaget Press, (2007), (2010) Background When the fighting resumed after the armistice of Malmö in 1849, the Danes attacked Sundeved and Schleswig. To support the offensive, the Danish Navy would carry out a diversionary attack on the town of Eckernförde and destroy the German coastal batteries there. A smaller force of 250 troops would also be put ashore to give the impression of a larger landing force. The German flanks were vulnerable to landings along the coasts of Schleswig and such a company could not be ignored by the Germans. Commander Frederik August Paludan was appointed commander of the operation. The Danish Squadron The Danish force assigned to the attack consisted of: *Ship of the line ''Christian VIII'' (84 guns) – Frederik Palu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lingua Franca
A lingua franca (; ; for plurals see ), also known as a bridge language, common language, trade language, auxiliary language, link language or language of wider communication (LWC), is a Natural language, language systematically used to make communication possible between groups of people who do not share a First language, native language or dialect, particularly when it is a third language that is distinct from both of the speakers' native languages. Linguae francae have developed around the world throughout human history, sometimes for commercial reasons (so-called "trade languages" facilitated trade), but also for cultural, religious, diplomatic and administrative convenience, and as a means of exchanging information between scientists and other scholars of different nationalities. The term is taken from the medieval Mediterranean Lingua Franca, a Romance languages, Romance-based pidgin language used especially by traders in the Mediterranean Basin from the 11th to the 19th c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toponym
Toponymy, toponymics, or toponomastics is the study of ''wikt:toponym, toponyms'' (proper names of places, also known as place names and geographic names), including their origins, meanings, usage, and types. ''Toponym'' is the general term for a proper name of any geographical feature, and full scope of the term also includes proper names of all cosmographical features. In a more specific sense, the term ''toponymy'' refers to an inventory of toponyms, while the discipline researching such names is referred to as ''toponymics'' or ''toponomastics''. Toponymy is a branch of onomastics, the study of proper names of all kinds. A person who studies toponymy is called ''toponymist''. Etymology The term ''toponymy'' comes from / , 'place', and / , 'name'. The ''Oxford English Dictionary'' records ''toponymy'' (meaning "place name") first appearing in English in 1876 in the context of geographical studies. Since then, ''toponym'' has come to replace the term ''place-name'' in profe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |