|
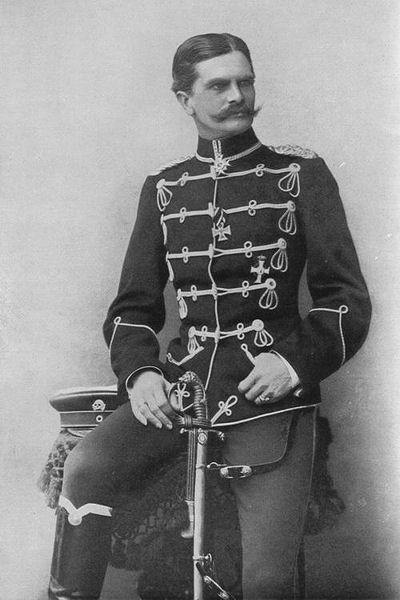
Eberhard Von Mackensen
Friedrich August Eberhard von Mackensen (24 September 1889 – 19 May 1969) was a German general and war criminal during World War II who served as commander of the 1st Panzer Army and the 14th Army. Following the war, Mackensen stood trial for war crimes before a British military tribunal in Italy where he was convicted and sentenced to death for his involvement in the Ardeatine massacre, in which hundreds of Italian civilians and political prisoners were shot. The sentence was later commuted and Mackensen was released in 1952. He died in West Germany in 1969. Early life Eberhard was born on 24 September 1889, in Bromberg, Kingdom of Prussia, German Empire, the fourth of five children to Field Marshal August von Mackensen and his wife Dorothea (née von Horn). Mackensen joined the Imperial German Army in 1906, where he became a '' Fahnenjunker'' (officer candidate) in the XVII Corps stationed in Danzig, and was promoted to lieutenant on 22 March 1910. Military career At t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bydgoszcz
Bydgoszcz is a city in northern Poland and the largest city in the historical region of Kuyavia. Straddling the confluence of the Vistula River and its bank (geography), left-bank tributary, the Brda (river), Brda, the strategic location of Bydgoszcz has made it an inland port and a vital centre for trade and transportation. With a city population of 339,053 as of December 2021, Bydgoszcz is the eighth-largest city in Poland. Today, it is the seat of Bydgoszcz County and one of the two capitals of the Kuyavian-Pomeranian Voivodeship as a seat of its centrally appointed governor, a voivode. Bydgoszcz metropolitan area comprising the city and several adjacent communities is inhabited by half a million people, and forms a part of an extended polycentric Bydgoszcz-Toruń metropolitan area with a population of approximately 0.8 million inhabitants. Since the Middle Ages, Bydgoszcz served as a Royal city in Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, royal city of the Crown of the Kingdom of Po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Invasion Of Poland
The invasion of Poland, also known as the September Campaign, Polish Campaign, and Polish Defensive War of 1939 (1 September – 6 October 1939), was a joint attack on the Second Polish Republic, Republic of Poland by Nazi Germany, the Slovak Republic (1939–1945), Slovak Republic, and the Soviet Union, which marked the beginning of World War II. The German invasion began on 1 September 1939, one week after the signing of the Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact between Germany and the Soviet Union, and one day after the Supreme Soviet of the Soviet Union had approved the pact. The Soviet invasion of Poland, Soviets invaded Poland on 17 September. The campaign ended on 6 October with Germany and the Soviet Union dividing and annexing the whole of Poland under the terms of the German–Soviet Frontier Treaty. The aim of the invasion was to disestablish Poland as a sovereign country, with its citizens destined for The Holocaust, extermination. German and Field Army Bernolák, Slovak forces ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Née
The birth name is the name of the person given upon their birth. The term may be applied to the surname, the given name or to the entire name. Where births are required to be officially registered, the entire name entered onto a births register or birth certificate may by that fact alone become the person's legal name. The assumption in the Western world is often that the name from birth (or perhaps from baptism or ''brit milah'') will persist to adulthood in the normal course of affairs—either throughout life or until marriage. Some possible changes concern middle names, diminutive forms, changes relating to parental status (due to one's parents' divorce or adoption by different parents), and changes related to gender transition. Matters are very different in some cultures in which a birth name is for childhood only, rather than for life. Maiden and married names The terms née (feminine) and né (masculine; both pronounced ; ), Glossary of French expressions in Englis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Italy
Italy, officially the Italian Republic, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe, Western Europe. It consists of Italian Peninsula, a peninsula that extends into the Mediterranean Sea, with the Alps on its northern land border, as well as List of islands of Italy, nearly 800 islands, notably Sicily and Sardinia. Italy shares land borders with France to the west; Switzerland and Austria to the north; Slovenia to the east; and the two enclaves of Vatican City and San Marino. It is the List of European countries by area, tenth-largest country in Europe by area, covering , and the third-most populous member state of the European Union, with nearly 59 million inhabitants. Italy's capital and List of cities in Italy, largest city is Rome; other major cities include Milan, Naples, Turin, Palermo, Bologna, Florence, Genoa, and Venice. The history of Italy goes back to numerous List of ancient peoples of Italy, Italic peoples—notably including the ancient Romans, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
War Crimes
A war crime is a violation of the laws of war that gives rise to individual criminal responsibility for actions by combatants in action, such as intentionally killing civilians or intentionally killing prisoners of war, torture, taking hostages, unnecessarily destroying civilian property, deception by perfidy, wartime sexual violence, pillaging, and for any individual that is part of the command structure who orders any attempt to committing mass killings (including genocide or ethnic cleansing), the granting of no quarter despite surrender, the conscription of children in the military, and flouting the legal distinctions of proportionality and military necessity. The formal concept of war crimes emerged from the codification of the customary international law that applied to warfare between sovereign states, such as the Lieber Code (1863) of the Union Army in the American Civil War and the Hague Conventions of 1899 and 1907 for international war. In the afterm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hans Georg Von Mackensen
Hans Georg von Mackensen (26 January 1883 – 28 September 1947) was a German diplomat who served at different stages as "State Secretary" at the Foreign Ministry, German ambassador in Rome and a SS Group Leader (''"Gruppenführer"''). Life Provenance and early years Mackensen came from an established military family. His father, August von Mackensen (1849–1945), was eventually, in 1915, promoted to the rank of Field Marshal: Even after 1918, August von Mackensen would remain an unapologetic high-profile monarchist traditionalist who in 1941, despite his advanced age and the difficulties of travelling in war time, made his way to Doorn (near Utrecht) where, dressed in his full military uniform from the imperial years, he attended the funeral of the former German emperor. Hans Georg von Mackensen's mother, born Dorothea von Horn (1854–1905), also came from a family of minor aristocrats. His younger brother, Eberhard von Mackensen became an army general. As a child Hans ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
August Von Mackensen
Anton Ludwig Friedrich August Mackensen (ennobled as von Mackensen in 1899; 6 December 1849 – 8 November 1945), was a German field marshal. He commanded Army Group Mackensen during World War I (1914–1918) and became one of the German Empire's most prominent and competent military leaders. After the armistice of 11 November 1918, the victorious Allies interned Mackensen in Serbia for a year. In 1920, he retired from the army. In 1933 Hermann Göring made him a Prussian state councillor. During the Nazi era (1933–1945), Mackensen remained a committed monarchist and sometimes appeared at official functions in his World War I uniform. Senior Nazi Party members suspected him of disloyalty, but nothing was proven against him. Early life and career Mackensen was born in Haus Leipnitz, near the village of Dahlenberg (today part of Trossin) in the Prussian Province of Saxony, to Ludwig and Marie Louise Mackensen. His father, an administrator of agricultural enterprises, sen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Knight's Cross Of The Iron Cross With Oak Leaves
The Knight's Cross of the Iron Cross (), or simply the Knight's Cross (), and its variants, were the highest awards in the military and paramilitary forces of Nazi Germany during World War II. While it was lower in precedence than the Grand Cross of the Iron Cross, the Grand Cross was never awarded at-large to Nazi German military and paramilitary forces. The Grand Cross's sole award was made to '' Reichsmarschall'' Hermann Göring in September 1939, making the Knight's Cross (specifically, the Knight's Cross with Golden Oak Leaves, Swords, and Diamonds grade) the ''de facto'' highest award among the decorations of Nazi Germany. The Knight's Cross was awarded for a wide range of reasons and across all ranks, from a senior commander for skilled leadership of his troops in battle to a low-ranking soldier for a single act of military valour. Presentations were made to members of the three military branches of the : the (army), the (navy) and the (air force), as well as the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
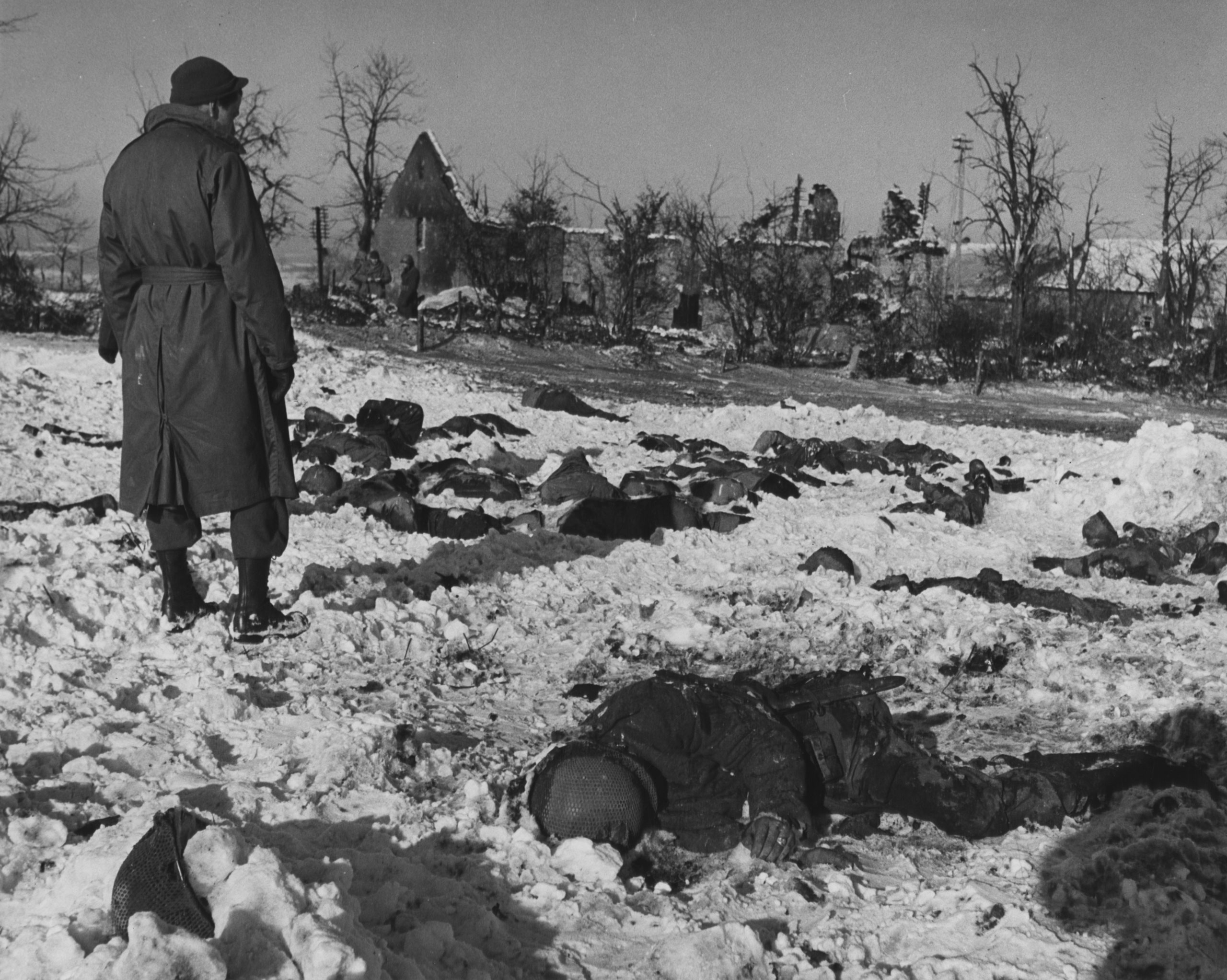
Operation Diadem
Operation Diadem, also referred to as the Fourth Battle of Monte Cassino or, in Canada, the Battle of the Liri Valley, was an offensive operation undertaken by the Allies of World War II ( U.S. Fifth Army and British Eighth Army) in May 1944, as part of the Italian Campaign of World War II. ''Diadem'' was supported by air attacks called Operation Strangle. The opposing force was the German 10th Army. The object of ''Diadem'' was to break the German defenses on the Gustav Line (the western half of the Winter Line) and open up the Liri Valley, the main route to Rome. General Sir Harold Alexander, Commander-in-Chief of the Allied Armies in Italy, planned ''Diadem'' to coordinate roughly with the invasion of Normandy, so that German forces would be tied down in Italy, and could not be redeployed to France. Four corps were employed in the attack. From right to left these were the Polish II Corps and the British XIII Corps, of the Eighth Army, and the French Corps (including ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Monte Cassino
The Battle of Monte Cassino, also known as the Battle for Rome, was a series of four military assaults by the Allies of World War II, Allies against Nazi Germany, German forces in Kingdom of Italy, Italy during the Italian Campaign (World War II), Italian Campaign of World War II. The objective was to break through the Winter Line and facilitate an advance towards Rome. In the beginning of 1944, the western half of the Winter Line was anchored by German forces holding the Rapido (river), Rapido-Gari (river), Gari, Liri, and Garigliano valleys and several surrounding peaks and ridges. Together, these features formed the Winter Line, Gustav Line. Monte Cassino, a historic hilltop abbey founded in 529 by Benedict of Nursia, dominated the nearby town of Cassino and the entrances to the Liri and Rapido valleys. Lying in a protected historic zone, it had been left unoccupied by the Germans, although they manned some positions set into the slopes below the abbey's walls. Repeated art ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
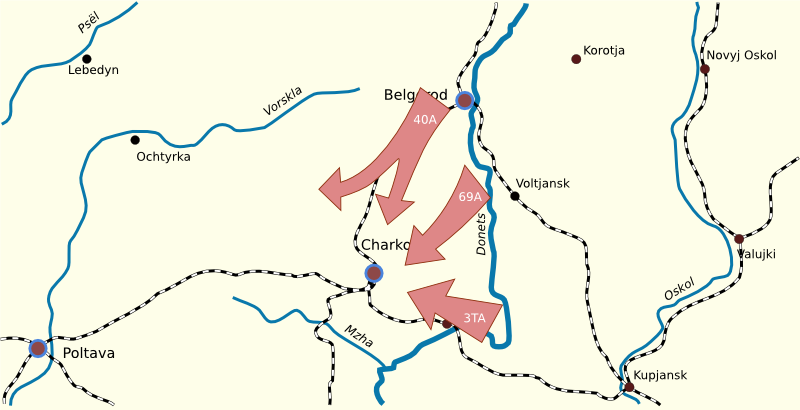
Third Battle Of Kharkov
The Third Battle of Kharkov was a series of battles on the Eastern Front (World War II), Eastern Front of World War II, undertaken by Nazi Germany's Army Group South against the Soviet Red Army, around the city of Kharkov between 19 February and 15 March 1943. Known to the German side as the Donets Campaign, and in the Soviet Union as the Donbass and Kharkov operations, the German counterstrike led to the recapture of the cities of Kharkov and Belgorod. As the German 6th Army (Wehrmacht), 6th Army was encircled in the Battle of Stalingrad, the Red Army undertook a series of wider attacks against the rest of Army Group South. These culminated on 2 January 1943 when the Red Army launched Operation Star and Operation Gallop, which between January and early February broke German defenses and led to the Soviet recapture of Kharkov, Belgorod, Kursk, as well as Voroshilovgrad and Izium. These victories caused participating Soviet units to over-extend themselves. Freed on 2 February ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |