|
East Central German
East Central German or East Middle German () is the eastern Central German language and is part of High German. Present-day Standard German as a High German variant, has actually developed from a compromise of East Central (especially Upper Saxon that was promoted by Johann Christoph Gottsched) and East Franconian German. East Central German dialects are mainly spoken in Central Germany and parts of Brandenburg, and were formerly also spoken in Silesia and Bohemia. Dialects East Central German is spoken in large parts of what is today known as the cultural area of Central Germany (''Mitteldeutschland''). It comprises according to Glottolog: * Central East Middle German ** High Prussian (''Hochpreußisch'') (nearly extinct) ** Thuringian (''Thüringisch'') ** Upper Saxon (''Obersächsisch'') *** ''Anhaltisch'' *** ''Meißnisch'' *** ''Osterländisch'' *** ''Westlausitzisch'' *** ''Erzgebirgisch'' ** ''Nordobersäschisch-Südmärkisch'' * Schlesisch–Wilmesau ** Silesian ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thuringia
Thuringia (; officially the Free State of Thuringia, ) is one of Germany, Germany's 16 States of Germany, states. With 2.1 million people, it is 12th-largest by population, and with 16,171 square kilometers, it is 11th-largest in area. Erfurt is the capital and largest city. Other cities include Jena, Gera and Weimar. Thuringia is bordered by Bavaria, Hesse, Lower Saxony, Saxony, and Saxony-Anhalt. It has been known as "the green heart of Germany" () from the late 19th century due to its broad, dense forest. Most of Thuringia is in the Saale drainage basin, a bank (geography), left-bank tributary of the Elbe. Thuringia is home to the Rennsteig, Germany's best-known hiking, hiking trail. Its winter resort of Oberhof, Germany, Oberhof makes it a well-equipped winter sports destination – half of Germany's 136 Winter Olympics, Winter Olympic gold medals had been won by Thuringian athletes as of 2014. Thuringia was favoured by or was the birthplace of three key intellectu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flight And Expulsion Of Germans (1944–1950)
During the later stages of World War II and the post-war period, Reichsdeutsche (German citizens) and Volksdeutsche (ethnic Germans living outside the Nazi state) fled and were expelled from various Eastern Europe, Eastern and Central European countries, including Czechoslovakia, and from the former German provinces of Province of Lower Silesia, Lower and Province of Upper Silesia, Upper Silesia, East Prussia, and the eastern parts of Province of Brandenburg, Brandenburg (Neumark) and Province of Pomerania (1815–1945), Pomerania (Farther Pomerania), which were annexed by Provisional Government of National Unity of Poland and by the Soviet Union. The idea to expel the Germans from the annexed territories had been proposed by Winston Churchill, in conjunction with the Polish government-in-exile, Polish and Czechoslovak government-in-exile, Czechoslovak governments-in-exile in London since at least 1942. Tomasz Arciszewski, the Prime ministers of the Polish government-in-exile, P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
West Central German
West Central German () belongs to the Central German, Central, High German languages, High German dialect family of German language, German. It includes the following sub-families: * Central Franconian () ** Ripuarian language, Ripuarian (), spoken in North Rhine-Westphalia (including ) and German-speaking Community of Belgium, German-speaking Belgium and a small edge of the south of the Limburg (Netherlands), Dutch province of Limbourg. ** Moselle Franconian dialects, Moselle Franconian (; ) in Rhineland-Palatinate, Saarland and France *** Luxembourgish language, Luxembourgish (; ; or ) in Luxembourg, Belgium and France *** Hunsrik (), spoken in Brazil and derived from the dialect of Moselle Franconian * Rhine Franconian dialects, Rhine Franconian (; ) ** Palatine German language, Palatinate Franconian (; ), spoken in Rhineland-Palatinate *** Lorraine Franconian (; ) in the French region of Lorraine *** Bukovina Germans, Bukovina German () in Bukovina (extinct) *** Pennsylvani ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
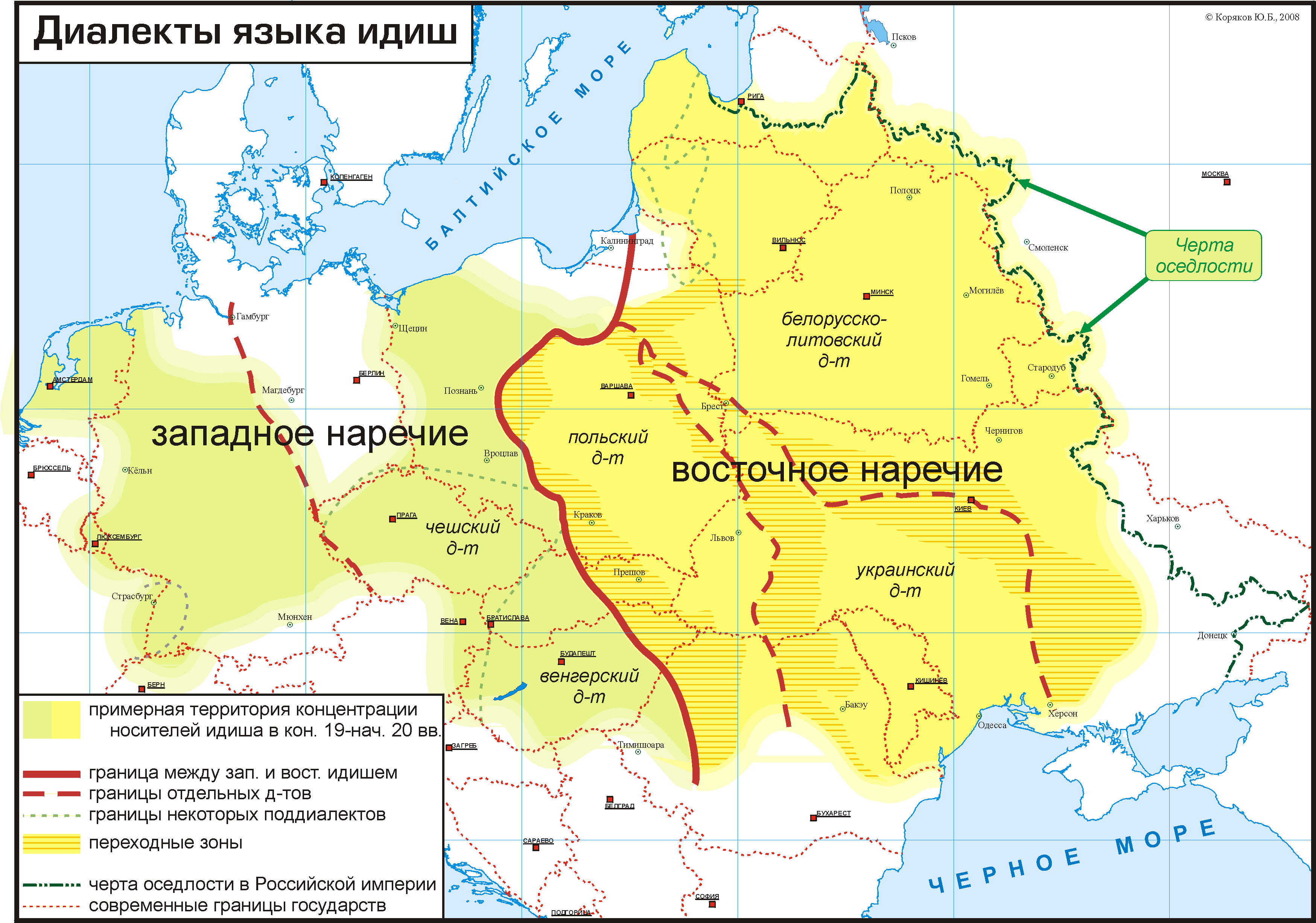
Western Yiddish
Yiddish dialects are varieties of the Yiddish language and are divided according to the region in Europe where each developed its distinctiveness. Linguistically, Yiddish is divided in distinct Eastern and Western dialects. While the Western dialects mostly died out in the 19th-century due to Jewish language assimilation into mainstream culture, the Eastern dialects were very vital until most of Eastern European Jewry was wiped out by the Shoah, called the Khurbn in Yiddish. The Northeastern dialects of Eastern Yiddish were dominant in 20th-century Yiddish culture and academia, but in the 21st-century, the Southern dialects of Yiddish that are preserved by many Hasidic communities have become the most commonly spoken form of Yiddish. Varieties Yiddish dialects are generally grouped into either Western Yiddish and Eastern Yiddish. Western Yiddish developed from the 9th century in Western-Central Europe, in the region which was called Ashkenaz by Jews, while Eastern Yiddish deve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yiddish
Yiddish, historically Judeo-German, is a West Germanic language historically spoken by Ashkenazi Jews. It originated in 9th-century Central Europe, and provided the nascent Ashkenazi community with a vernacular based on High German fused with many elements taken from Hebrew language, Hebrew (notably Mishnaic Hebrew, Mishnaic) and to some extent Aramaic. Most varieties of Yiddish include elements of Slavic languages and the vocabulary contains traces of Romance languages.Aram Yardumian"A Tale of Two Hypotheses: Genetics and the Ethnogenesis of Ashkenazi Jewry".University of Pennsylvania. 2013. Yiddish has traditionally been written using the Hebrew alphabet. Prior to World War II, there were 11–13 million speakers. 85% of the approximately 6 million Jews who were murdered in the Holocaust were Yiddish speakers,Solomon Birnbaum, ''Grammatik der jiddischen Sprache'' (4., erg. Aufl., Hamburg: Buske, 1984), p. 3. leading to a massive decline in the use of the language. Jewish ass ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eastern Yiddish
Yiddish dialects are varieties of the Yiddish language and are divided according to the region in Europe where each developed its distinctiveness. Linguistically, Yiddish is divided in distinct Eastern and Western dialects. While the Western dialects mostly died out in the 19th-century due to Jewish language assimilation into mainstream culture, the Eastern dialects were very vital until most of Eastern European Jewry was wiped out by the Shoah, called the Khurbn in Yiddish. The Northeastern dialects of Eastern Yiddish were dominant in 20th-century Yiddish culture and academia, but in the 21st-century, the Southern dialects of Yiddish that are preserved by many Hasidic communities have become the most commonly spoken form of Yiddish. Varieties Yiddish dialects are generally grouped into either Western Yiddish and Eastern Yiddish. Western Yiddish developed from the 9th century in Western-Central Europe, in the region which was called Ashkenaz by Jews, while Eastern Yiddish deve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zipser German
Zipser German (German: Zipserisch or Zipserdeutsch; Hungarian: ''szepességi szász nyelv'' or ''cipszer nyelv''; ) is a dialect of the German language which developed in the Upper Zips region (, ) of what is now northeastern Slovakia among people who settled there from present-day central Germany and the northern Lower Rhine river (e.g. contemporary Flanders and Luxembourg) beginning in the 13th century (or during the High Middle Ages as part of the Ostsiedlung).Karl Julius Schröer, ''Die deutschen Mundarten des ungrischen Berglandes'' (1864) These German settlers are collectively known as Zipser Germans in Central and Eastern Europe and part of the Carpathian Germans () in their native Slovakia. The Lower Zips was inhabited by other Germans who spoke a different dialect called "Gründlerisch". The Upper Zipser German dialect is also close or related to the Transylvanian Saxon dialect () of the Transylvanian Saxons (). The Zipser German dialect has been spoken for centurie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thuringian Dialect
Thuringian is an East Central German dialect group spoken in much of the modern German Free State of Thuringia north of the Rennsteig ridge, southwestern Saxony-Anhalt and adjacent territories of Hesse and Bavaria. It is close to Upper Saxon spoken mainly in the state of Saxony, therefore both are also regarded as one Thuringian-Upper Saxon dialect group. Thuringian dialects are among the Central German dialects with the highest number of speakers. History Thuringian emerged during the medieval German '' Ostsiedlung'' migration from about 1100, when settlers from Franconia ( Main Franconia), Bavaria, Saxony, and Flanders settled in the areas east of the Saale River previously inhabited by Polabian Slavs. Characteristics The Thuringian dialect is characterized by a rounding of the vowels, the weakening of consonants of Standard German (the lenition of the consonants "p," "t," and "k"), a marked difference in the pronunciation of the "g" sound (which is most common in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glottolog
''Glottolog'' is an open-access online bibliographic database of the world's languages. In addition to listing linguistic materials ( grammars, articles, dictionaries) describing individual languages, the database also contains the most up-to-date language affiliations based on the work of expert linguists. Glottolog was first developed and maintained at the Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Anthropology in Leipzig, Germany, and between 2015 and 2020 at the Max Planck Institute of Geoanthropology in Jena, Germany. Its main curators include Harald Hammarström and Martin Haspelmath. Overview Sebastian Nordhoff and Harald Hammarström established the Glottolog/Langdoc project in 2011. The creation of ''Glottolog'' was partly motivated by the lack of a comprehensive language bibliography, especially in ''Ethnologue''. Glottolog provides a catalogue of the world's languages and language families and a bibliography on individual languages. It differs from ''Ethnologue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bohemia
Bohemia ( ; ; ) is the westernmost and largest historical region of the Czech Republic. In a narrow, geographic sense, it roughly encompasses the territories of present-day Czechia that fall within the Elbe River's drainage basin, but historically it could also refer to a wider area consisting of the Lands of the Bohemian Crown ruled by the List of Bohemian monarchs, Bohemian kings, including Moravia and Czech Silesia, in which case the smaller region is referred to as Bohemia Proper as a means of distinction. Bohemia became a part of Great Moravia, and then an independent principality, which became a Kingdom of Bohemia, kingdom in the Holy Roman Empire. This subsequently became a part of the Habsburg monarchy and the Austrian Empire. After World War I and the establishment of an History of Czechoslovakia (1918–1938), independent Czechoslovak state, the whole of Bohemia became a part of Czechoslovakia, defying claims of the German-speaking inhabitants that regions with German ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Germany (cultural Area)
Central Germany ( ) is an economic and cultural region in Germany. Its exact borders depend on context, but it is often defined as being a region within the federal states of Saxony, Thuringia and Saxony-Anhalt, or a smaller part of this region, such as the metropolitan area of Leipzig and Halle plus the surrounding counties. The name dates from the German Empire, when the region was approximately in the centre of the country. Since the German Empire's eastern territories became part of Poland and Russia in the aftermath of World War II, "Central Germany" has been located east of the centre of the country, but the name is still often used in business, media and by the Central German Metropolitan Region. Against this background, the term is not or no longer to be understood as a geographic term. History Historically also including most of Hesse, parts of Franconia and the south of Lower Saxony, the region is described as an area south of the linguistic Benrath line where C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
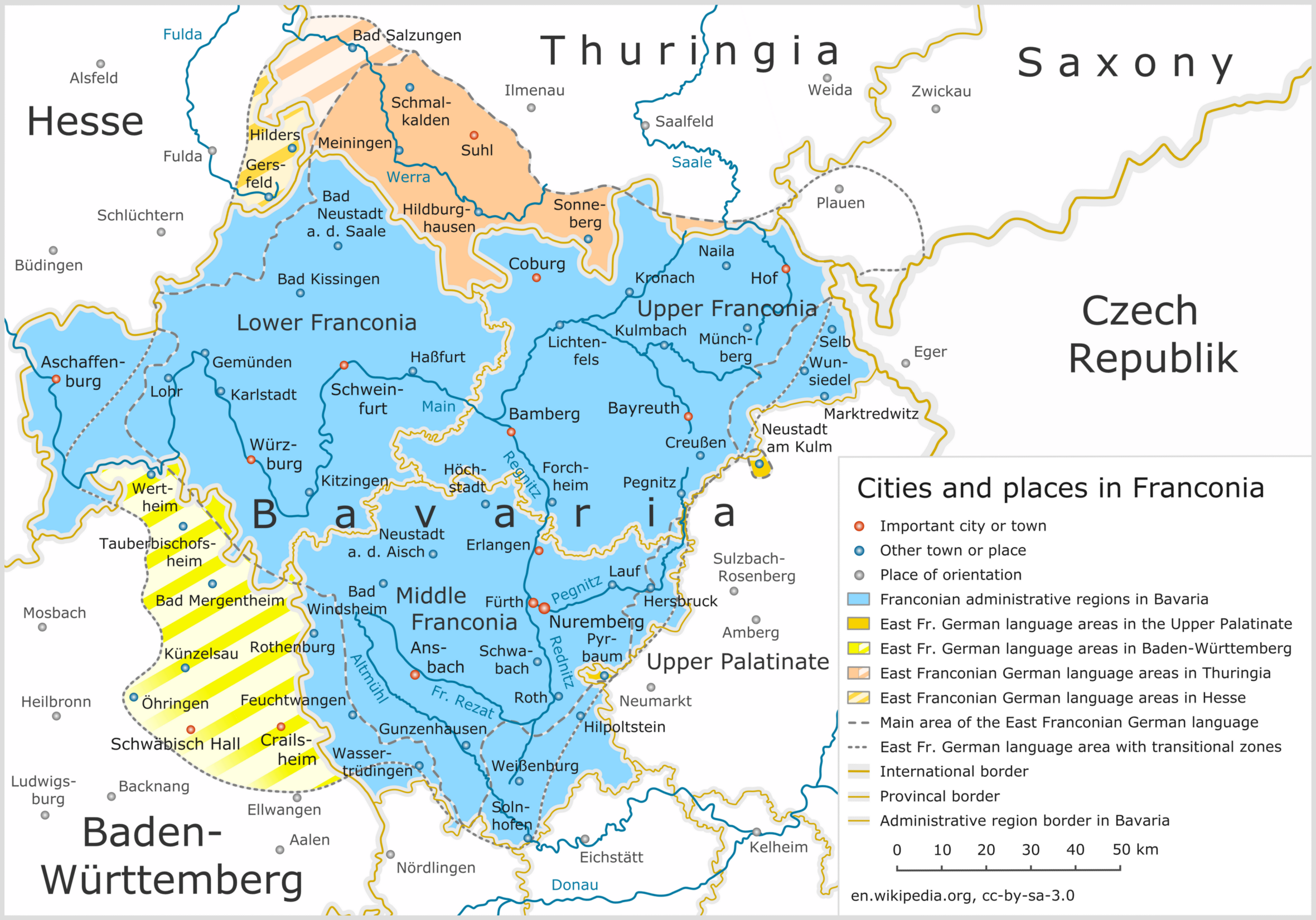
East Franconian German
East Franconian ( ), usually referred to as Franconian (' ) in German, is a dialect spoken in Franconia, the northern part of the federal state of Bavaria and other areas in Germany around Nuremberg, Bamberg, Coburg, Würzburg, Hof, Bayreuth, Meiningen, Bad Mergentheim, and Crailsheim. The major subgroups are ' (spoken in Lower Franconia and southern Thuringia), ' (spoken in Upper and Middle Franconia) and ' (spoken in some parts of Middle Franconia and Hohenlohe). Until the wholesale expulsion of Germans from Bohemia, the dialect was also spoken around Saaz (today: Žatec). In the transitional area between Rhine Franconian in the northwest and the Austro-Bavarian dialects in the southeast, East Franconian has elements of Central German and Upper German. The same goes only for South Franconian German in adjacent Baden-Württemberg Baden-Württemberg ( ; ), commonly shortened to BW or BaWü, is a states of Germany, German state () in Southwest Germany, east of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |