|
Earthquake Swarms
In seismology, an earthquake swarm is a sequence of seismic events occurring in a local area within a relatively short period. The time span used to define a swarm varies, but may be days, months, or years. Such an energy release is different from the situation when a major earthquake (main shock) is followed by a series of aftershocks: in earthquake swarms, no single earthquake in the sequence is obviously the main shock. In particular, a cluster of aftershocks occurring after a mainshock ''is not'' a swarm. History and generalities The Ore Mountains (Erzgebirge), which form the border between the Czech Republic and Germany, western Bohemia and the Vogtland region, have been known since the 16th century as being prone to frequent earthquake swarms, which typically last a few weeks to a few months. In 1899, Austrian geologist Josef Knett, while studying a swarm of about a hundred events felt in western Bohemia/Vogtland between January and February 1824, coined the noun ''Schwar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1964 Niigata Earthquake
The 1964 Niigata earthquake () struck at 13:01 local time (04:01 UTC) on 16 June with a magnitude of either 7.5 or 7.6. The epicenter was on the continental shelf off the northwest coast of Honshu, Japan, in Niigata Prefecture, about north of the city of Niigata. The earthquake caused liquefaction over large parts of the city. Geology The northwestern side of Honshu lies on the southeastern margin of the Sea of Japan, an area of oceanic crust created by back-arc spreading from the late Oligocene to middle Miocene. The extensional tectonics associated with the spreading formed a series of N–S trending extensional faults and associated basins. Currently the area is being deformed by contractional tectonics, causing inversion of these earlier basins, forming anticlinal structures. The earthquake is thought to have occurred due to reverse movement on one of these reactivated faults. Damage There were 3,534 houses destroyed and a further 11,000 were damaged. This level of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crust (geology)
In geology, the crust is the outermost solid shell of a planet, dwarf planet, or natural satellite. It is usually distinguished from the underlying mantle by its chemical makeup; however, in the case of icy satellites, it may be defined based on its phase (solid crust vs. liquid mantle). The crusts of Earth, Mercury, Venus, Mars, Io, the Moon and other planetary bodies formed via igneous processes and were later modified by erosion, impact cratering, volcanism, and sedimentation. Most terrestrial planets have fairly uniform crusts. Earth, however, has two distinct types: continental crust and oceanic crust. These two types have different chemical compositions and physical properties and were formed by different geological processes. Types of crust Planetary geologists divide crust into three categories based on how and when it formed. Primary crust / primordial crust This is a planet's "original" crust. It forms from solidification of a magma ocean. Toward the end o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scotland
Scotland is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It contains nearly one-third of the United Kingdom's land area, consisting of the northern part of the island of Great Britain and more than 790 adjacent Islands of Scotland, islands, principally in the archipelagos of the Hebrides and the Northern Isles. To the south-east, Scotland has its Anglo-Scottish border, only land border, which is long and shared with England; the country is surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean to the north and west, the North Sea to the north-east and east, and the Irish Sea to the south. The population in 2022 was 5,439,842. Edinburgh is the capital and Glasgow is the most populous of the cities of Scotland. The Kingdom of Scotland emerged as an independent sovereign state in the 9th century. In 1603, James VI succeeded to the thrones of Kingdom of England, England and Kingdom of Ireland, Ireland, forming a personal union of the Union of the Crowns, three kingdo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
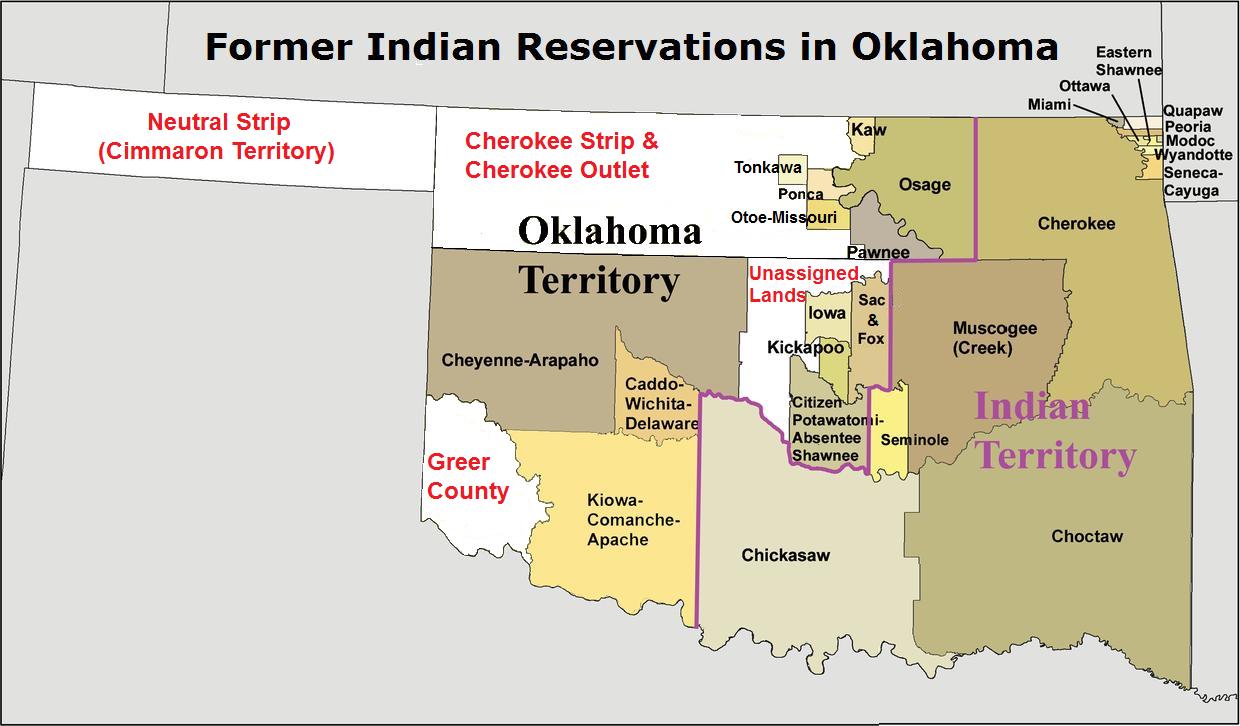
Oklahoma
Oklahoma ( ; Choctaw language, Choctaw: , ) is a landlocked U.S. state, state in the South Central United States, South Central region of the United States. It borders Texas to the south and west, Kansas to the north, Missouri to the northeast, Arkansas to the east, New Mexico to the west, and Colorado to the northwest. Partially in the western extreme of the Upland South, it is the List of U.S. states and territories by area, 20th-most extensive and the List of U.S. states and territories by population, 28th-most populous of the 50 United States. Its residents are known as Oklahomans and its capital and largest city is Oklahoma City. The state's name is derived from the Choctaw language, Choctaw words , 'people' and , which translates as 'red'. Oklahoma is also known informally by its List of U.S. state and territory nicknames, nickname, "The Sooner State", in reference to the Sooners, American pioneer, American settlers who staked their claims in formerly American Indian-o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nevada
Nevada ( ; ) is a landlocked state in the Western United States. It borders Oregon to the northwest, Idaho to the northeast, California to the west, Arizona to the southeast, and Utah to the east. Nevada is the seventh-most extensive, the 32nd-most populous, and the ninth-least densely populated U.S. state. Nearly three-quarters of Nevada's population live in Clark County, which contains the Las Vegas–Paradise metropolitan area, including three of the state's four largest incorporated cities. Nevada's capital is Carson City. Las Vegas is the largest city in the state. Nevada is officially known as the "Silver State" because of the importance of silver to its history and economy. It is also known as the "Battle Born State" because it achieved statehood during the Civil War (the words "Battle Born" also appear on its state flag); due to the presidency of Abraham Lincoln, the Union benefited immensely from the support of newly awarded statehood by the infusion of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plate Tectonics
Plate tectonics (, ) is the scientific theory that the Earth's lithosphere comprises a number of large tectonic plates, which have been slowly moving since 3–4 billion years ago. The model builds on the concept of , an idea developed during the first decades of the 20th century. Plate tectonics came to be accepted by Earth science, geoscientists after seafloor spreading was validated in the mid-to-late 1960s. The processes that result in plates and shape Earth's crust are called ''tectonics''. Tectonic plates also occur in other planets and moons. Earth's lithosphere, the rigid outer shell of the planet including the crust (geology), crust and upper mantle, is fractured into seven or eight major plates (depending on how they are defined) and many minor plates or "platelets". Where the plates meet, their relative motion determines the type of plate boundary (or fault (geology), fault): , , or . The relative movement of the plates typically ranges from zero to 10 cm annu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vosges
The Vosges ( , ; ; Franconian and ) is a range of medium mountains in Eastern France, near its border with Germany. Together with the Palatine Forest to the north on the German side of the border, they form a single geomorphological unit and low mountain range of around in area. It runs in a north-northeast direction from the Burgundian Gate (the Belfort– Ronchamp– Lure line) to the Börrstadt Basin (the Winnweiler– Börrstadt– Göllheim line), and forms the western boundary of the Upper Rhine Plain. The Grand Ballon is the highest peak at , followed by the Storkenkopf (), and the Hohneck ().IGN maps available oGéoportail/ref> Geography Geographically, the Vosges Mountains are wholly in France, far above the Col de Saverne separating them from the Palatinate Forest in Germany. The latter area logically continues the same Vosges geologic structure but traditionally receives this different name for historical and political reasons. From 1871 to 1918 the Vos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrothermal Circulation
Hydrothermal circulation in its most general sense is the circulation of hot water (Ancient Greek ὕδωρ, ''water'',Liddell, H.G. & Scott, R. (1940). ''A Greek-English Lexicon. revised and augmented throughout by Sir Henry Stuart Jones. with the assistance of. Roderick McKenzie.'' Oxford: Clarendon Press. and θέρμη, ''heat'' ). Hydrothermal circulation occurs most often in the vicinity of sources of heat within the Earth's Crust (geology), crust. In general, this occurs near volcanic activity, but can occur in the shallow to mid crust along deeply penetrating fault irregularities or in the deep crust related to the intrusion of granite, or as the result of orogeny or metamorphism. Hydrothermal circulation often results in Hydrothermal mineral deposit, hydrothermal mineral deposits. Seafloor hydrothermal circulation Hydrothermal circulation in the ocean, oceans is the passage of the water through mid-oceanic ridge systems. The term includes both the circulation of the well- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quaternary
The Quaternary ( ) is the current and most recent of the three periods of the Cenozoic Era in the geologic time scale of the International Commission on Stratigraphy (ICS), as well as the current and most recent of the twelve periods of the Phanerozoic eon. It follows the Neogene Period and spans from 2.58 million years ago to the present. The Quaternary Period is divided into two epochs: the Pleistocene (2.58 million years ago to 11.7 thousand years ago) and the Holocene (11.7 thousand years ago to today); a proposed third epoch, the Anthropocene, was rejected in 2024 by IUGS, the governing body of the ICS. The Quaternary is typically defined by the Quaternary glaciation, the cyclic growth and decay of continental ice sheets related to the Milankovitch cycles and the associated climate and environmental changes that they caused. Research history In 1759 Giovanni Arduino proposed that the geological strata of northern Italy could be divided into four succ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iceland
Iceland is a Nordic countries, Nordic island country between the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic and Arctic Oceans, on the Mid-Atlantic Ridge between North America and Europe. It is culturally and politically linked with Europe and is the region's westernmost and most list of countries and dependencies by population density, sparsely populated country. Its Capital city, capital and largest city is Reykjavík, which is home to about 36% of the country's roughly 380,000 residents (excluding nearby towns/suburbs, which are separate municipalities). The official language of the country is Icelandic language, Icelandic. Iceland is on a rift between Plate tectonics, tectonic plates, and its geologic activity includes geysers and frequent Types of volcanic eruptions, volcanic eruptions. The interior consists of a volcanic plateau with sand and lava fields, mountains and glaciers, and many Glacial stream, glacial rivers flow to the sea through the Upland and lowland, lowlands. Iceland i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
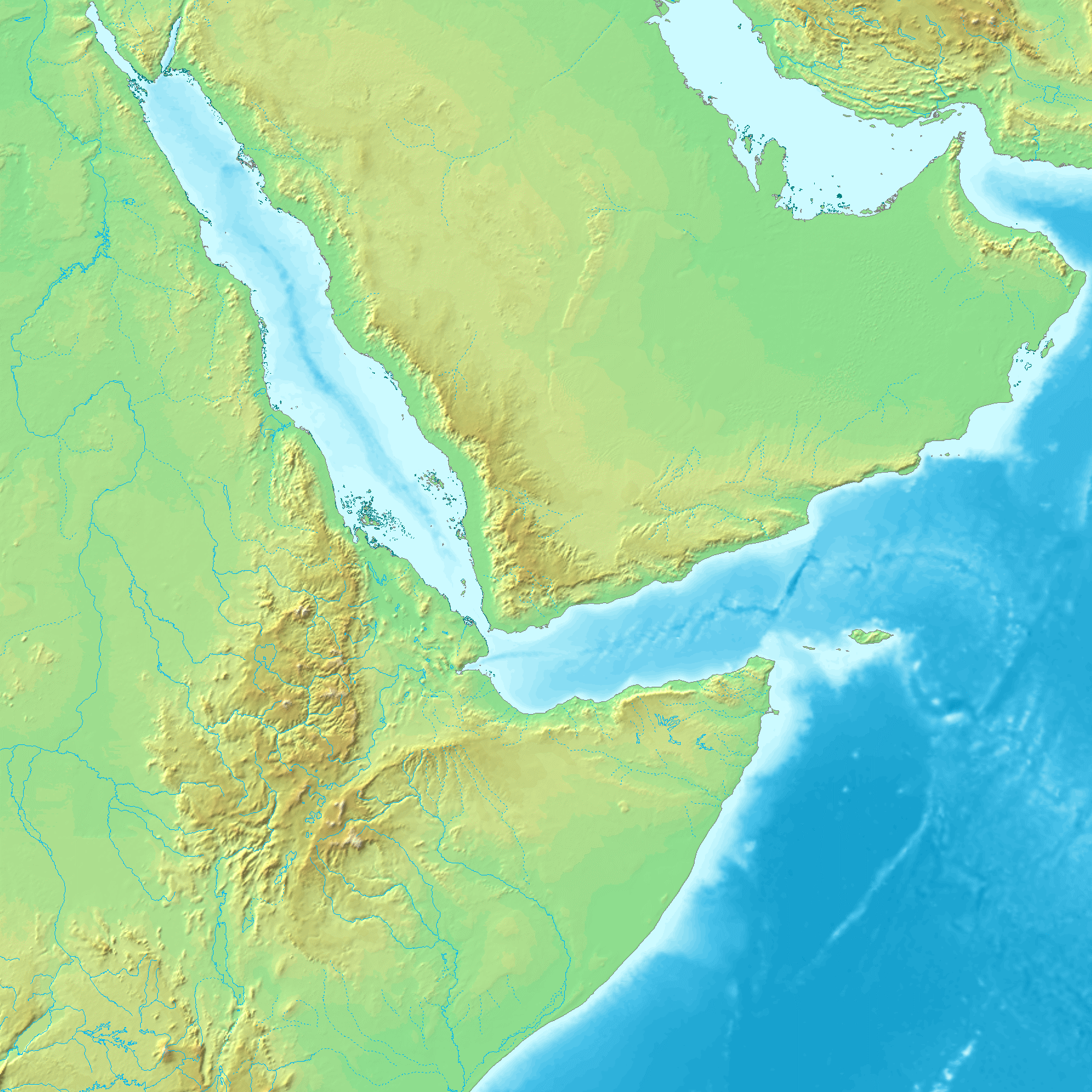
Afar Triangle
The Afar Triangle (also called the Afar Depression) is a geological depression caused by the Afar triple junction, which is part of the Great Rift Valley in East Africa. The region has disclosed fossil specimens of the very earliest hominins; that is, the earliest of the human clade, and it is thought by some paleontologists to be the cradle of the evolution of humans. The Depression overlaps the borders of Eritrea, Djibouti and the entire Afar Region of Ethiopia; and it contains the lowest point in Africa, Lake Assal, Djibouti, at below sea level. The Awash River is the main waterflow into the region, but it runs dry during the annual dry season, and ends as a chain of saline lakes. The northern part of the Afar Depression is also known as the Danakil Depression. The lowlands are affected by heat, drought, and minimal air circulation, and contain the hottest places (year-round average temperatures) of anywhere on Earth. The Afar Triangle is bordered as follows (see the topo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |