|
EP-B2
Endoprotease B, isoform 2 (EP-B2) is a cysteine protease found in barley. In studies, it has shown promise as a possible therapeutic for coeliac disease. Aspergillopepsin from ''Aspergillus niger ''Aspergillus niger'' is a mold classified within the ''Nigri'' section of the ''Aspergillus'' genus. The ''Aspergillus'' genus consists of common molds found throughout the environment within soil and water, on vegetation, in fecal matter, on de ...'' has been shown to enhance the effects of EP-B2. References Further reading * * * * * EC 3.4.22 {{enzyme-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coeliac Disease
Coeliac disease (British English) or celiac disease (American English) is a long-term autoimmune disorder, primarily affecting the small intestine, where individuals develop intolerance to gluten, present in foods such as wheat, rye and barley. Classic symptoms include gastrointestinal problems such as chronic diarrhoea, abdominal distention, malabsorption, loss of appetite, and among children failure to grow normally. This often begins between six months and two years of age. Non-classic symptoms are more common, especially in people older than two years. There may be mild or absent gastrointestinal symptoms, a wide number of symptoms involving any part of the body, or no obvious symptoms. Coeliac disease was first described in childhood; however, it may develop at any age. It is associated with other autoimmune diseases, such as Type 1 diabetes mellitus and Hashimoto's thyroiditis, among others. Coeliac disease is caused by a reaction to gluten, a group of various pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cysteine Protease
Cysteine proteases, also known as thiol proteases, are hydrolase enzymes that degrade proteins. These proteases share a common catalytic mechanism that involves a nucleophilic cysteine thiol in a catalytic triad or dyad. Discovered by Gopal Chunder Roy in 1873, the first cysteine protease to be isolated and characterized was papain, obtained from ''Carica papaya''. Cysteine proteases are commonly encountered in fruits including the papaya, pineapple, fig and kiwifruit. The proportion of protease tends to be higher when the fruit is unripe. In fact, the latex of dozens of different plant families are known to contain cysteine proteases. Cysteine proteases are used as an ingredient in meat tenderizers. Classification The MEROPS protease classification system counts 14 superfamilies plus several currently unassigned families (as of 2013) each containing many families. Each superfamily uses the catalytic triad or dyad in a different protein fold and so represent co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barley
Barley (''Hordeum vulgare''), a member of the grass family, is a major cereal grain grown in temperate climates globally. It was one of the first cultivated grains, particularly in Eurasia as early as 10,000 years ago. Globally 70% of barley production is used as animal fodder, while 30% as a source of fermentable material for beer and certain distilled beverages, and as a component of various foods. It is used in soups and stews, and in barley bread of various cultures. Barley grains are commonly made into malt in a traditional and ancient method of preparation. In 2017, barley was ranked fourth among grains in quantity produced () behind maize, rice and wheat. Etymology The Old English word for barley was ', which traces back to Proto-Indo-European and is cognate to the Latin word ' "flour" (''see corresponding entries''). The direct ancestor of modern English ''barley'' in Old English was the derived adjective ''bærlic'', meaning "of barley". The first citation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
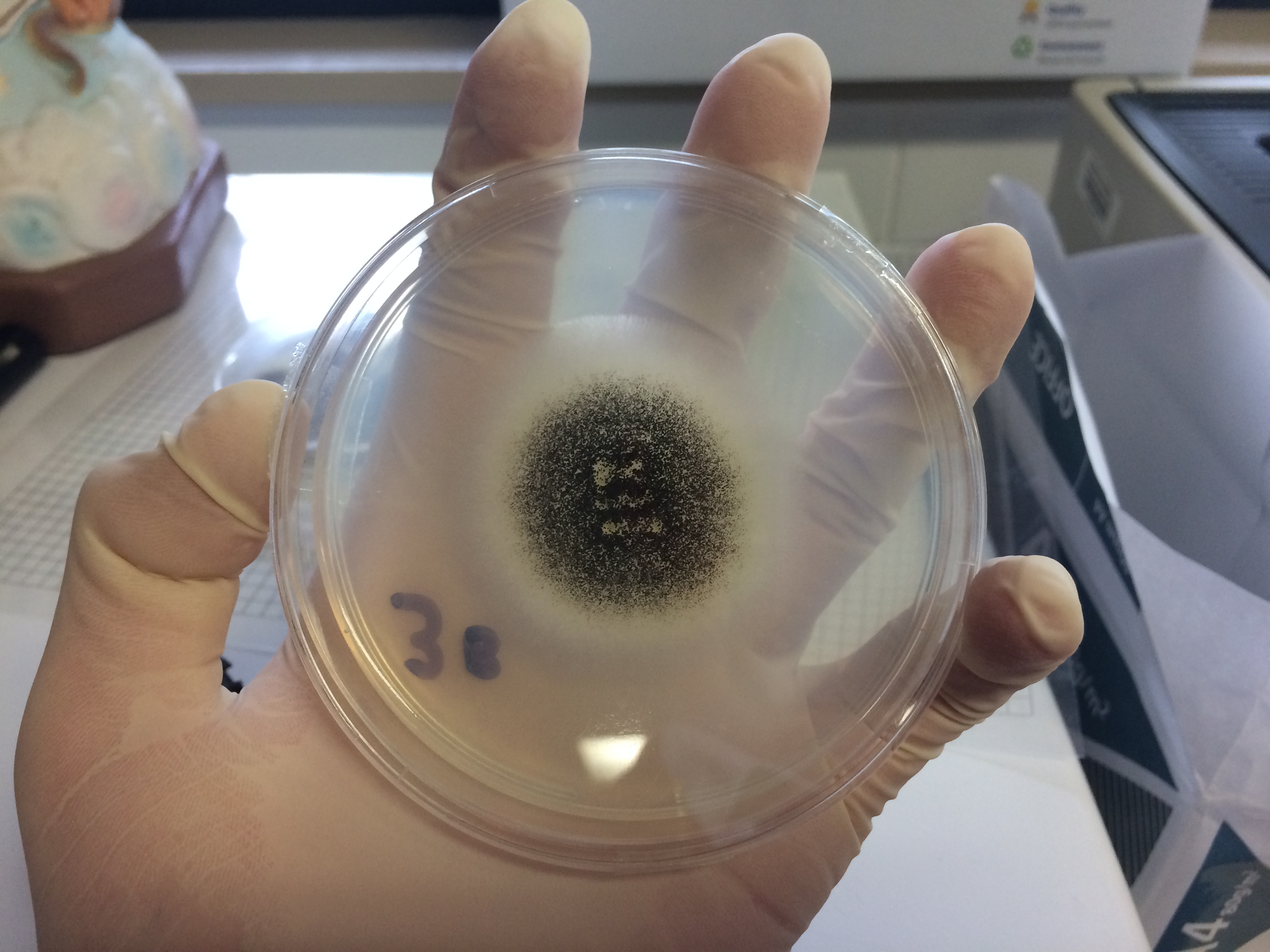
Aspergillus Niger
''Aspergillus niger'' is a mold classified within the ''Nigri'' section of the ''Aspergillus'' genus. The ''Aspergillus'' genus consists of common molds found throughout the environment within soil and water, on vegetation, in fecal matter, on decomposing matter, and suspended in the air. Species within this genus often grow quickly and can sporulate within a few days of germination. A combination of characteristics unique to ''A. niger'' makes the microbe invaluable to the production of many acids, proteins and bioactive compounds. Characteristics including extensive metabolic diversity, high production yield, secretion capability, and the ability to conduct post-translational modifications are responsible for ''A. niger's'' robust production of secondary metabolites. ''A. niger's'' capability to withstand extremely acidic conditions makes it especially important to the industrial production of citric acid. ''A. niger'' causes a disease known as "black mold" on certain fruits an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |