|
EIA-708
CTA-708 (formerly EIA-708 and CEA-708) is the standard for closed captioning for ATSC digital television (DTV) streams in the United States and Canada. It was developed by the Consumer Electronics sector of the Electronic Industries Alliance, which later became the standalone organization Consumer Technology Association. Unlike RLE DVB and DVD subtitles, CTA-708 captions are low bandwidth and textual like traditional EIA-608 captions and EBU Teletext subtitles. However, unlike EIA-608 byte pairs, CTA-708 captions are not able to be modulated on an ATSC receiver's NTSC VBI line 21 composite output and must be pre-rendered by the receiver with the digital video frames, they also include more of the Latin-1 character set, and include stubs to support full UTF-32 captions, and downloadable fonts. CTA-708 caption streams can also optionally encapsulate EIA-608 byte pairs internally, a fairly common usage. CTA-708 captions are injected into MPEG-2 video streams in the picture u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
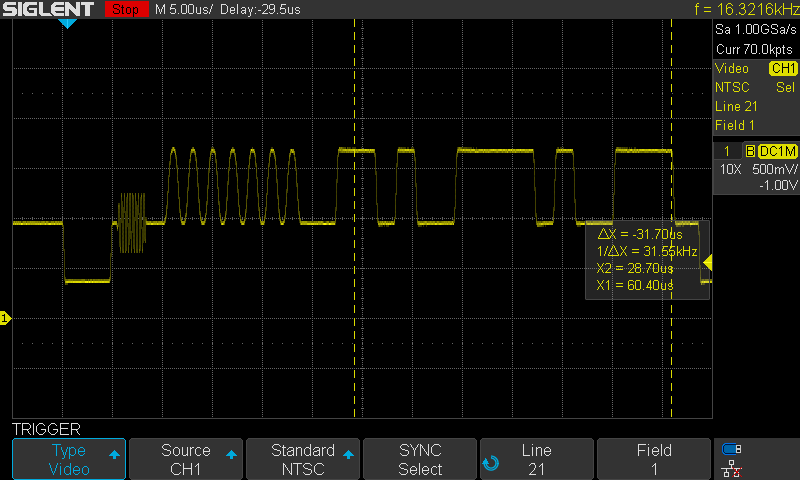
EIA-608
EIA-608, also known as line 21 captions or CEA-608, is a standard used for displaying closed captioning on analog NTSC television broadcasts in the United States, Canada, and Mexico. Developed by the Electronic Industries Alliance (EIA), it allows text such as dialogue and sound effects to be shown on screen, helping people who are deaf or hard of hearing follow television programs. The system works by sending the caption data on a part of the TV signal that viewers don't normally see, called line 21 of the vertical blanking interval. In addition to captions, the standard also supports extra information known as "Extended Data Services" (XDS), which can include details like program titles or instructions for recording shows. This is similar to features found in some European TV systems that use a different signal format. Description EIA-608 captions are transmitted on either the odd or even fields of Line 21 with an odd parity bit in the non-visible active video data area in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Closed Caption
Closed captioning (CC) is the process of displaying text on a television, video screen, or other visual display to provide additional or interpretive information, where the viewer is given the choice of whether the text is displayed. Closed captions are typically used as a transcription of the audio portion of a program as it occurs (either verbatim or in edited form), sometimes including descriptions of non-speech elements. Other uses have included providing a textual alternative language translation of a presentation's primary audio language that is usually burned-in (or "open") to the video and unselectable. HTML5 defines subtitles as a "transcription or translation of the dialogue when sound is available but not understood" by the viewer (for example, dialogue in a foreign language) and captions as a "transcription or translation of the dialogue, sound effects, relevant musical cues, and other relevant audio information when sound is unavailable or not clearly audible" (for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MPEG User Data
The MPEG user data feature provides a means to inject application-specific data into an MPEG elementary stream. User data can be inserted on three different levels: *The sequence level *The group of pictures (GOP) level *The picture data level Applications that process MPEG data do not need to be able to understand data encapsulated in this way, but should be able to preserve it. Examples of information embedded in MPEG streams as user data are: *Aspect ratio information *"Hidden" information per the Active Format Description specification *Closed captioning per the EIA-708 CTA-708 (formerly EIA-708 and CEA-708) is the standard for closed captioning for ATSC digital television (DTV) streams in the United States and Canada. It was developed by the Consumer Electronics sector of the Electronic Industries Alliance, ... standard External links ATSC [Baidu] |
Non-breaking Space
In word processing and digital typesetting, a non-breaking space (), also called NBSP, required space, hard space, or fixed space (in most typefaces, it is not of fixed width), is a space character that prevents an automatic line break at its position. In some formats, including HTML, it also prevents consecutive whitespace characters from collapsing into a single space. Non-breaking space characters with other widths also exist. Uses Despite having layout and uses similar to those of whitespace, it differs in contextual behavior. Non-breaking behavior Text-processing software typically assumes that an automatic line break may be inserted anywhere a space character occurs; a non-breaking space prevents this from happening (provided the software recognizes the character). For example, if the text "100 km" will not quite fit at the end of a line, the software ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Telnet
Telnet (sometimes stylized TELNET) is a client-server application protocol that provides access to virtual terminals of remote systems on local area networks or the Internet. It is a protocol for bidirectional 8-bit communications. Its main goal was to connect terminal devices and terminal-oriented processes. The name "Telnet" refers to two things: a protocol itself specifying how two parties are to communicate and a software application that implements the protocol as a service. User data is interspersed in-band with Telnet control information in an 8-bit byte oriented data connection over the Transmission Control Protocol (TCP). Telnet transmits all information including usernames and passwords in plaintext so it is not recommended for security-sensitive applications such as remote management of routers. Telnet's use for this purpose has waned significantly in favor of SSH. Some extensions to Telnet which would provide encryption have been proposed. Description The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PSIP
The Program and System Information Protocol (PSIP) is the MPEG (Moving Picture Experts Group, a video and audio industry group) and privately defined program-specific information originally defined by General Instrument for the DigiCipher 2 system and later extended for the ATSC standards, ATSC digital television system for carrying metadata about each communication channel, channel in the Broadcasting, broadcast MPEG transport stream of a television station and for publishing information about television programs so that viewers can select what to watch by title and description. Its FM radio equivalent is Radio Data System (RDS). Function PSIP defines virtual channels and Television content rating systems, content ratings, as well as electronic program guides with titles and (optionally) descriptions to be decoded and displayed by the ATSC tuner. PSIP can also send: * the exact time referenced to UTC and GPS time; * the nickname, short name, which some stations use to publish th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SMPTE Timecode
SMPTE timecode ( or ) is a set of cooperating standards to label individual frames of video or film with a timecode. The system is defined by the Society of Motion Picture and Television Engineers in the SMPTE 12M specification. SMPTE revised the standard in 2008, turning it into a two-part document: SMPTE 12M-1 and SMPTE 12M-2, including new explanations and clarifications. Timecodes are added to film, video or audio material, and have also been adapted to synchronize music and theatrical production. They provide a time reference for editing, synchronization and identification. Timecode is a form of media metadata. The invention of timecode made modern videotape editing possible and led eventually to the creation of non-linear editing systems. Basic concepts SMPTE timecode is presented in ''hour:minute:second:frame'' format and is typically represented in 32 bits using binary-coded decimal. There are also ''drop-frame'' and ''color framing'' flags and three extra ''bin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Material Exchange Format
Material Exchange Format (MXF) is a container format for professional digital video and audio media defined by a set of SMPTE standards. A typical example of its use is for delivering advertisements to TV stations and tapeless archiving of broadcast TV programs. It is also used as part of the Digital Cinema Package for delivering movies to commercial theaters. Summary MXF, when used in the form of "Operational Pattern OP1A" or "OPAtom", can be used as a ''container'', ''wrapper'' or ''reference file'' format which supports a number of different streams of coded "essence", encoded in any of a variety of video and audio compression formats, together with a metadata wrapper which describes the material contained within the MXF file. Other "Operational Patterns" can contain or reference multiple materials, just like a simple timeline of a video editing program. MXF has full timecode and metadata support and is intended as a platform-agnostic stable standard for future professio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SMPTE 291M
Ancillary data is data that has been added to given data and uses the same form of transport. Common examples are cover art images for media files or streams, or digital data added to radio or television broadcasts. Television Ancillary data (commonly abbreviated as ANC data), in the context of television systems, refers to a means which by non-video information (such as audio, other forms of essence, and metadata) may be ''embedded'' within the serial digital interface. Ancillary data is standardized by SMPTE as ''SMPTE 291M: Ancillary Data Packet and Space Formatting''. Ancillary data can be located in non-picture portions of horizontal scan lines, known as Horizontal ANCillary data (HANC). Ancillary data can also be located in non-picture regions of the video frame, known as Vertical ANCillary data (VANC). Technical details Location Ancillary data packets may be located anywhere within a serial digital data stream, with the following exceptions: * They should not be located ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |