|
E85
E85 is an abbreviation typically referring to an ethanol fuel blend of 85% ethanol fuel and 15% gasoline or other hydrocarbon by volume. In the United States, the exact ratio of fuel ethanol to hydrocarbon may vary according to ASTM 5798 that specifies the allowable ethanol content in E85 as ranging from 51% to 83%.afdc.energy.gov ''Handbook for Handling, Storing, and Dispensing E85 and Other Ethanol-Gasoline Blends.'' US Department of Energy. Retrieved October 2, 2013. This is due to the lower heating value of neat ethanol making it difficult to start engines in relatively cold climates w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flexible-fuel Vehicle
A flexible-fuel vehicle (FFV) or dual-fuel vehicle (colloquially called a flex-fuel vehicle) is an alternative fuel vehicle with an internal combustion engine designed to run on more than one fuel, usually gasoline blended with either ethanol fuel, ethanol or methanol fuel, and both fuels are stored in the same common tank. Modern flex-fuel engines are capable of burning any proportion of the resulting blend in the combustion chamber as fuel injection and ignition timing, spark timing are adjusted automatically according to the actual blend detected by a fuel composition sensor. Flex-fuel vehicles are distinguished from bi-fuel vehicles, where two fuels are stored in separate tanks and the engine runs on one fuel at a time, for example, compressed natural gas (CNG), Autogas, liquefied petroleum gas (LPG), or Hydrogen vehicle, hydrogen. The most common commercially available FFV in the world market is the ethanol flexible-fuel vehicle, with about 60 million automobiles, mot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
E85 Fuel
E85 is an abbreviation typically referring to an ethanol fuel blend of 85% ethanol fuel and 15% gasoline or other hydrocarbon by volume. In the United States, the exact ratio of fuel ethanol to hydrocarbon may vary according to ASTM 5798 that specifies the allowable ethanol content in E85 as ranging from 51% to 83%.afdc.energy.gov ''Handbook for Handling, Storing, and Dispensing E85 and Other Ethanol-Gasoline Blends.'' US Department of Energy. Retrieved October 2, 2013. This is due to the of ethanol m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
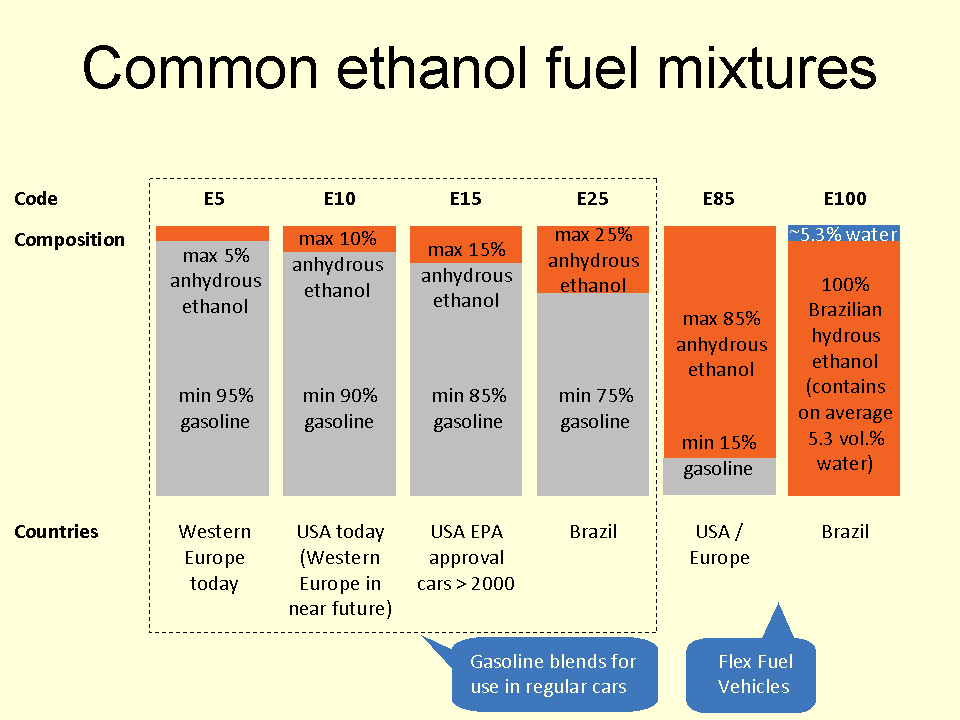
Common Ethanol Fuel Mixtures
Several common ethanol fuel mixtures are in use around the world. The use of pure anhydrous, hydrous or anhydrous ethanol in internal combustion engines (ICEs) is only possible if the engines are designed or modified for that purpose, and used only in automobiles, light-duty trucks and motorcycles. Anhydrous ethanol can be blended with :gasoline (petrol) for use in gasoline engines, but with high ethanol content only after engine modifications to meter increased fuel volume since pure ethanol contains only 2/3 of the BTUs of an equivalent volume of pure gasoline. High percentage ethanol mixtures are used in some racing engine applications as the very high octane rating of ethanol is compatible with very high compression ratios. Ethanol fuel mixtures have "E" numbers which describe the percentage of ethanol fuel in the mixture by volume, for example, E85 is 85% anhydrous ethanol and 15% gasoline. Low-ethanol blends are typically from E5 to E25, although internationally the most c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethanol Fuel
Ethanol fuel is fuel containing ethyl alcohol, the same type of alcohol as found in alcoholic beverages. It is most often used as a motor fuel, mainly as a biofuel additive for gasoline. Several common ethanol fuel mixtures are in use around the world. The use of pure hydrous or anhydrous ethanol in internal combustion engines (ICEs) is possible only if the engines are designed or modified for that purpose. Anhydrous ethanol can be blended with :gasoline (petrol) for use in gasoline engines, but with a high ethanol content only after engine modifications to meter increased fuel volume since pure ethanol contains only 2/3 the energy of an equivalent volume of pure gasoline. High percentage ethanol mixtures are used in some racing engine applications since the very high octane rating of ethanol is compatible with very high compression ratios. The first production car running entirely on ethanol was the Fiat 147, introduced in 1978 in Brazil by Fiat. Ethanol is commonly mad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Octane Rating
An octane rating, or octane number, is a standard measure of a liquid fuel, fuel's ability to withstand Compression ratio, compression in an internal combustion engine without causing engine knocking. The higher the octane number, the more compression the fuel can withstand before detonating. Octane rating does not relate directly to the power output or the energy content of the fuel per unit mass or volume, but simply indicates the resistance to detonating under pressure without a spark. Whether a higher octane fuel improves or impairs an engine's performance depends on the design of the engine. In broad terms, fuels with a higher octane rating are used in higher-compression Petrol engine, gasoline engines, which may yield higher power for these engines. The added power in such cases comes from the way the engine is designed to compress the air/fuel mixture, and not directly from the rating of the gasoline. In contrast, fuels with lower octane (but higher cetane numbers) are idea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gasoline
Gasoline ( North American English) or petrol ( Commonwealth English) is a petrochemical product characterized as a transparent, yellowish, and flammable liquid normally used as a fuel for spark-ignited internal combustion engines. When formulated as a fuel for engines, gasoline is chemically composed of organic compounds derived from the fractional distillation of petroleum and later chemically enhanced with gasoline additives. It is a high-volume profitable product produced in crude oil refineries. The ability of a particular gasoline blend to resist premature ignition (which causes knocking and reduces efficiency in reciprocating engines) is measured by its octane rating. Tetraethyl lead was once widely used to increase the octane rating but is not used in modern automotive gasoline due to the health hazard. Aviation, off-road motor vehicles, and racing car engines still use leaded gasolines. Other substances are frequently added to gasoline to improve chemical st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Koenigsegg CCXR
The Koenigsegg CCX is a mid-engine sports car manufactured by Swedish automotive manufacturer Koenigsegg Automotive AB. The project began with the aim of making a global car, designed and engineered to comply with global safety and environment regulations, particularly to enter the United States car market. To sell cars in the US, many alterations were made to the design of the CCR; the previously used Ford Modular engine was replaced by an in-house developed Koenigsegg engine designed to run on 91 octane fuel, readily available in the United States, and to meet Californian emission standards. The name ''CCX'' is an abbreviation for ''Competition Coupé X'', the X commemorating the 10th anniversary (X being the Roman numeral for ten) of the completion and test drive of the first CC prototype in 1996. Overview The CCX was unveiled at the 2006 Geneva Motor Show, sporting body modifications to meet US vehicle regulations and a new in-house developed 4.7L twin supercharged ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fuel Efficiency
Fuel efficiency (or fuel economy) is a form of thermal efficiency, meaning the ratio of effort to result of a process that converts chemical energy, chemical potential energy contained in a carrier (fuel) into kinetic energy or Mechanical work, work. Overall fuel efficiency may vary per device, which in turn may vary per application, and this spectrum of variance is often illustrated as a continuous energy profile. Non-transportation applications, such as Industrial sector, industry, benefit from increased fuel efficiency, especially fossil fuel power plants or industries dealing with combustion, such as ammonia production during the Haber process. In the context of transport, fuel economy is the energy efficiency in transportation, energy efficiency of a particular vehicle, given as a ratio of distance traveled per unit of Motor fuel, fuel consumed. It is dependent on several factors including engine efficiency, transmission (mechanics), transmission design, and tire design. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bartending Terminology
Various unique terms are used in bartending. Definitions and usage Straight, up, and straight up In bartending, the terms "straight up" and "up" ordinarily refer to an alcoholic drink that is shaken or stirred with ice and then strained and served in a stemmed glass without ice. "Straight" ordinarily refers to a single, unmixed liquor served without any water, ice, or other mixer. In this sense, "straight" can sometimes be used as a synonym for ''either'' "straight up" or " neat". Furthermore, "straight" is also a term of art for a particular type of whiskey produced in the United States. United States federal law defines the term "straight whiskey" as whiskey that has met particular requirements for its ingredients, production process, and aging. For example, the label of a bottle of top-shelf bourbon typically identifies the product as "Kentucky straight bourbon whiskey". While the meaning of "up" and "neat" is ordinarily clear, some clarification may be needed for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnesium
Magnesium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Mg and atomic number 12. It is a shiny gray metal having a low density, low melting point and high chemical reactivity. Like the other alkaline earth metals (group 2 of the periodic table), it occurs naturally only in combination with other elements and almost always has an oxidation state of +2. It reacts readily with air to form a thin Passivation (chemistry), passivation coating of magnesium oxide that inhibits further corrosion of the metal. The free metal burns with a brilliant-white light. The metal is obtained mainly by electrolysis of magnesium Salt (chemistry), salts obtained from brine. It is less dense than aluminium and is used primarily as a component in strong and lightweight magnesium alloy, alloys that contain aluminium. In the cosmos, magnesium is produced in large, aging stars by the sequential addition of three Helium nucleus, helium nuclei to a carbon nucleus. When such stars explo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrocarbon
In organic chemistry, a hydrocarbon is an organic compound consisting entirely of hydrogen and carbon. Hydrocarbons are examples of group 14 hydrides. Hydrocarbons are generally colourless and Hydrophobe, hydrophobic; their odor is usually faint, and may be similar to that of gasoline or Naphtha, lighter fluid. They occur in a diverse range of molecular structures and phases: they can be gases (such as methane and propane), liquids (such as hexane and benzene), low melting solids (such as paraffin wax and naphthalene) or polymers (such as polyethylene and polystyrene). In the fossil fuel industries, ''hydrocarbon'' refers to naturally occurring petroleum, natural gas and coal, or their hydrocarbon derivatives and purified forms. Combustion of hydrocarbons is the main source of the world's energy. Petroleum is the dominant raw-material source for organic commodity chemicals such as solvents and polymers. Most anthropogenic (human-generated) emissions of greenhouse gases are eithe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |