|
Dulaglutide
Dulaglutide, sold under the brand name Trulicity among others, is a medication used for the treatment of type 2 diabetes in combination with diet and exercise. It is also approved in the United States for the reduction of major adverse cardiovascular events in adults with type 2 diabetes who have established cardiovascular disease or multiple cardiovascular risk factors. The most common side effects are nausea, diarrhea, vomiting, abdominal pain, and decreased appetite. It is a glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist (GLP-1 agonist) consisting of GLP-1(7-37) covalently linked to an Fc fragment of human IgG4. GLP-1 is a hormone that is involved in normalizing the level of glucose in blood (glycemia). The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved dulaglutide for use in the United States in September 2014. It was approved for use in the European Union in November 2014. In 2022, it was the 74th most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with more than 8million ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonist
Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists, also known as GLP-1 analogs, GLP-1RAs, or incretin mimetics, are a class of anorectic drugs that reduce blood sugar and energy intake by activating the glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor, GLP-1 receptor. They mimic the actions of the endogenous incretin hormone GLP-1, which is released by the gut after eating. GLP-1 agonists were initially developed for type 2 diabetes. The 2022 American Diabetes Association standards of medical care recommend GLP-1 agonists as a first-line therapy for type 2 diabetes, specifically in patients with atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease or obesity. The drugs were also noted to reduce food intake and body weight significantly, and some have been approved to treat obesity and other components of the metabolic syndrome in the absence of diabetes. They are also in development for other indications, such as non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, polycystic ovary syndrome, and diseases of the reward system su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glucagon-like Peptide-1
Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) is a 30- or 31-amino-acid-long peptide hormone deriving from tissue-specific posttranslational processing of the proglucagon peptide. It is produced and secreted by intestinal enteroendocrine L-cells and certain neurons within the nucleus of the solitary tract in the brainstem upon food consumption. The initial product GLP-1 (1–37) is susceptible to amidation and proteolytic cleavage, which gives rise to the two truncated and equipotent biologically active forms, GLP-1 (7–36) amide and GLP-1 (7–37). Active GLP-1 protein secondary structure includes two α-helices from amino acid position 13–20 and 24–35 separated by a linker region. Alongside glucose-dependent insulinotropic peptide (GIP), GLP-1 is an incretin; thus, it has the ability to decrease blood sugar levels in a glucose-dependent manner by enhancing the secretion of insulin. Beside the insulinotropic effects, GLP-1 has been associated with numerous regulatory and prot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subcutaneous Injection
Subcutaneous administration is the insertion of medications beneath the skin either by injection or infusion. A subcutaneous injection is administered as a bolus (medicine), bolus into the subcutis, the layer of skin directly below the dermis and Epidermis (skin), epidermis, collectively referred to as the Cutis (anatomy), cutis. The instruments are usually a hypodermic needle and a syringe. Subcutaneous injections are highly effective in administering medications such as insulin, morphine, heroin, diacetylmorphine and goserelin. Subcutaneous administration may be List of medical abbreviations, abbreviated as SC, SQ, subcu, sub-Q, SubQ, or subcut. Subcut is the preferred abbreviation to reduce the risk of misunderstanding and potential errors. Subcutaneous tissue has few blood vessels and so drugs injected into it are intended for slow, sustained rates of absorption, often with some amount of depot injection, depot effect. Compared with other route of administration, routes of ad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nausea
Nausea is a diffuse sensation of unease and discomfort, sometimes perceived as an urge to vomit. It can be a debilitating symptom if prolonged and has been described as placing discomfort on the chest, abdomen, or back of the throat. Over 30 definitions of nausea were proposed in a 2011 book on the topic. Nausea is a non-specific symptom, which means that it has many possible causes. Some common causes of nausea are gastroenteritis and other gastrointestinal disorders, food poisoning, motion sickness, dizziness, migraine, fainting, low blood sugar, anxiety, hyperthermia, dehydration and lack of sleep. Nausea is a side effect of many medications including chemotherapy, or morning sickness in early pregnancy. Nausea may also be caused by disgust and depression. Medications taken to prevent and treat nausea and vomiting are called antiemetics. The most commonly prescribed antiemetics in the US are promethazine, metoclopramide, and the newer ondansetron. The word na ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
L Cell
L, or l, is the twelfth letter of the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its name in English is ''el'' (pronounced ), plural ''els''. History Lamedh may have come from a pictogram of an ox goad or cattle prod. Some have suggested that it represents a shepherd's staff. Typographic variants In most sans-serif typefaces, the lowercase letter ''ell'' , written as the glyph , may be difficult to distinguish from the uppercase letter "eye" (written as the glyph ); in some serif typefaces, the glyph may be confused with the glyph , the digit ''one''. To avoid such confusion, some newer computer fonts (such as Trebuchet MS) have a finial, a curve to the right at the bottom of the lowercase letter ''ell''. Other style variants are provided in script typefaces and display typefaces. All these variants of the letter are encoded in Unicode as or , allowing presentation to be chosen accor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia
Multiple endocrine neoplasia (abbreviated MEN) is a condition which encompasses several distinct syndromes featuring tumors of endocrine glands, each with its own characteristic pattern. In some cases, the tumors are malignant, in others, benign. Benign or malignant tumors of nonendocrine tissues occur as components of some of these tumor syndromes. MEN syndromes are inherited as autosomal dominant disorders. Presentation Related conditions Although not officially categorized as multiple endocrine neoplasia syndromes, Von Hippel–Lindau disease and Carney complex are two other autosomal dominant endocrine tumor syndromes with features that overlap the clinical features of the MEN syndromes. Although not transmitted in the germline, McCune–Albright syndrome is a genetic disorder characterized by endocrine neoplastic features involving endocrine glands that overlap with those involved in MEN1 or MEN2. Comparison Percentages in the table below refer to the percentage of peo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
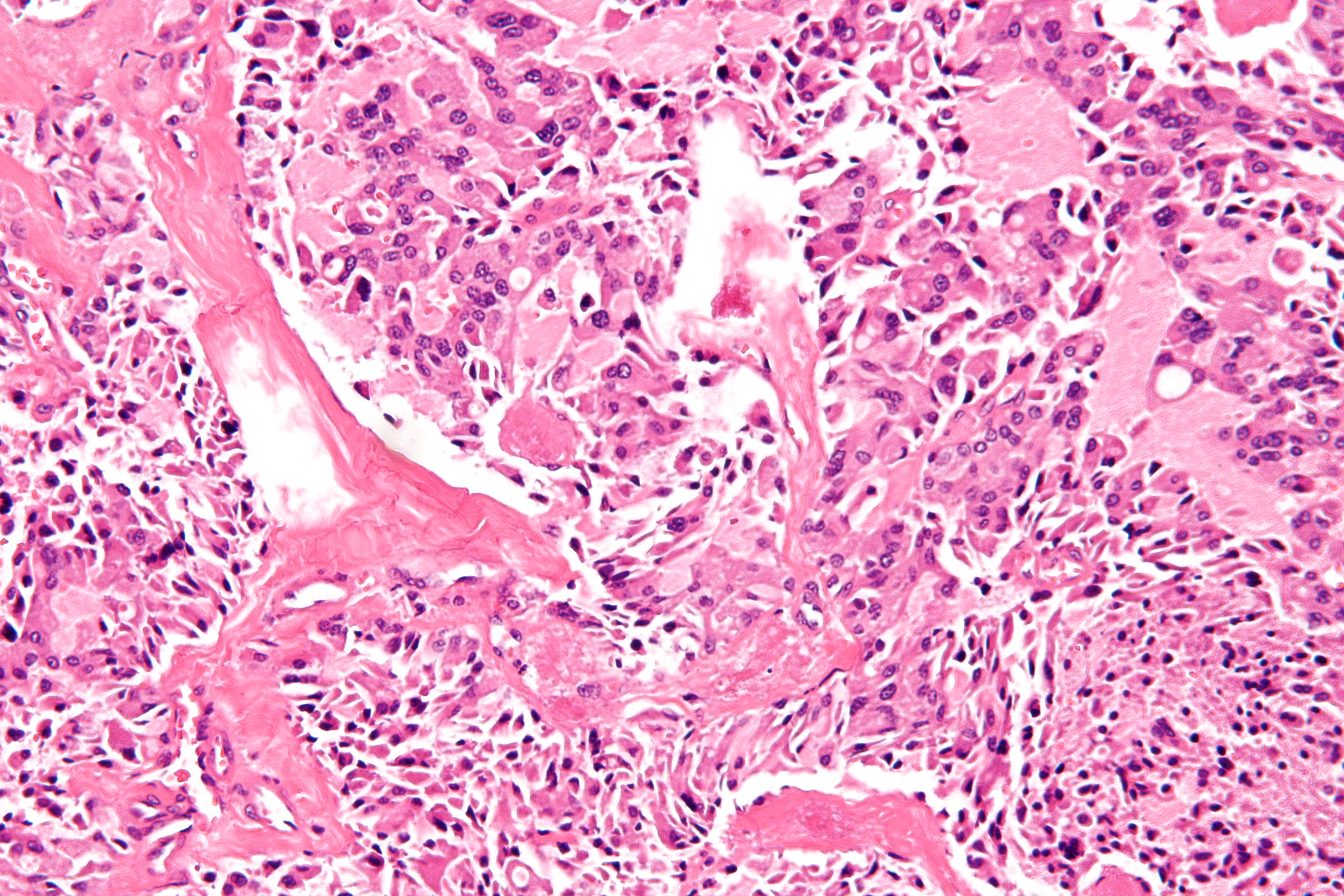
Medullary Thyroid Cancer
Medullary thyroid cancer is a form of thyroid carcinoma which originates from the parafollicular cells (C cells), which produce the hormone calcitonin.Hu MI, Vassilopoulou-Sellin R, Lustig R, Lamont JP"Thyroid and Parathyroid Cancers"in Pazdur R, Wagman LD, Camphausen KA, Hoskins WJ (EdsCancer Management: A Multidisciplinary Approach 11 ed. 2008. Medullary tumors are the third most common of all thyroid cancers and together make up about 3% of all thyroid cancer cases. MTC was first characterized in 1959. Approximately 25% of medullary thyroid cancer cases are genetic in nature, caused by a mutation in the RET proto-oncogene. When MTC occurs by itself it is termed sporadic medullary thyroid cancer. Medullary thyroid cancer is seen in people with multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2, subtypes 2A and 2B. When medullary thyroid cancer due to a hereditary genetic disorder occurs without other endocrine tumours it is termed familial medullary thyroid cancer. Signs and symptoms The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Active Ingredient
An active ingredient is any ingredient that provides biologically active or other direct effect in the diagnosis, cure, mitigation, treatment, or prevention of disease or to affect the structure or any function of the body of humans or animals. The similar terms active pharmaceutical ingredient (abbreviated as API) and bulk active are also used in medicine. The term active substance may be used to describe the effective chemical used to control bacteria or pests. Some medication products can contain more than one active ingredient. The traditional word for the active pharmaceutical agent is pharmacon or pharmakon (from , adapted from '' pharmacos'') which originally denoted a magical substance or drug. The terms active constituent or active principle are often chosen when referring to the active substance of interest in a plant (such as salicylic acid in willow bark or arecoline in areca nuts), since the word "ingredient" can be taken to connote a sense of human agency (tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypersensitivity
Hypersensitivity (also called hypersensitivity reaction or intolerance) is an abnormal physiological condition in which there is an undesirable and adverse immune response to an antigen. It is an abnormality in the immune system that causes Immune disorder, immune diseases including allergies and autoimmunity. It is caused by many types of particles and substances from the external environment or from within the body that are recognized by the immune cells as antigens. The immune reactions are usually referred to as an over-reaction of the immune system and they are often damaging and uncomfortable. In 1963, Philip George Houthem Gell and Robin Coombs introduced a systematic classification of the different types of hypersensitivity based on the types of antigens and immune responses involved. According to this system, known as the #Gell and Coombs classification, Gell and Coombs classification or Gell-Coombs's classification, there are four types of hypersensitivity, namely: Typ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medullary Thyroid Carcinoma
Medullary thyroid cancer is a form of thyroid carcinoma which originates from the parafollicular cells (C cells), which produce the hormone calcitonin.Hu MI, Vassilopoulou-Sellin R, Lustig R, Lamont JP"Thyroid and Parathyroid Cancers"in Pazdur R, Wagman LD, Camphausen KA, Hoskins WJ (EdsCancer Management: A Multidisciplinary Approach 11 ed. 2008. Medullary tumors are the third most common of all thyroid cancers and together make up about 3% of all thyroid cancer cases. MTC was first characterized in 1959. Approximately 25% of medullary thyroid cancer cases are genetic in nature, caused by a mutation in the RET proto-oncogene. When MTC occurs by itself it is termed sporadic medullary thyroid cancer. Medullary thyroid cancer is seen in people with multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2, subtypes 2A and 2B. When medullary thyroid cancer due to a hereditary genetic disorder occurs without other endocrine tumours it is termed familial medullary thyroid cancer. Signs and symptoms The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Renal Impairment
Kidney failure, also known as renal failure or end-stage renal disease (ESRD), is a medical condition in which the kidneys can no longer adequately filter waste products from the blood, functioning at less than 15% of normal levels. Kidney failure is classified as either acute kidney failure, which develops rapidly and may resolve; and chronic kidney failure, which develops slowly and can often be irreversible. Symptoms may include leg swelling, feeling tired, vomiting, loss of appetite, and confusion. Complications of acute and chronic failure include uremia, hyperkalemia, and volume overload. Complications of chronic failure also include heart disease, high blood pressure, and anaemia. Causes of acute kidney failure include low blood pressure, blockage of the urinary tract, certain medications, muscle breakdown, and hemolytic uremic syndrome. Causes of chronic kidney failure include diabetes, high blood pressure, nephrotic syndrome, and polycystic kidney disease. Diagn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypoglycemia
Hypoglycemia (American English), also spelled hypoglycaemia or hypoglycæmia (British English), sometimes called low blood sugar, is a fall in blood sugar to levels below normal, typically below 70 mg/dL (3.9 mmol/L). Whipple's triad is used to properly identify hypoglycemic episodes. It is defined as blood glucose below 70 mg/dL (3.9 mmol/L), symptoms associated with hypoglycemia, and resolution of symptoms when blood sugar returns to normal. Hypoglycemia may result in headache, tiredness, clumsiness, trouble talking, confusion, fast heart rate, sweating, shakiness, nervousness, hunger, loss of consciousness, seizures, or death. Symptoms typically come on quickly. Symptoms can remain even soon after raised blood level. The most common cause of hypoglycemia is diabetes medication, medications used to treat diabetes such as insulin (medication), insulin, sulfonylureas, and biguanides. Risk is greater in diabetics who have eaten less than usual, recently exe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |