|
Duke Of Urach
The title of Duke of Urach ( German: ''Herzog von Urach'') was created in the Kingdom of Württemberg on 28 March 1867 for Friedrich Wilhelm Alexander Ferdinand, Count of Württemberg, with the style of Serene Highness. The first Duke of Urach was the first head of the House of Urach. Family Wilhelm, 1st Duke of Urach, was the son of Duke Wilhelm of Württemberg (1761-1830) and his morganatic wife, Baroness (Freiin) Wilhelmine von Tunderfeldt-Rhodis (1777-1822), whom he married at Coswig on 23 August 1800. His paternal grandfather was Duke Friedrich II Eugen (1732-1797), from whom all claimants to the Kingdom of Württemberg are descended. Because of his first marriage to Théodolinde de Beauharnais, the first Duke had converted to Catholicism. His second marriage to Her Serene Highness Princess Florestine of Monaco in 1863 led in part to Wilhelm's elevation in 1867 from being a Count of Wurttemberg to Duke (Herzog) von Urach. He had served the Kingdom well in his career ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wappen Des Herzogs Von Urach
A coat of arms is a heraldry, heraldic communication design, visual design on an escutcheon (heraldry), escutcheon (i.e., shield), surcoat, or tabard (the last two being outer garments), originating in Europe. The coat of arms on an escutcheon forms the central element of the full achievement (heraldry), heraldic achievement, which in its whole consists of a shield, supporters, a crest (heraldry), crest, and a motto. A coat of arms is traditionally unique to the armiger (e.g. an individual person, family, state, organization, school or corporation). The term "coat of arms" itself, describing in modern times just the heraldic design, originates from the description of the entire medieval chainmail "surcoat" garment used in combat or preparation for the latter. Roll of arms, Rolls of arms are collections of many coats of arms, and since the early Modern Age centuries, they have been a source of information for public showing and tracing the membership of a nobility, noble family, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
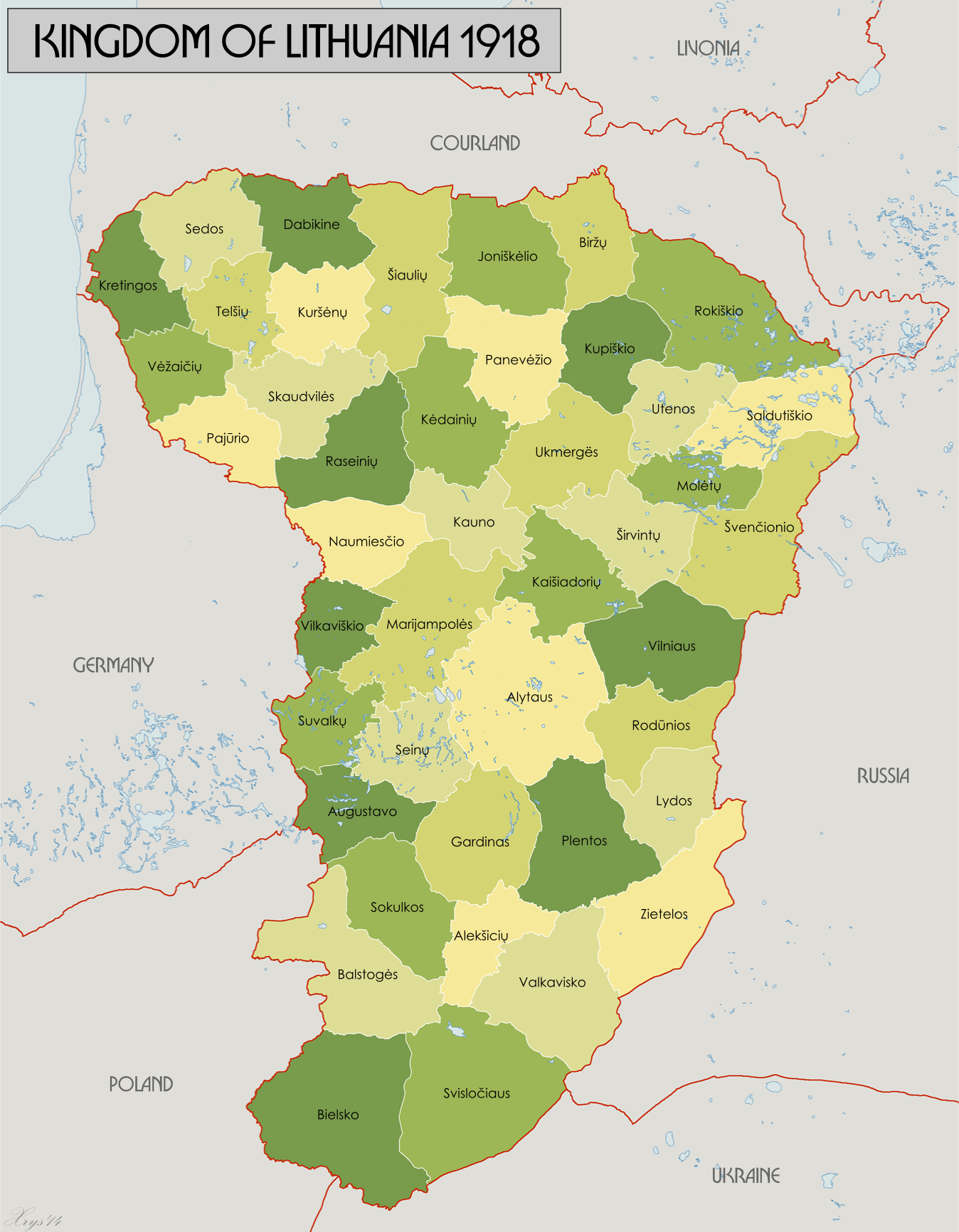
Kingdom Of Lithuania (1918)
The Kingdom of Lithuania was an attempt to establish an independent constitutional Lithuanian monarchy in February 1918. It was created towards the end of World War I when Lithuanian-speaking lands were under military occupation by the German Empire. The state was officially dissolved in November 1918. The Council of Lithuania declared Lithuania's independence on 16 February 1918, but the council was unable to form a government, police, or other state institutions due to the continued presence of German troops. The Germans presented various proposals to incorporate Lithuania into the German Empire, particularly Prussia. The Lithuanians resisted this idea and hoped to preserve their independence by creating a separate constitutional monarchy. On 4 June 1918, they voted to offer the Lithuanian throne to the German noble Wilhelm Karl, Duke of Urach. He accepted the offer in July 1918 and took the regnal name Mindaugas II. However, he never visited Lithuania. His election stirre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uradel
(, German: "ancient nobility"; adjective or ) is a genealogical term introduced in late 18th-century Germany to distinguish those families whose noble rank can be traced to the 14th century or earlier. The word stands opposed to '' Briefadel'', a term used for titles of nobility created in the early modern period or modern history by letters patent. Since the earliest known such letters were issued in the 14th century, those knightly families in northern European nobility whose noble rank predates these are designated . and families are generally further divided into categories with their ranks of titles: ''adlig'' (untitled nobility), ''freiherrlich'' (baronial), '' gräflich'' ( comital), ''fürstlich'' (princely) and '' herzoglich'' ( ducal) houses. The latter two are also referred to as '' Hochadel'' (High Nobility). Introduction and usage The first use of the word to designate the oldest nobility dates from 1788, and it had assumed its present-day meaning by no later t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Württemberg
History is the systematic study of the past, focusing primarily on the human past. As an academic discipline, it analyses and interprets evidence to construct narratives about what happened and explain why it happened. Some theorists categorize history as a social science, while others see it as part of the humanities or consider it a hybrid discipline. Similar debates surround the purpose of history—for example, whether its main aim is theoretical, to uncover the truth, or practical, to learn lessons from the past. In a more general sense, the term ''history'' refers not to an academic field but to the past itself, times in the past, or to individual texts about the past. Historical research relies on primary and secondary sources to reconstruct past events and validate interpretations. Source criticism is used to evaluate these sources, assessing their authenticity, content, and reliability. Historians strive to integrate the perspectives of several sources to devel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coat Of Arms Of Württemberg
The coat of arms of the Kingdom of Württemberg shows an impalement of the three black antlers that represent Württemberg on the dexter (viewer's left) side, and the three black lions passant of medieval Swabia on the sinister (viewer's right) side, both on a gold field. History The coat of arms was formally adopted by King William I of Württemberg on 30 December 1817,Flags of the World Kingdom of Württemberg. Accessed 2009-04-12. lasting between 1817 and 1922, and occasionally seen on state s of this period. This version derived from the escutcheon found in the centre of the much larger and more ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Federal Republic Of Germany
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It lies between the Baltic Sea and the North Sea to the north and the Alps to the south. Its sixteen constituent states have a total population of over 84 million in an area of , making it the most populous member state of the European Union. It borders Denmark to the north, Poland and the Czech Republic to the east, Austria and Switzerland to the south, and France, Luxembourg, Belgium, and the Netherlands to the west. The nation's capital and most populous city is Berlin and its main financial centre is Frankfurt; the largest urban area is the Ruhr. Settlement in the territory of modern Germany began in the Lower Paleolithic, with various tribes inhabiting it from the Neolithic onward, chiefly the Celts. Various Germanic tribes have inhabited the northern parts of modern Germany since classical antiquity. A region named Germania was documented before AD 100. In 962, the Kingdom of Germa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weimar Republic
The Weimar Republic, officially known as the German Reich, was the German Reich, German state from 1918 to 1933, during which it was a constitutional republic for the first time in history; hence it is also referred to, and unofficially proclaimed itself, as the German Republic. The period's informal name is derived from the city of Weimar, which hosted the constituent assembly that established its government. In English, the republic was usually simply called "Germany", with "Weimar Republic" (a term introduced by Adolf Hitler in 1929) not commonly used until the 1930s. The Weimar Republic had a semi-presidential system. Toward the end of the First World War (1914–1918), Germany was exhausted and suing for peace, sued for peace in desperate circumstances. Awareness of imminent defeat sparked a German Revolution of 1918–1919, revolution, Abdication of Wilhelm II, the abdication of Kaiser Wilhelm II, the proclamation of the Weimar Republic on 9 November 1918, and formal cessa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karl Gero, Duke Of Urach
Prince Karl Gero Albrecht Joseph Wilhelm Anton Maria of Urach, Count of Württemberg, 3rd Duke of Urach (19 August 1899 – 15 August 1981) was the head of the morganatic Urach branch of the House of Württemberg. Life He was born in Lichtenstein, then part of the Kingdom of Württemberg, at his family's Lichtenstein Castle, being the second son of Duke Wilhelm of Urach and his first wife Duchess Amalie in Bavaria. In 1917 he graduated from the Karls-Gymnasium school in Stuttgart. After graduation he served in the First World War as a lieutenant. He was heavily wounded in 1918. After the war Karl Gero von Urach studied architecture, and later worked as an architect in Munich. In 1928, on his father's death, Karl Gero became the third Duke (Herzog) of Urach, as his elder brother Wilhelm had resolved to marry morganatically (he was a director at Mercedes-Benz for most of his life, and had two daughters). In 1935 he entered Wehrmacht and became a Hauptmann, and in 1940 w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wilhelm Karl, Duke Of Urach
Prince Wilhelm of Urach, Count of Württemberg, 2nd Duke of Urach (''Wilhelm Karl Florestan Gero Crescentius''; German: ''Fürst Wilhelm von Urach, Graf von Württemberg, 2. Herzog von Urach''; 3 March 1864 – 24 March 1928), was a German prince who was elected in June 1918 as King of Lithuania, with the regnal name of Mindaugas II. He never assumed the crown, however, as German authorities declared the election invalid; the invitation was withdrawn in November 1918. From 17 July 1869 until his death, he was the head of the morganatic Urach branch of the House of Württemberg. Early life Born as Wilhelm Karl Florestan Gero Crescentius, Count of Württemberg, he was the elder son of Wilhelm, 1st Duke of Urach (the head of a morganatic branch of the Royal House of the Kingdom of Württemberg), and his second wife, Princess Florestine of Monaco, occasional Regent of Monaco and daughter of Florestan I, Prince of Monaco. At the age of four, Wilhelm succeeded his father as Duke ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wilhelm I
Wilhelm I (Wilhelm Friedrich Ludwig; 22 March 1797 – 9 March 1888) was King of Prussia from 1861 and German Emperor from 1871 until his death in 1888. A member of the House of Hohenzollern, he was the first head of state of a united Germany. He was regent of Prussia from 1858 to 1861 for his brother Frederick William IV. During the reign of his grandson Wilhelm II, he was known as Emperor Wilhelm the Great (German: ''Kaiser Wilhelm der Große''). The second son of Frederick William III of Prussia, Prince Frederick William and Louise of Mecklenburg-Strelitz, Wilhelm was not expected to ascend to the throne. His grandfather, King Frederick William II of Prussia, Frederick William II died the year he was born, and his father was crowned Frederick William III of Prussia, Frederick William III. Wilhelm fought with distinction during the War of the Sixth Coalition, and afterwards became a prominent figure within the Prussian Army. In 1840, his childless elder brother became King of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wilhelm, Duke Of Urach
Count Friedrich Wilhelm Alexander Ferdinand of Württemberg, 1st Duke of Urach (6 July 1810 – 17 July 1869), was the son of William Frederick Philip, Duke of Württemberg, Duke Wilhelm of Württemberg (1761–1830), younger brother of Frederick of Württemberg, King Frederick I of Württemberg, by his morganatic wife, Baroness Wilhelmine von Tunderfeldt-Rhodis (1777–1822), who had married in 1800. He was the first Head of the House of Urach. Wilhelm served as a cavalry officer in the army of the then-independent Kingdom of Württemberg. He also tested cannon for the Army of Württemberg, some of which can still be seen at Lichtenstein Castle (Württemberg), Lichtenstein Castle, which he substantially rebuilt in the 1840s. He was inspired by the romantic historical novel Lichtenstein (novel), ''Lichtenstein'' by Wilhelm Hauff (1826). Hauff was in turn inspired by the works of Walter Scott. He was created Duke of Urach on 28 March 1867, with the style of His Serene Highness, S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |