|
Dukamaje Formation
The Dukamaje Formation is a geological formation in Niger and Nigeria whose strata date back to the Late Cretaceous The Late Cretaceous (100.5–66 Ma) is the more recent of two epochs into which the Cretaceous Period is divided in the geologic time scale. Rock strata from this epoch form the Upper Cretaceous Series. The Cretaceous is named after ''cre .... Dinosaur remains are among the fossils that have been recovered from the formation.Weishampel, David B; et al. (2004). "Dinosaur distribution (Late Cretaceous, Africa)." In: Weishampel, David B.; Dodson, Peter; and Osmólska, Halszka (eds.): The Dinosauria, 2nd, Berkeley: University of California Press. Pp. 604-605. . A wealth of Mosasaur fossils have also been recovered from this formation, particularly from the area around Mt. Igdaman. Fossil content ;Other reptiles * '' Sokotosuchus ianwilsoni'' * '' Palaeophis sp.'' * '' Podocnemis sp.'' * '' Trematochampsa taqueti'' * '' Libycosuchus sp.'' ;Fishes * '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geological Formation
A geological formation, or simply formation, is a body of rock having a consistent set of physical characteristics (lithology) that distinguishes it from adjacent bodies of rock, and which occupies a particular position in the layers of rock exposed in a geographical region (the stratigraphic column). It is the fundamental unit of lithostratigraphy, the study of strata or rock layers. A formation must be large enough that it can be mapped at the surface or traced in the subsurface. Formations are otherwise not defined by the thickness (geology), thickness of their rock strata, which can vary widely. They are usually, but not universally, tabular in form. They may consist of a single lithology (rock type), or of alternating beds of two or more lithologies, or even a heterogeneous mixture of lithologies, so long as this distinguishes them from adjacent bodies of rock. The concept of a geologic formation goes back to the beginnings of modern scientific geology. The term was used by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mosasaur
Mosasaurs (from Latin ''Mosa'' meaning the 'Meuse', and Ancient Greek, Greek ' meaning 'lizard') are an extinct group of large aquatic reptiles within the family Mosasauridae that lived during the Late Cretaceous. Their first fossil remains were discovered in a limestone quarry at Maastricht on the Meuse in 1764. They belong to the order Squamata, which includes lizards and snakes. During the last 20 million years of the Cretaceous period (Turonian–Maastrichtian ages), with the extinction of the ichthyosaurs and Pliosauridae, pliosaurs, mosasaurids became the dominant marine predators. They themselves became extinct as a result of the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event, K-Pg event at the end of the Cretaceous period, about 66 million years ago. Description Mosasaurs breathed air, were powerful swimmers, and were well-adapted to living in the warm, shallow Inland sea (geology), inland seas prevalent during the Late Cretaceous period. Mosasaurs were so well adapted to thi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
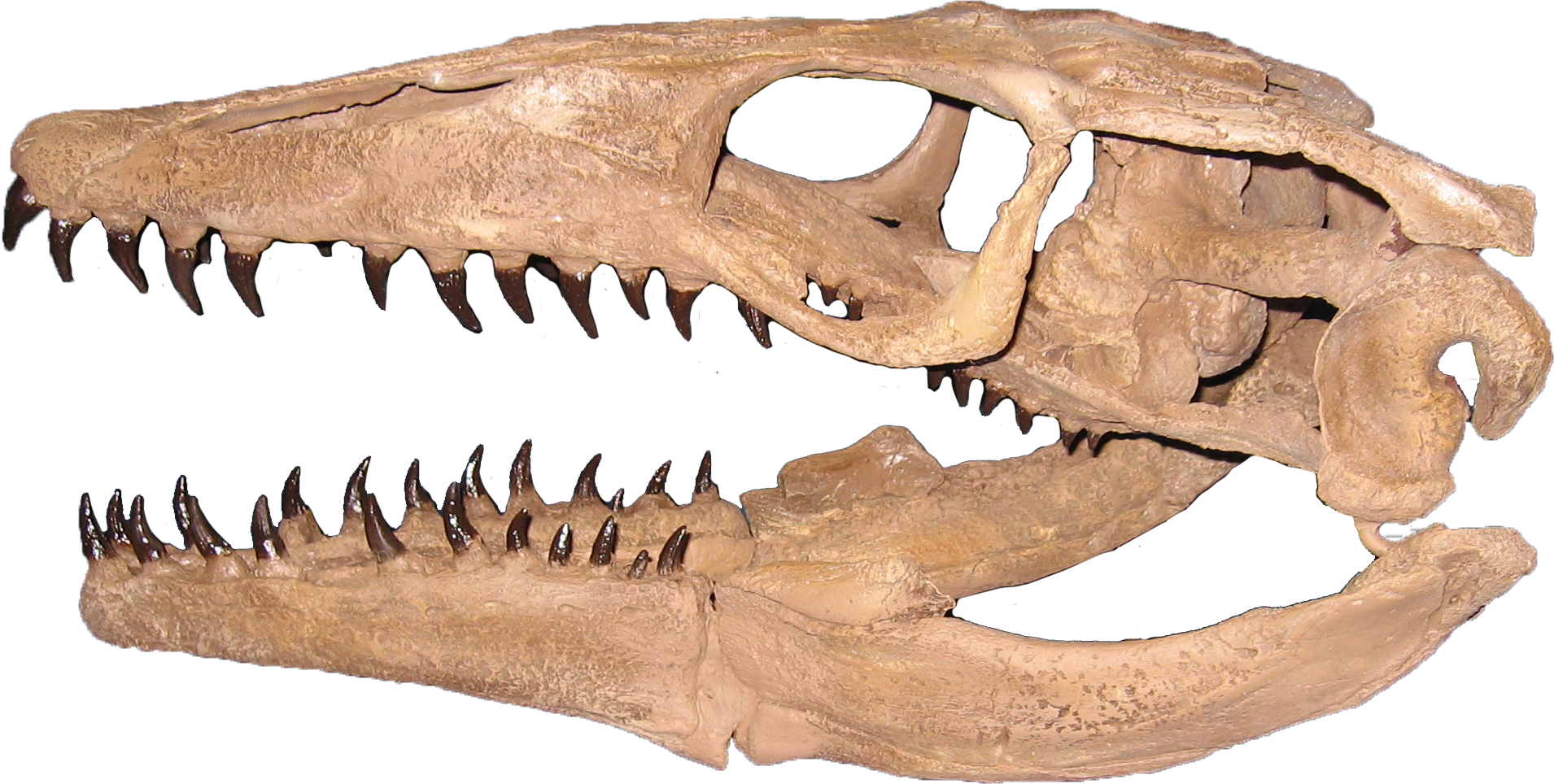
Trematochampsa
''Trematochampsa'' is a dubious extinct genus of crocodyliform from the Late Cretaceous (Coniacian-Santonian age) In Beceten Formation of Niger. Taxonomy The type species, ''T. taqueti'', was described by Eric Buffetaut in 1974. A second species, ''T. oblita'', was named from Madagascar in 1979, but was renamed '' Miadanasuchus'' in 2009. ''Trematochampsa'' gives its name to the Trematochampsidae, a poorly known group of fossil crocodiles. However, the labile phylogenetic position of ''Trematochampsa'' in many studies has been attributed to character conflict, leading many authors to exclude this genus from many cladistic analyses, but Sertich et al. (2014) noted that the referred material of ''Trematochampsa'' consists of more than one crocodyliform taxon, so they opted to use only the cranial material in the dataset for the cladistic analysis of '' Rukwasuchus'' and recommended removing the postcranial material from ''Trematochampsa''. The analysis recovered ''Trematochampsa' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Podocnemis
''Podocnemis'' is a genus of aquatic turtles, commonly known as South American river turtles, in the Family (biology), family Podocnemididae. The genus consists of six Extant taxon, extant species occurring in tropical South America.''Podocnemis'' The Reptile Database. www.reptile-database.org. Four additional species are known only from fossils. These turtles have pig-like noses but are not closely related to the pig-nosed turtle. Species These six species are extant. *''Podocnemis erythrocephala'' – red-headed Amazon River turtle *''Podocnemis expansa'' – Arrau turtle *''Podocnemis lewyana'' – Magdalena River turtle *''Podocnemis sextuberculata'' – six-tubercled Amazon River turtle *''Podocnemis unifilis'' – yellow-spotted rive ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palaeophis
''Palaeophis'' ('ancient snake') is an extinct genus of marine snake that is the type genus of the extinct snake family Palaeophiidae. Described species within this genus lived in the Eocene epoch, with some unnamed or questionable records from Cenomanian and Maastrichtian. Fossils of species within this genus have been found in England, France, Denmark, Morocco and Mali. Remains have also been found in North America, including Maryland and Virginia (from the early Eocene Nanjemoy Formation),Blake, S. F. "Note on a vertebra of Palaeophis from the Eocene of Maryland." Journal of the Washington Academy of Sciences 31.12 (1941): 501-503. GeorgiaParmley, Dennis, and Harold W. Reed. "Size and age class estimates of North American Eocene palaeopheid snakes." Georgia Journal of Science 61.4 (2003): 220. and Mississippi.Holman, J. Alan. "Palaeophis casei, new species, a tiny palaeophid snake from the early Eocene of Mississippi." Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology 2.2 (1982): 163-166. D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fossilworks
Fossilworks was a portal which provides query, download, and analysis tools to facilitate access to the Paleobiology Database, a large relational database assembled by hundreds of paleontologists from around the world. History Fossilworks was created in 1998 by John Alroy and housed at Macquarie University Macquarie University ( ) is a Public university, public research university in Sydney, New South Wales, Australia. Founded in 1964 by the New South Wales Government, it was the third university to be established in the Sydney metropolitan area. .... It included many analysis and data visualization tools formerly included in the Paleobiology Database.{{cite web, title=Frequently asked questions, url=http://www.fossilworks.org/cgi-bin/bridge.pl?page=FAQ, publisher=Fossilworks, access-date=17 December 2021, archive-date=18 May 2022, archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220518205516/http://www.fossilworks.org/cgi-bin/bridge.pl?page=FAQ, url-status=dead Fossilworks was sh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
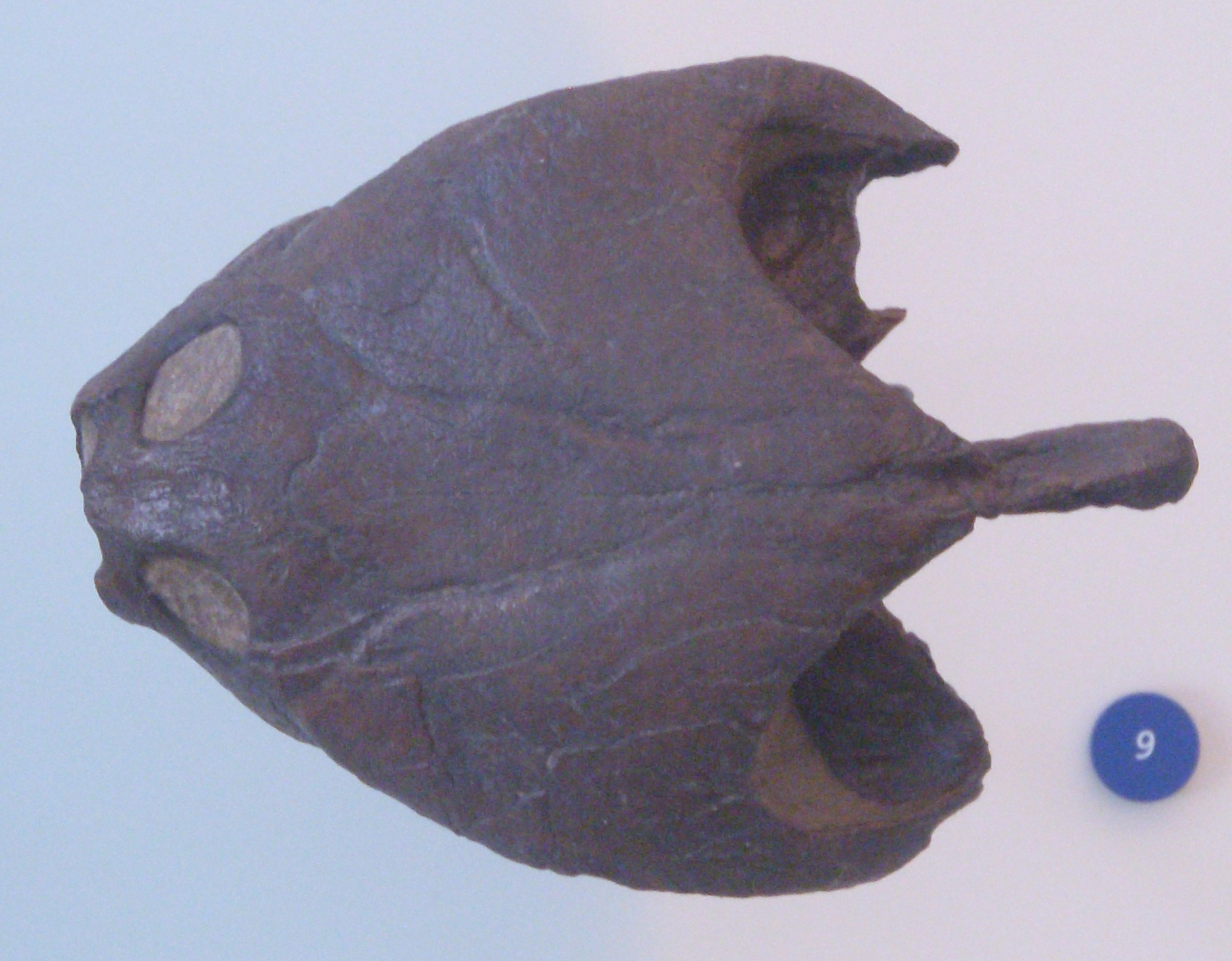
Sokotosuchus
''Sokotosuchus'' is an extinct genus of dyrosaurid crocodyliform which existed during the Maastrichtian in western Africa. Fossils of the genus were found in the Dukamaje Formation of Nigeria, and some cranial material has possibly been found in Mali Mali, officially the Republic of Mali, is a landlocked country in West Africa. It is the List of African countries by area, eighth-largest country in Africa, with an area of over . The country is bordered to the north by Algeria, to the east b .... References Bibliography * Further reading * L. B. Halstead. 1975. ''Sokotosuchus ianwilsoni'' n. g., g. sp., a new teleosaur crocodile from the Upper Cretaceous of Nigeria. Journal of Mining and Geology 11(1–2):101-103 Dyrosauridae Prehistoric pseudosuchian genera Prehistoric marine crocodylomorphs Maastrichtian genera Late Cretaceous crocodylomorphs of Africa Cretaceous Nigeria Fossils of Nigeria Fossil taxa described in 1975 Fossils of Mali {{paleo-ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mosasaurus
''Mosasaurus'' (; "lizard of the Meuse (river), Meuse River") is the type genus (defining example) of the mosasaurs, an extinct group of aquatic Squamata, squamate reptiles. It lived from about 82 to 66 million years ago during the Campanian and Maastrichtian Stage (stratigraphy), stages of the Late Cretaceous. The genus was one of the first Mesozoic marine reptiles known to science—the first fossils of ''Mosasaurus'' were found as skulls in a chalk quarry near the Dutch city of Maastricht in the late 18th century, and were initially thought to be crocodiles or whales. One skull discovered around 1780 was famously nicknamed the "great animal of Maastricht". In 1808, naturalist Georges Cuvier concluded that it belonged to a giant marine lizard with similarities to monitor lizards but otherwise unlike any known living animal. This concept was revolutionary at the time and helped support the then-developing ideas of extinction. Cuvier did not designate a scientific name for the an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Platecarpus
''Platecarpus'' ("oar wrist") is an extinct genus of aquatic lizards belonging to the mosasaur family, living around 84–81 million years ago during the middle Santonian to early Campanian, of the Late Cretaceous period. Fossils have been found in the United States and possible specimens in Belgium and Africa. A well-preserved specimen of ''Platecarpus'' shows that it fed on moderate-sized fish, and it has been hypothesized to have fed on squid, and ammonites as well. Like other mosasaurs, it was initially thought to have swum in an eel-like fashion, although another study suggests that it swam more like modern sharks. An exceptionally well-preserved specimen of ''P. tympaniticus'' known as LACM 128319 shows skin impressions, pigments around the nostrils, bronchial tubes, and the presence of a high-profile tail fluke, showing that it and other mosasaurs did not necessarily have an eel-like swimming method, but were more powerful, fast swimmers. It is held in the Natural History Mu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plioplatecarpus
''Plioplatecarpus'' is a genus of mosasaur lizard. Like all mosasaurs, it lived in the late Cretaceous period, about 73-68 million years ago. Discovery ''Plioplatecarpus'' has been found in many locations around the world (most mosasaurs were fairly widespread). ''Plioplatecarpus'' has been found in the Pierre Shale of Kansas, Demopolis Chalk of Alabama, and also in Mississippi, Tennessee, North Dakota, South Dakota, Canada, Sweden, The Netherlands. It was first found in Europe by paleontologist Louis Dollo (''P. marshi''), in 1882. It was relatively incomplete, but more fossils would soon turn up. In North America, Edward Drinker Cope found another mosasaur in 1869, but had identified it as ''Mosasaurus''. It would later be reclassified as ''Plioplatecarpus'', as would Cope's ''Liodon'', in 1870. ''Liodon'' would be reclassified as ''Platecarpus'', and later as ''Prognathodon'' or this genus. Possible freshwater occurrence In 1999, Holmes and colleagues described an incomplete ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Halisaurus
''Halisaurus'' is an extinct genus of mosasaur named by Othniel Charles Marsh in 1869. The holotype, consisting of an angular and a basicranium fragment discovered near Hornerstown, New Jersey, already revealed a relatively unique combination of features and prompted a new genus to be described. Its name is a portmanteau of the Ancient Greek ἅλς (''háls''; "sea") and σαῦρος (''saûros''; "lizard"). It was renamed by Marsh to ''Baptosaurus'' in 1870, since he believed the name to already be preoccupied by the fish '' Halosaurus''. According to modern rules, a difference of a letter is enough and the substitute name is unneeded, making "''Baptosaurus''" a junior synonym. Since its description, more complete remains have been uncovered from fossil deposits throughout the world with particularly complete remains found in North America and North Africa. The genus remains a key taxon in mosasaur systematics due to its unique set of features and as the most complete repres ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Angolasaurus
''Angolasaurus'' ("Angola lizard") is an extinct genus of mosasaur. Definite remains from this genus have been recovered from the Turonian and Coniacian of Angola, and possibly the Coniacian of the United States, the Turonian of Brazil, and the Maastrichtian of Niger. While at one point considered a species of ''Platecarpus'', recent phylogenetic analyses have placed it between the (then) plioplatecarpines ''Ectenosaurus'' and ''Selmasaurus'', maintaining a basal position within the plioplatecarpinae. Its wide geographic range make it one of the only Turonian mosasaurs with a transatlantic range. Description ''Angolasaurus'' was a small mosasaur, with a skull length estimated at , suggesting a possible total length of about 4 meters (13 feet) based on the ratio provided by Russell (1967). It shared much of a body plan with its relative ''Platecarpus'', but with a slightly longer skull relative to body length. Its skull housed 11 maxillary teeth, 4 premaxillary teeth, and 12 de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |