|
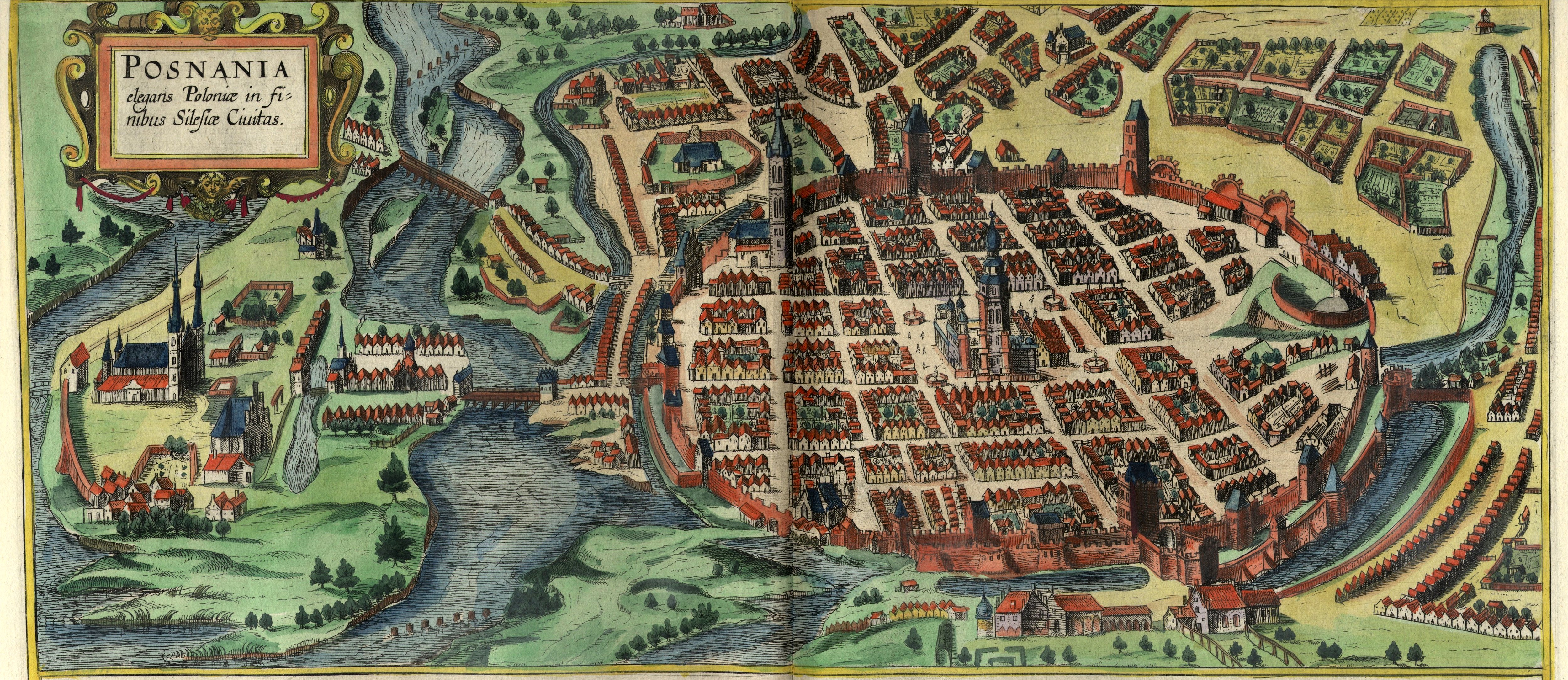
Duchy Of Poznań
The Duchy of Poznań ( Polish: ''Księstwo poznańskie''; Latin: ''Ducatus Posnaniensis'') was a feudal district duchy in the Greater Poland, centered on the Poznań Land. Its capital was Poznań. The state was established in 1177, in the partition of the Duchy of Greater Poland, after the rebellion against Mieszko III. Duke Odon of the Piast dynasty become its first ruler. It existed until 1279, when, it got united with duchies of Gniezno and Kalisz, under the rule of Przemysł II, forming the Duchy of Greater Poland. It remained a fiefdom within the Duchy of Poland Civitas Schinesghe (; ), also known as the Duchy of Poland or the Principality of Poland, is the historiographical name given to a polity in Central Europe, which existed during the medieval period and was the predecessor state of the Kingdom of ..., until 1227, and after that, it become an independent state.Jerzy Wyrozumski, ''Historia Polski do roku 1505'', pp. 104–111. References Citations Bibliography ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
High Middle Ages
The High Middle Ages, or High Medieval Period, was the periodization, period of European history between and ; it was preceded by the Early Middle Ages and followed by the Late Middle Ages, which ended according to historiographical convention. Key historical trends of the High Middle Ages include the medieval demography, rapidly increasing population of Europe, which brought about great social and political change from the preceding era, and the Renaissance of the 12th century, including the first developments of rural exodus and urbanization. By 1350, the robust population increase had greatly benefited the European economy, which had reached levels that would not be seen again in some areas until the 19th century. That trend faltered in the early 14th century, as the result of numerous events which together comprised the crisis of the late Middle Ages—most notable among them being the Black Death, in addition to various regional wars and economic stagnation. From , Europ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duchy Of Gniezno
The Duchy of Gniezno was a feudal district duchy in the Greater Poland, centered on the Kalisz Region. Its capital was Gniezno. The state was established in 1177, in the partition of the Duchy of Greater Poland, after the rebellion against Mieszko III. Duke Casimir II the Just of the Piast dynasty become its first ruler. It existed until 1279, when, it got united with duchies of Kalisz and Poznań, under the rule of Przemysł II, forming the Duchy of Greater Poland. It remained a fiefdom within the Duchy of Poland Civitas Schinesghe (; ), also known as the Duchy of Poland or the Principality of Poland, is the historiographical name given to a polity in Central Europe, which existed during the medieval period and was the predecessor state of the Kingdom of ..., until 1227, and after that, it become an independent state.Jerzy Wyrozumski, ''Historia Polski do roku 1505'', pp. 104–111. Citations Notes References Bibliography *Józef Dobosz, ''Kazimierz II Sprawiedliwy' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
States And Territories Established In 1177
State most commonly refers to: * State (polity), a centralized political organization that regulates law and society within a territory **Sovereign state, a sovereign polity in international law, commonly referred to as a country **Nation state, a state where the majority identify with a single nation (with shared culture or ethnic group) ** Constituent state, a political subdivision of a state ** Federated state, constituent states part of a federation *** U.S. state * State of nature, a concept within philosophy that describes the way humans acted before forming societies or civilizations State may also refer to: Arts, entertainment, and media Literature * ''State Magazine'', a monthly magazine published by the U.S. Department of State * ''The State'' (newspaper), a daily newspaper in Columbia, South Carolina, United States * ''Our State'', a monthly magazine published in North Carolina and formerly called ''The State'' * The State (Larry Niven), a fictional future government ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
13th-century Disestablishments In Poland
The 13th century was the century which lasted from January 1, 1201 (represented by the Roman numerals MCCI) through December 31, 1300 (MCCC) in accordance with the Julian calendar. The Mongol Empire was founded by Genghis Khan, which stretched from Eastern Asia to Eastern Europe. The conquests of Hulagu Khan and other Mongol invasions changed the course of the Muslim world, most notably the Siege of Baghdad (1258) and the destruction of the House of Wisdom. Other Muslim powers such as the Mali Empire and Delhi Sultanate conquered large parts of West Africa and the Indian subcontinent, while Buddhism witnessed a decline through the conquest led by Bakhtiyar Khilji. The earliest Islamic states in Southeast Asia formed during this century, most notably Samudera Pasai. The Kingdoms of Sukhothai and Hanthawaddy would emerge and go on to dominate their surrounding territories. Europe entered the apex of the High Middle Ages, characterized by rapid legal, cultural, and religious evo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
12th-century Establishments In Poland
1 (one, unit, unity) is a number, numeral, and glyph. It is the first and smallest positive integer of the infinite sequence of natural numbers. This fundamental property has led to its unique uses in other fields, ranging from science to sports, where it commonly denotes the first, leading, or top thing in a group. 1 is the unit of counting or measurement, a determiner for singular nouns, and a gender-neutral pronoun. Historically, the representation of 1 evolved from ancient Sumerian and Babylonian symbols to the modern Arabic numeral. In mathematics, 1 is the multiplicative identity, meaning that any number multiplied by 1 equals the same number. 1 is by convention not considered a prime number. In digital technology, 1 represents the "on" state in binary code, the foundation of computing. Philosophically, 1 symbolizes the ultimate reality or source of existence in various traditions. In mathematics The number 1 is the first natural number after 0. Each natural number, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Former Administrative Regions Of Greater Poland
A former is an object, such as a template, gauge or cutting die, which is used to form something such as a boat's hull. Typically, a former gives shape to a structure that may have complex curvature. A former may become an integral part of the finished structure, as in an aircraft fuselage, or it may be removable, being used in the construction process and then discarded or re-used. Aircraft formers Formers are used in the construction of aircraft fuselage, of which a typical fuselage has a series from the nose cone to the empennage, typically perpendicular to the longitudinal axis of the aircraft. The primary purpose of formers is to establish the shape of the fuselage and reduce the column length of stringers to prevent instability. Formers are typically attached to longerons, which support the skin of the aircraft. The "former-and-longeron" technique (also called stations and stringers) was adopted from boat construction, and was typical of light aircraft built until t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Poznań
Poznań, today Poland's fifth largest city, is also one of the country's oldest cities, and was an important political and religious center in the early Polish state of the 10th century. Poznań Cathedral is the oldest church in the country, containing the tombs of the first Polish rulers, Duke Mieszko I and King Bolesław I Chrobry. Although the centre of national political power moved to Kraków in the 11th century, and later to Warsaw, Poznań remained an important regional center, being the chief city of the Greater Poland (Wielkopolska) region. It came under Kingdom of Prussia, Prussian (later Germany, German) rule for most of the period from 1793 to 1918, during which it expanded significantly, and was also heavily Poznań Fortress, fortified. The city resumed its role as a Polish voivodeships of Poland, voivodeship capital in the Second Polish Republic, and later, following the 1939–1945 Occupation of Poland (1939–1945), Nazi German occupation, in the communist Polish Pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Poland During The Piast Dynasty
The period of rule by the Piast dynasty between the 10th and 14th centuries is the first major stage of the history of the Polish state. The dynasty was founded by a series of dukes listed by the chronicler Gall Anonymous in the early 12th century: Siemowit, Lestek and Siemomysł. It was Mieszko I, the son of Siemomysł, who is now considered the proper founder of the Polish state at about 960 AD. The ruling house then remained in power in the Polish lands until 1370. Mieszko converted to Christianity of the Western Latin Church in an event known as the Baptism of Poland in 966, which established a major cultural boundary in Europe based on religion. He also completed a unification of the Lechitic tribal lands that was fundamental to the existence of the new country of Poland. Following the emergence of the Polish state, a series of rulers converted the population to Christianity, created a kingdom of Poland in 1025 and integrated Poland into the prevailing culture of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fiefdoms Of Poland
A fief (; ) was a central element in medieval contracts based on feudal law. It consisted of a form of property holding or other rights granted by an overlord to a vassal, who held it in fealty or "in fee" in return for a form of feudal allegiance, services or payments. The fees were often lands, land revenue or revenue-producing real property like a watermill, held in feudal land tenure: these are typically known as fiefs or fiefdoms. However, not only land but anything of value could be held in fee, including governmental office, rights of exploitation such as hunting, fishing or felling trees, monopolies in trade, money rents and tax farms. There never existed a standard feudal system, nor did there exist only one type of fief. Over the ages, depending on the region, there was a broad variety of customs using the same basic legal principles in many variations. Terminology In ancient Rome, a "benefice" (from the Latin noun , meaning "benefit") was a gift of land () for life ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duchies Of Poland
A duchy, also called a dukedom, is a country, territory, fiefdom, fief, or domain ruled by a duke or duchess, a ruler hierarchically second to the king or Queen regnant, queen in Western European tradition. There once existed an important difference between "sovereign dukes" and dukes who were ordinary noblemen throughout Europe. Some historic duchies were sovereign in areas that would become part of nation-states only during the modern era, such as happened in Germany (once a federal empire) and Italy (previously a unified kingdom). In contrast, others were subordinate districts of those Kingdom (politics), kingdoms that had unified either partially or completely during the medieval era, such as France, Spain, Sicily, Naples, and the Papal States. Examples In France, several duchies existed in the medieval period, including Duchy of Normandy, Normandy, Duchy of Burgundy, Burgundy, Brittany, and Aquitaine. The medieval German Stem duchy, stem duchies (, literally "tribal duchy," ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Former Monarchies Of Europe
A former is an object, such as a template, gauge or cutting die, which is used to form something such as a boat's hull. Typically, a former gives shape to a structure that may have complex curvature. A former may become an integral part of the finished structure, as in an aircraft fuselage, or it may be removable, being used in the construction process and then discarded or re-used. Aircraft formers Formers are used in the construction of aircraft fuselage, of which a typical fuselage has a series from the nose cone to the empennage, typically perpendicular to the longitudinal axis of the aircraft. The primary purpose of formers is to establish the shape of the fuselage and reduce the column length of stringers to prevent instability. Formers are typically attached to longerons, which support the skin of the aircraft. The "former-and-longeron" technique (also called stations and stringers) was adopted from boat construction, and was typical of light aircraft built until ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |