|
Drung Parish
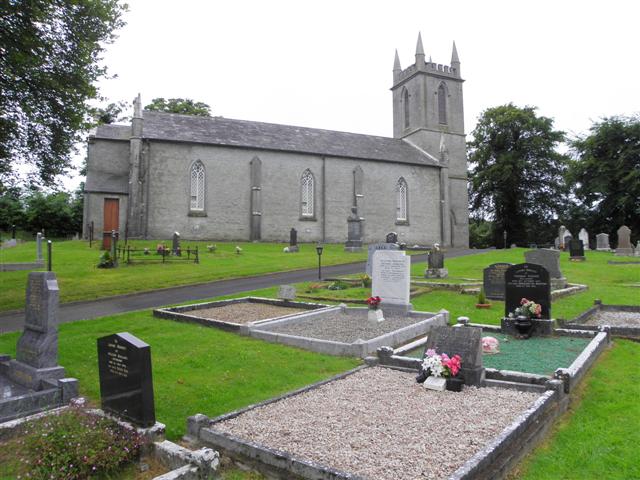
Drung () is a civil and ecclesiastical parish in County Cavan in Ireland. It takes its name from a townland of the same name. The Catholic parish is in the Diocese of Kilmore and the Church of Ireland parish is in the Diocese of Kilmore, Elphin and Ardagh. The civil parish of Drung is within the historical barony of Tullygarvey. The R188 regional road, between Cootehill and Cavan Town, passes through Drung. The landscape of the area includes a number of drumlins and lakes. Until the early 20th century, the parish had been dominated years by a small number of landowners. These included the Clements family of Rathkenny and the Burrowes family of Stradone House, who owned estates in Drung. Before these Anglo-Irish families were granted their estates by the British Crown, the townlands in the parish had been owned by the O'Reilly dynasty, a Gaelic aristocratic family, who lost their land after the 1641 Rebellion The Irish Rebellion of 1641 was an uprising in Ireland, initiat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dring, County Cavan
Dring ( or 'crowd') is a small townland in the civil parish of Kildallan, Barony (Ireland), barony of Tullyhunco, County Cavan, Ireland. Geography Dring is bounded on the west by Cornacrum townland, on the east by Clonkeen and Kildallan townlands, on the south by Drumminnion townland and on the north by Ardlougher and Clontygrigny townlands. Its chief geographical features are Clonty Lough, the Rag River, small streams, dug wells, spring wells and a gravel pit. Dring is traversed by minor public roads and rural lanes. The townland covers , including 14 acres of water. History The Ulster Plantation Baronial map of 1609 depicts the name as ''Dringe''. The Ulster Plantation grants of 1611 spell the townland name as ''Dronge''. A 1615 lease spells the name as ''Dronge''. A 1629 inquisition spells the name as ''Dronge''. A 1630 inquisition spells the name as ''Dronge''. A 1631 grant spells the name as ''Dronge''. The 1652 Commonwealth Survey spells the townland as ''Dring''. From ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Placenames Database Of Ireland
The Placenames Database of Ireland (), also known as , is a database and archive of place names in Ireland. It was created by Fiontar, Dublin City University in collaboration with the Placenames Branch of the Department of Tourism, Culture, Arts, Gaeltacht, Sport and Media. The website is a public resource primarily aimed at journalists and translators, students and teachers, historians and researchers in genealogy. Placenames Commission and Placenames Branch The Placenames Commission () was established by the Department of Finance in 1946 to advise Ordnance Survey Ireland and the government of what the Irish name of places should be. Although both the 1922 Constitution of the Irish Free State and the current constitution adopted in 1937 recognised Irish as the national language, the law in regard to placenames was carried over from the 19th-century UK statutes which established the Ordnance Survey and Griffith's Valuation, under which only an English-language name had offi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Irish Rebellion Of 1641
The Irish Rebellion of 1641 was an uprising in Kingdom of Ireland, Ireland, initiated on 23 October 1641 by Catholic gentry and military officers. Their demands included an end to anti-Catholic discrimination, greater Irish self-governance, and return of plantations of Ireland, confiscated Catholic lands. Planned as a swift ''coup d'état'' to gain control of the Protestant-dominated Dublin Castle administration, central government, instead it led to the 1641–1653 Irish Confederate Wars, part of the wider Wars of the Three Kingdoms. Despite failing to seize Dublin Castle, rebels under Felim O'Neill of Kinard, Felim O'Neill quickly over-ran most of Ulster, centre of the most recent Plantation of Ulster, land confiscations. O'Neill then issued the Proclamation of Dungannon, a forgery claiming he had been authorised by Charles I of England to secure Ireland against his opponents in Kingdom of England, England and Kingdom of Scotland, Scotland. Many Cavalier, Royalist Normans in I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gaelic Ireland
Gaelic Ireland () was the Gaelic political and social order, and associated culture, that existed in Ireland from the late Prehistory of Ireland, prehistoric era until the 17th century. It comprised the whole island before Anglo-Norman invasion of Ireland, Anglo-Normans conquered parts of Ireland in the 1170s. Thereafter, it comprised that part of the country not under foreign dominion at a given time (i.e. the part beyond The Pale). For most of its history, Gaelic Ireland was a "patchwork" hierarchy of territories ruled by a hierarchy of kings or chiefs, who were chosen or elected through tanistry. Gaelic warfare, Warfare between List of Irish kingdoms, these territories was common. Traditionally, a powerful ruler was acknowledged as High King of Ireland. Society was made up of Irish clans, clans and, like the rest of History of Europe, Europe, was structured hierarchically according to Social class, class. Throughout this period, the economy was mainly Pastoralism, pastoral a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
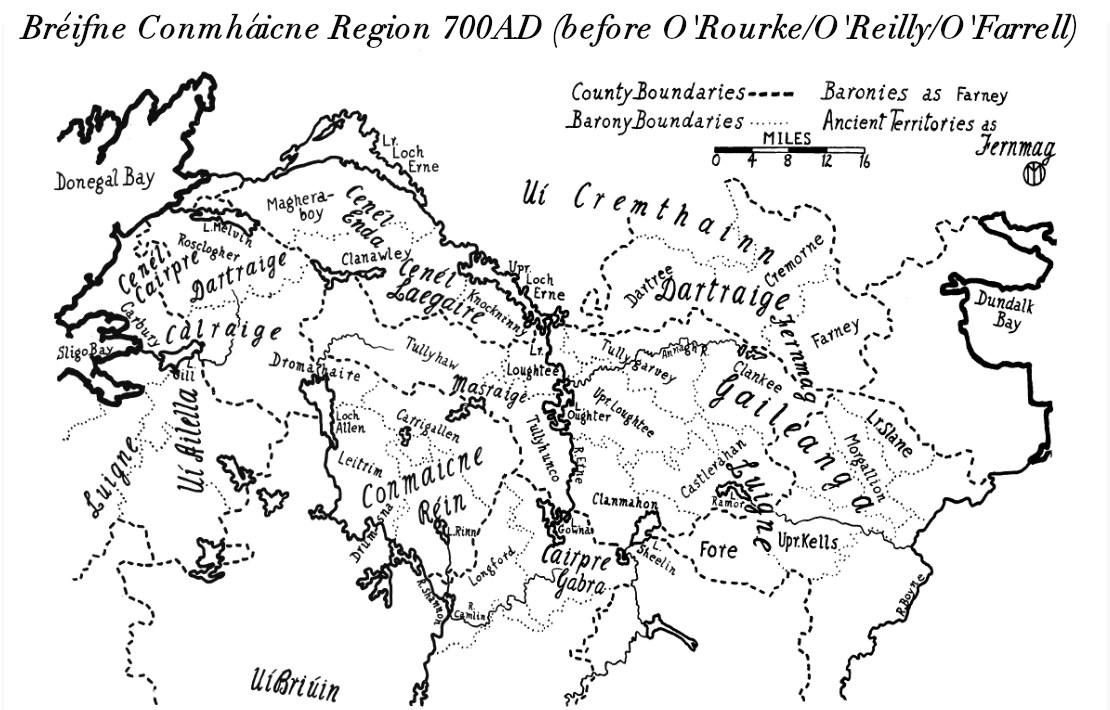
O'Reilly
O'Reilly () is a common Irish surname. The O'Reillys were historically the kings of East Bréifne in what is today County Cavan. The clan were part of the Connachta's Uí Briúin Bréifne kindred and were closely related to the Ó Ruairc (O'Rourkes) of West Bréifne. O'Reilly is ranked tenth in the top twenty list of most common Irish surnames. It is also the patronymic form of the Irish name Reilly (). The name is commonly found throughout Ireland, with the greatest concentration of the surname found in County Cavan followed by Longford, Meath, Westmeath, Fermanagh and Monaghan, and the Province of Leinster. Naming conventions Overview Usually anglicised as Reilly, O'Reilly or Riley, the original form of the name, Ó Raghallaigh, denotes "descendant of Raghallach". The Ó Raghallaigh family were part of the Connachta, with the eponymous Raghallach said to have died at the Battle of Clontarf in 1014. The family became the kings of East Breifne, modern-day Coun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Crown
The Crown is a political concept used in Commonwealth realms. Depending on the context used, it generally refers to the entirety of the State (polity), state (or in federal realms, the relevant level of government in that state), the executive government specifically or only to the monarch and their Viceroy, direct representatives. The term can be used to refer to the rule of law; or to the functions of executive (government), executive (the Crown-King-in-Council, in-council), legislative (the Crown-in-parliament), and judicial (the Crown on the bench) governance and the civil service. The concept of the Crown as a corporation sole developed first in the Kingdom of England as a separation of the physical crown and property of the kingdom from the person and personal property of the monarch. It spread through English and later British colonisation and developed into an imperial crown, which rooted it in the legal lexicon of all 15 Commonwealth realms, their various dependencies, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anglo-Irish People
Anglo-Irish people () denotes an ethnic, social and religious grouping who are mostly the descendants and successors of the English Protestant Ascendancy in Ireland. They mostly belong to the Anglican Church of Ireland, which was the State religion, established church of Ireland until 1871, or to a lesser extent one of the English Dissenters, English Dissenting churches, such as the Methodism, Methodist Church, though some were Catholic Church, Catholics. They often defined themselves as simply "British", and less frequently "Anglo-Irish", "Irish" or "English". Many became eminent as administrators in the British Empire and as senior Irish military diaspora#Britain, army and naval officers since the Kingdom of England and Kingdom of Great Britain, Great Britain were in a real union with the Kingdom of Ireland for over a century, before politically uniting into the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland in 1801. The term is not usually applied to Presbyterianism, Presbyteri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cavan Town
Cavan ( ; ) is the county town of County Cavan in Ireland. The town lies in Ulster, near the border with County Fermanagh in Northern Ireland. The town is bypassed by the main N3 road that links Dublin (to the south) with Enniskillen, Ballyshannon and Donegal Town (to the north). History Gaelic Cavan 1300–1607 Cavan was founded by the Irish clan chief and Lord of East Breifne, Giolla Íosa Ruadh O’Reilly, between 1300 and his death in 1330. During his lordship, a friary run by the Dominican Order was established close to the O’Reilly stronghold at Tullymongan and was at the centre of the settlement close to a crossing over the river and to the town's marketplace. It is recorded that the (Cavan) Dominicans were expelled in 1393, replaced by an Order of Conventual Franciscan friars. The friary's location is marked by an eighteenth-century tower in the graveyard at Abbey Street which appears to incorporate remains of the original medieval friary tower. The imprint of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cootehill
Cootehill (; ) is a market town and townland in County Cavan, Ireland. Cootehill was formerly part of the neighbouring townland of Munnilly. Both townlands lie within the barony of Tullygarvey. Cootehill is 20 km north-east of Cavan town and 20 km south-west of Monaghan town. As of the 2022 census, the population was 1,856. The English language name of the town is a portmanteau of "Coote" and "Hill", the family names of a local 18th century landowning family. Name The town's Irish name, ''Muinchille'', derives from the Irish language term meaning a ridge or "sleeve". The town's name in English, Cootehill, is a portmanteau attributed to the intermarriage of the landowning Coote and Hill families in the early 1700s. This involved the marriage of Thomas Coote (c. 1620–25 Nov 1671) and Frances Hill from Hillsborough, County Down, who were involved in the linen trade. The Coote family of Cootehill had some notable members, including the aforementioned Thomas Coote w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
R188 Road (Ireland)
The R188 road is a Regional road (Ireland), regional road in Republic of Ireland, Ireland, located in County Cavan and County Monaghan. References Regional roads in the Republic of Ireland Roads in County Cavan Roads in County Monaghan {{Ireland-road-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tullygarvey
Tullygarvey () is one of eight Baronies in the County of Cavan. The area has been in constant occupation since pre-4000 BC. The Barony of Tullygarvey consists of the parishes of Kill and Drung and parts of Annagh, Drumgoon and Laragh. Tullygarvey derives its name from the Irish meaning "Gairbhéith's household", Gairbhéith was a member of the Uí Briúin dynasty of Connacht. He was an ancestor of the O'Reilly clan and lived c.860 AD. He was not connected to the McGarvey clan of Donegal. It is located in the northeast of County Cavan, along the Annagh River. History In 1579, East Breifne, then part of Connacht, was made a shire. The shire was named Cavan after the area's main town. The administration remained in the control of the local Irish dynasty and subject to the Brehon and Canon Law. In 1584, Sir John Perrot formed the shire into a county in Ulster Ulster (; or ; or ''Ulster'') is one of the four traditional or historic provinces of Ireland, Irish provin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drung Church Of Ireland - Geograph
Drung may refer to: *Derung people, an ethnic group of China *Derung language Dulong () or Drung, Derung, Rawang, or Trung, is a Sino-Tibetan language in China. Dulong is closely related to the Rawang language of Myanmar (Burma). Although almost all ethnic Derung people speak the language to some degree, most are multil ..., spoken by the Derung people of China * Drung Hill, a hill in County Kerry, Ireland * Drung, County Cavan, a civil parish in Ireland {{Dab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |