|
Drink Offering
The drink offering (Hebrew: נֶסֶך, ''nesekh'') was a form of libation forming one of the sacrifices and offerings of the Law of Moses. Etymology The Hebrew noun ''nesekh'' is formed from the Qal form of the verb ''nasakh'', "to pour," hence "thing poured." The verb and the noun frequently come together, such as ''nasakh lehanesekh'', literally "pour n ita poured thing" as in the only pre-Exodus use, that of Jacob's libation at a pillar in Genesis 35:14. The etymology "poured thing" explains the existence of the rarer secondary use of the verb ''nasakh'' for "cast" (an idol), and the noun ''nesekh'' for a "thing poured" (also an idol). Hebrew Bible The drink offering accompanied various sacrifices and offerings on various feast days. Usually the offering was of wine, but in one instance also of "strong drink" (Numbers 28:7). This "strong drink" (Hebrew ''shekhar'' שֵׁכָר, Septuagint ''sikera'' σίκερα as Luke 1:15, but also ''methusma'' in Judges 13:4 and Micah 2: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hebrew Language
Hebrew (; ''ʿÎbrit'') is a Northwest Semitic language within the Afroasiatic language family. A regional dialect of the Canaanite languages, it was natively spoken by the Israelites and remained in regular use as a first language until after 200 CE and as the liturgical language of Judaism (since the Second Temple period) and Samaritanism. The language was revived as a spoken language in the 19th century, and is the only successful large-scale example of linguistic revival. It is the only Canaanite language, as well as one of only two Northwest Semitic languages, with the other being Aramaic, still spoken today. The earliest examples of written Paleo-Hebrew date back to the 10th century BCE. Nearly all of the Hebrew Bible is written in Biblical Hebrew, with much of its present form in the dialect that scholars believe flourished around the 6th century BCE, during the time of the Babylonian captivity. For this reason, Hebrew has been referred to by Jews as '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tel Aviv
Tel Aviv-Yafo ( or , ; ), sometimes rendered as Tel Aviv-Jaffa, and usually referred to as just Tel Aviv, is the most populous city in the Gush Dan metropolitan area of Israel. Located on the Israeli Mediterranean coastline and with a population of 495,600, it is the economic and technological center of the country and a global high tech hub. If East Jerusalem is considered part of Israel, Tel Aviv is the country's second-most-populous city, after Jerusalem; if not, Tel Aviv is the most populous city, ahead of West Jerusalem. Tel Aviv is governed by the Tel Aviv-Yafo Municipality, headed by Mayor Ron Huldai, and is home to most of Israel's foreign embassies. It is a beta+ world city and is ranked 53rd in the 2022 Global Financial Centres Index. Tel Aviv has the third- or fourth-largest economy and the largest economy per capita in the Middle East. Tel Aviv is ranked the 4th top global startup ecosystem hub. The city currently has the highest cost of living in the wor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
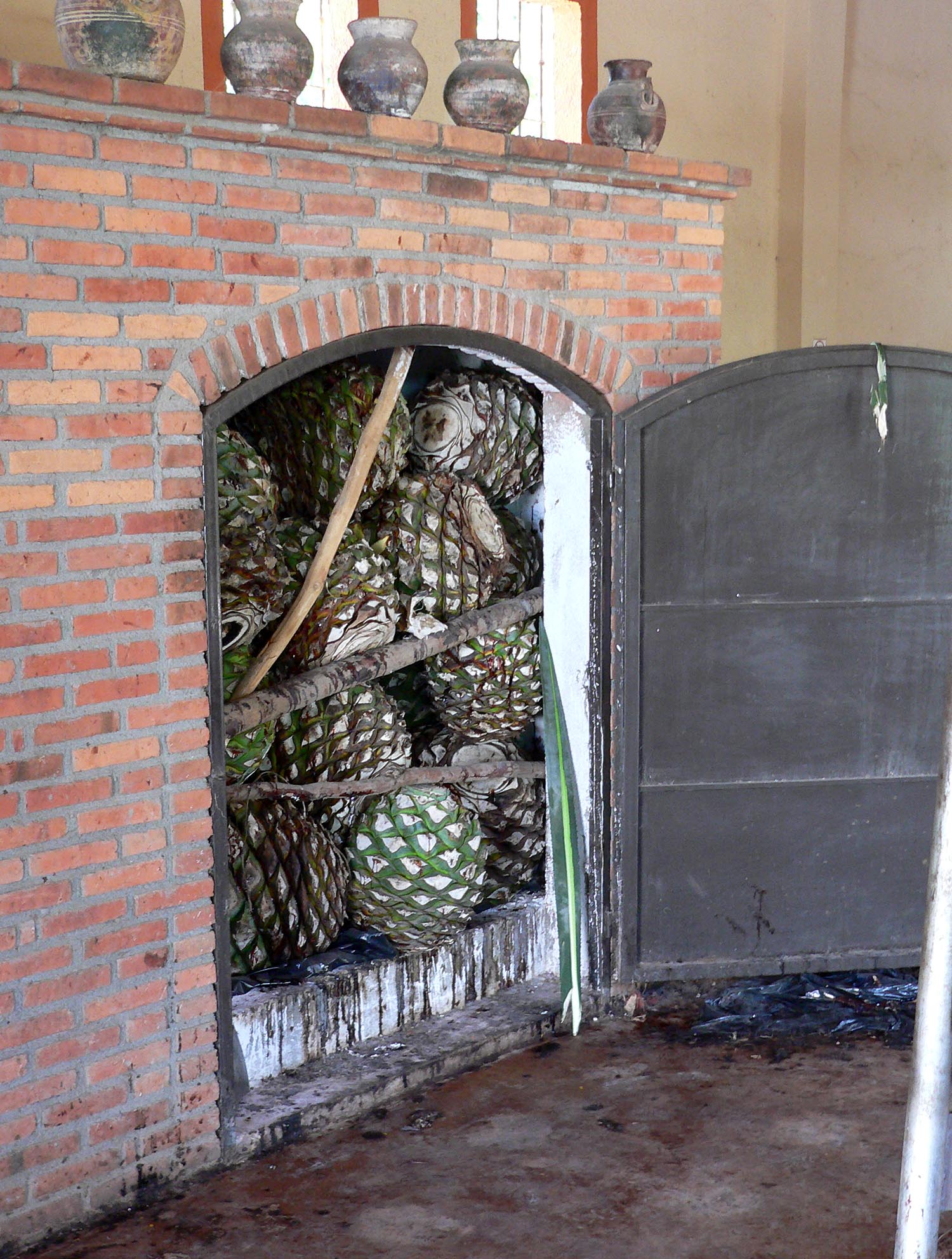
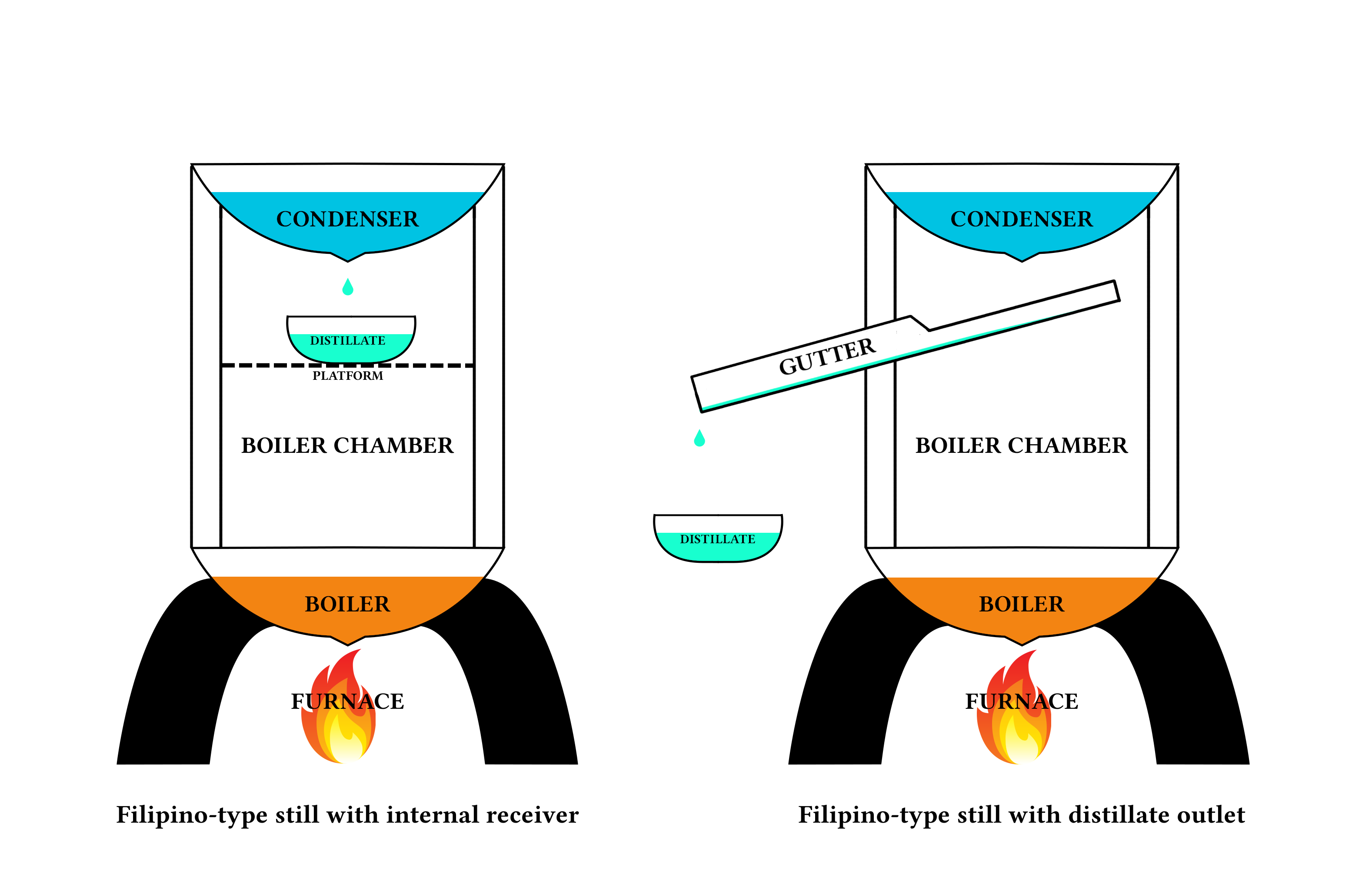
Mezcal
Mezcal (, ), sometimes spelled mescal, is a liquor, distilled alcoholic beverage made from any type of agave. Agaves or magueys are endemic to the Americas and found globally as ornamental plants. The ''Agave'' genus is a member of the Agavoideae subfamily of the Asparagaceae plant family which has list of Agave species, almost 200 species. Mezcal is made from over 30 ''Agave'' species, varieties, and subvarieties. Native fermented drinks from agave plants, such as ''pulque'', existed before the arrival of the Spanish, but the origin of mezcal is tied to the introduction of Filipino-type stills to New Spain by Filipino people, Filipino migrants via the Manila galleons in the late 1500s and early 1600s. These stills were initially used to make ''vino de coco'', but they were quickly adopted by the indigenous peoples of the Pacific coastal regions of Mexico and applied to the distillation of agave to make mezcal. Mezcal is made from the heart of the agave plant, called the . Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tequila
Tequila (; ) is a liquor, distilled beverage made from the blue agave plant, primarily in the area surrounding the city of Tequila, Jalisco, Tequila northwest of Guadalajara, Jalisco, Guadalajara, and in the Jaliscan Highlands (''Los Altos (Jalisco), Los Altos de Jalisco'') of the central western Mexican state of Jalisco. The red volcanic soils in the region of Tequila are well suited for growing the blue agave, and more than 300 million plants are harvested there each year. Agave grows differently depending on the region. Blue agaves grown in the highlands Los Altos region are larger and sweeter in aroma and taste. Agaves harvested in the valley region have a more herbaceous fragrance and flavor. Due to its historical and cultural importance, the region near Tequila was declared a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 2006, the ''Agave Landscape and Ancient Industrial Facilities of Tequila''. Tequila differs from other mezcals—distilled spirits from the agave plant—because it is m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
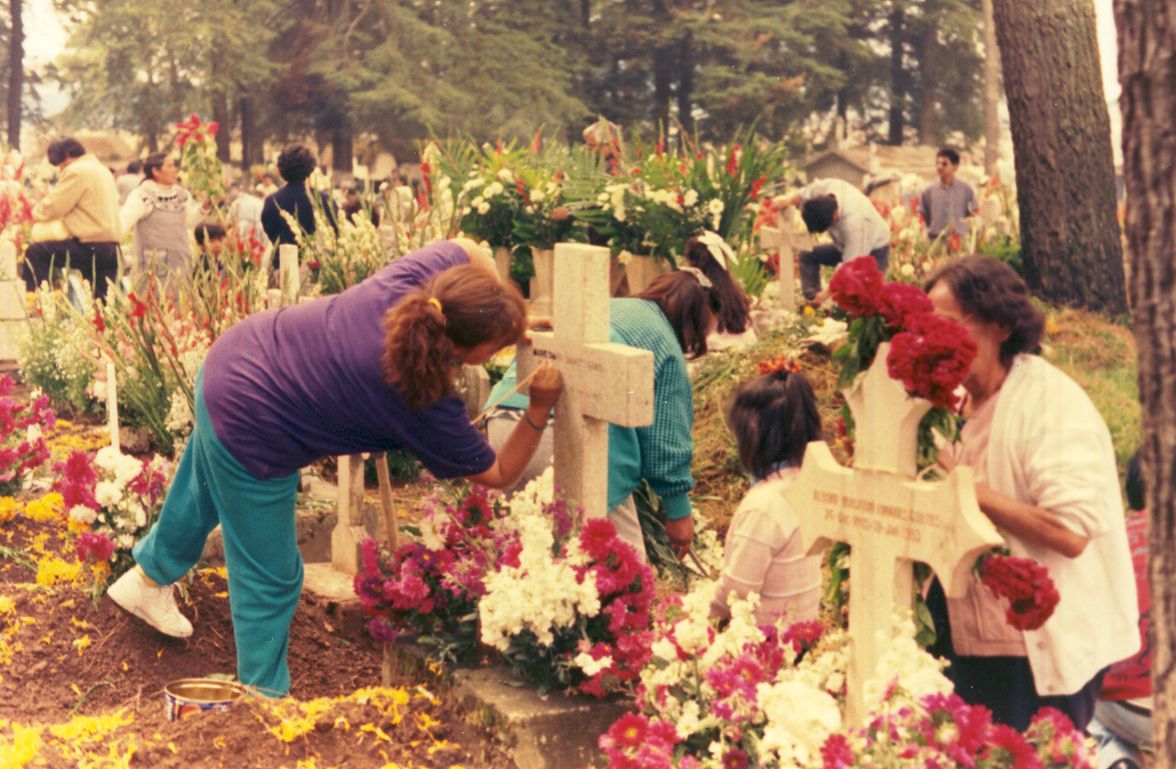
Día De Los Muertos
The Day of the Dead () is a holiday traditionally celebrated on November 1 and 2, though other days, such as October 31 or November 6, may be included depending on the locality. The multi-day holiday involves family and friends gathering to pay respects and remember friends and family members who have died. These celebrations can take a humorous tone, as celebrants remember amusing events and anecdotes about the departed. It is widely observed in Mexico, where it largely developed, and is also observed in other places, especially by people of Mexican heritage. The observance falls during the Christian period of Allhallowtide. Some argue that there are Indigenous Mexican or ancient Aztec influences that account for the custom, though others see it as a local expression of the Allhallowtide season that was brought to the region by the Spanish; the Day of the Dead has become a way to remember those forebears of Mexican culture. The Day of the Dead is largely seen as having a fest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
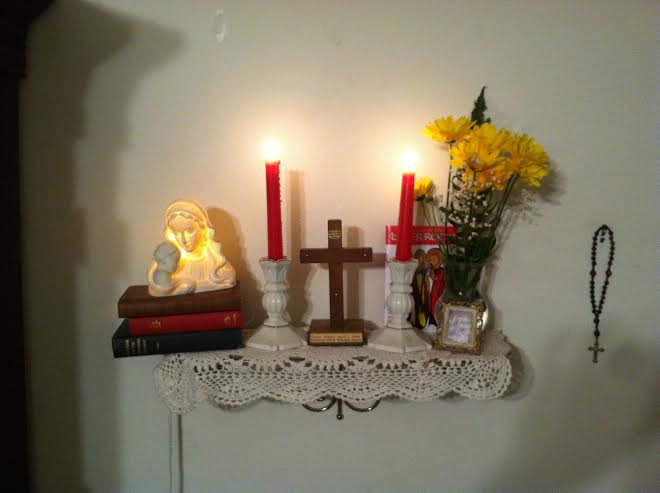
Home Altar
A home altar or family altar is a shrine kept in the home of some Western Christian families used for Christian prayer and family worship. Home altars often contain a cross or crucifix, an image of Jesus Christ, a copy of the Bible (especially a Family Bible), a breviary and/or other prayer book, a daily devotional, and prayer beads, among other religious articles specific to the individual's Christian denomination, for example, the images of the saints for Catholics, the Small Catechism for Lutherans, and the Anglican prayer beads for Anglicans. History ''The Christian Treasury'' traces the origin of the family altar to the prophet Abraham erecting one in the Old Testament (). Since at least the 2nd century, believers such as Hipparchus, hung or painted a Christian cross, to which they prostrated in front of, on the eastern wall of their home in order to indicate the eastward direction of prayer during the seven fixed prayer times, as an "expression of their undying beli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ofrenda
An ''ofrenda'' (Spanish: "Sacrifice, offering") is the offering placed in a home altar during the annual and traditionally Mexican ''Día de los Muertos'' celebration. An ''ofrenda'', which may be quite large and elaborate, is usually created by the family members of a person who has died and is intended to welcome the deceased to the altar setting. __TOC__ Background This display coincides with the Mexico, Día de Muertos, which is a tradition some believe originated with the Aztecs, though others dispute this. The Aztec culture considered souls to continuously live and enter different realms when a body would die. This view the Aztecs held was commingled with the Christian beliefs that the soul is eternal (whether it be in heaven, purgatory, or hell) during the Spanish conquest of the Aztec Empire when the two cultures were merged. The ofrenda is presented in one's home in order to commemorate the souls of loved ones in the family. Regional variations Different regi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aqhat
Danel (, Ugaritic: 𐎄𐎐𐎛𐎍 DNỈL, " El is judge"), father of Aqhat, was a culture hero who appears in an incomplete Ugaritic text of the fourteenth century BCE at Ugarit (now Ras Shamra), Syria. Tale of Aqhat The text in ''Corpus Tablettes Alphabétiques'' '' TA' 17–19 is often referred to as the '' Tale of Aqhat''. Danel was depicted as "judging the cause of the widow, adjudicating the case of the fatherless" in the city gate. He passed through trials: his son Aqhat was destroyed but apparently in the missing conclusion was revived or replaced by Danel's patron god, Rpʼu, who sits and judges with Hadad and Astarte and was likely considered to be the equivalent of El. The text was published and translated in 1936 by Charles Virolleaud and has been extensively analysed since then. The Rephaim The text of ''The Rephaim'', a title given to the text by Mark S. Smith, also mentions Danel, who appears there and in the Tale of Aqhat as "a model figure in family matt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Avodah Zarah (tractate)
''Avodah Zarah'' (Hebrew: , or "foreign worship", meaning "idolatry" or "strange service") is the name of a tractate of the Talmud, located in ''Nezikin'', the fourth Order of the Talmud dealing with damages. The main topic of the tractate is laws pertaining to Jews living amongst Gentiles, including regulations about the interaction between Jews and "avodei ha kochavim", which literally interpreted is "Worshipers of the stars", but is most often translated as "idolaters", "pagans", or "heathen." Mishna The tractate consists of five chapters. The number of mishnayot is according to the standard numbering; however, different versions split up the individual mishnayot, or combine them, and the chapter breaks may vary, as well. Chapter One (nine mishnayot) deals with the prohibition of trade with idolaters around their festivals, such as Saturnalia and Kalenda (so as not to be complicit in the festive idolatry) and with the items that are forbidden to be sold to idolaters ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Babylonian Talmud
The Talmud (; ) is the central text of Rabbinic Judaism and the primary source of Jewish religious law (''halakha'') and Jewish theology. Until the advent of modernity, in nearly all Jewish communities, the Talmud was the centerpiece of Jewish cultural life and was foundational to "all Jewish thought and aspirations", serving also as "the guide for the daily life" of Jews. The Talmud includes the teachings and opinions of thousands of rabbis on a variety of subjects, including halakha, Jewish ethics, philosophy, customs, history, and folklore, and many other topics. The Talmud is a commentary on the Mishnah. This text is made up of 63 tractates, each covering one subject area. The language of the Talmud is Jewish Babylonian Aramaic. Talmudic tradition emerged and was compiled between the destruction of the Second Temple in 70 CE and the Arab conquest in the early seventh century. Traditionally, it is thought that the Talmud itself was compiled by Rav Ashi and Ravina II a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Terumot
Terumot (, lit. "Priestly dues" and often, "heave-offering") is the sixth tractate of '' Seder Zeraim'' ("Order of Seeds") of the Mishnah and of the Jerusalem Talmud. This tractate discusses the laws of teruma, a gift of produce that an Israelite farmer was required to set aside and give to a ''kohen'' (priest). There were two kinds of ''terumot'' given to the priest: the regular heave-offering, known also as the ''terumah gedolah'' ("great heave-offering"), which the Israelites were required to give to the priest from the produce of their fields; the other was the ''terumat ma'aser'' ("tithe of the heave-offering"), namely, the gift that the Levites were required to put aside for the priests from the tithe which ordinary Israelites had been required to give to them. The laws detailed in this tractate are derived from the Torah in and , and for ''terumat ma'aser'' from . The mitzvah (commandment) applies only to produce grown in the Land of Israel and continues to be obs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jerusalem Talmud
The Jerusalem Talmud (, often for short) or Palestinian Talmud, also known as the Talmud of the Land of Israel, is a collection of rabbinic notes on the second-century Jewish oral tradition known as the Mishnah. Naming this version of the Talmud after Palestine or the Land of Israelrather than Jerusalemis considered more accurate, as the text originated mainly from Galilee in Byzantine Palaestina Secunda rather than from Jerusalem, where no Jews were allowed to live at the time. The Jerusalem Talmud predates its counterpart, the Babylonian Talmud (known in Hebrew as the ), by about a century. It was written primarily in Galilean Aramaic. It was compiled between the late fourth century to the first half of the fifth century. Both versions of the Talmud have two parts, the Mishnah (of which there is only one version), which was finalized by Judah ha-Nasi around the year 200 CE, and either the Babylonian or the Jerusalem Gemara. The Gemara is what differentiates the Jerusalem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |