|
Dreidel
A dreidel, also dreidle or dreidl ( ; yi, דרײדל, dreydl, plural: ''dreydlech''; he, סביבון, sevivon) is a four-sided spinning top, played during the Jewish holiday of Hanukkah. The dreidel is a Jewish variant on the teetotum, a gambling toy found in many European cultures. Each side of the dreidel bears a letter of the Hebrew alphabet: ('' nun''), ('' gimel''), ('' hei''), (''shin''). These letters are represented in Yiddish as a mnemonic for the rules of a gambling game derived from teetotum played with a dreidel: ''nun'' stands for the word (''nisht'', "not", meaning "nothing"), ''gimel'' for (''gants'', "entire, whole"), ''hei'' for (''halb'', "half"), and ''shin'' for (''shtel arayn'', "put in"). However, according to folk etymology, they represent the Hebrew phrase (''nes gadól hayá sham'', "a great miracle happened there"), referring to the miracle of the cruse of oil. For this reason, most dreidels in Israel replace the letter ''shin'' with a l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dreidel 001
A dreidel, also dreidle or dreidl ( ; yi, דרײדל, dreydl, plural: ''dreydlech''; he, סביבון, sevivon) is a four-sided spinning top, played during the Jewish holiday of Hanukkah. The dreidel is a Jewish variant on the teetotum, a gambling toy found in many European cultures. Each side of the dreidel bears a letter of the Hebrew alphabet: ('' nun''), (''gimel''), ('' hei''), ('' shin''). These letters are represented in Yiddish as a mnemonic for the rules of a gambling game derived from teetotum played with a dreidel: ''nun'' stands for the word (''nisht'', "not", meaning "nothing"), ''gimel'' for (''gants'', "entire, whole"), ''hei'' for (''halb'', "half"), and ''shin'' for (''shtel arayn'', "put in"). However, according to folk etymology, they represent the Hebrew phrase (''nes gadól hayá sham'', "a great miracle happened there"), referring to the miracle of the cruse of oil. For this reason, most dreidels in Israel replace the letter ''shin'' with a le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hanukkah
or English translation: 'Establishing' or 'Dedication' (of the Temple in Jerusalem) , nickname = , observedby = Jews , begins = 25 Kislev , ends = 2 Tevet or 3 Tevet , celebrations = Lighting candles each night. Singing special songs, such as Ma'oz Tzur. Reciting the Hallel prayer. Eating foods fried in oil, such as latkes and sufganiyot, and dairy foods. Playing the '' dreidel'' game, and giving Hanukkah ''gelt'' , type = Jewish , significance = The Maccabees successfully revolted against Antiochus IV Epiphanes. According to the Talmud, the Temple was purified and the wicks of the menorah miraculously burned for eight days, even though there was only enough sacred oil for one day's lighting. , relatedto = Purim, as a rabbinically decreed holiday. , date = , date = , date = , date = , date = Hanukkah (; ) is a Jewish festival commemorating the recovery of Jerusalem and subsequent rededication of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dreydlekh
Dreydlekh (plural of ''dreidel'') or "spins" are musical ornaments of klezmer music, particularly violin, used to produce its characteristic "tear in the voice" sound., by Yale Strom, "The absolutely complete klezmer songbook", 2006, Introduction/ref>Yale Strom, ''Shpil: The Art of Playing Klezmer'', 2012p. 94/ref> The main ''dreydlekh'' are ''glitshn'' (glissandos), ''krekhtsn'' ("sobs", "wails"), ''kneytshn'' ("wrinkles"), ''tshoks'' (a kind of bent notes of cackle-like sound), and flageolets (string harmonics). Sometimes the term ''dreydlekh'' is used only for trills, while other use it for all Klezmer ornaments. Krekhts or krekhtsn (Yiddish for "sobs") are kind of ''dreydlekh'' ornamentation in klezmer music, especially on the violin. In an article about Jewish music in Romania, Bob Cohen of Di Naye Kapelye describes krekhts as "a sort of weeping or hiccoughing combination of backwards slide and flick of the little finger high above the base note, while the bow does, we ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jewish Holiday
Jewish holidays, also known as Jewish festivals or ''Yamim Tovim'' ( he, ימים טובים, , Good Days, or singular , in transliterated Hebrew []), are holidays observed in Judaism and by JewsThis article focuses on practices of mainstream Rabbinic Judaism. Karaite Judaism#The calendar, Karaite Jews and Samaritans#Samaritanism, Samaritans also observe the biblical festivals, but not in an identical fashion and not always at exactly the same time. throughout the Hebrew calendar. They include religious, cultural and national elements, derived from three sources: biblical ''mitzvot'' ("commandments"), rabbinic mandates, and the history of Judaism and the State of Israel. Jewish holidays occur on the same dates every year in the Hebrew calendar, but the dates vary in the Gregorian. This is because the Hebrew calendar is a lunisolar calendar (based on the cycles of both the sun and moon), whereas the Gregorian is a solar calendar. General concepts Groupings Certain term ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
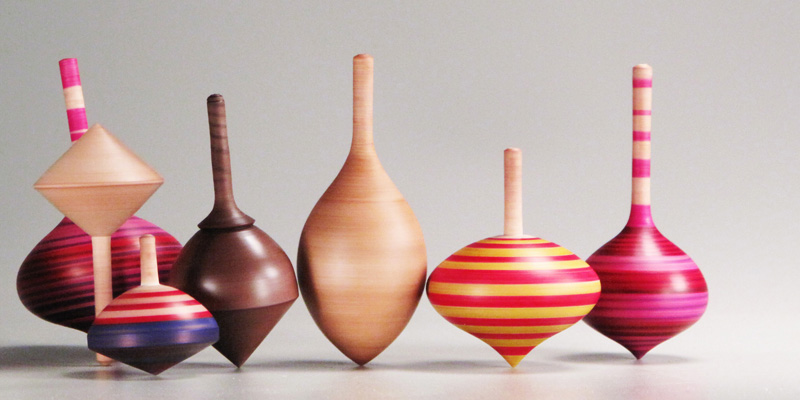
Spinning Top
A spinning top, or simply a top, is a toy with a squat body and a sharp point at the bottom, designed to be spun on its vertical axis, balancing on the tip due to the gyroscopic effect. Once set in motion, a top will usually wobble for a few seconds, spin upright for a while, then start to wobble again with increasing amplitude as it loses energy, and finally tip over and roll on its side. Tops exist in many variations and materials, chiefly wood, metal, and plastic, often with a metal tip. They may be set in motion by twirling a handle with the fingers, by pulling a rope coiled around the body, or by means of a built-in auger (spiral plunger). Such toys have been used since antiquity in solitary or competitive games, where each player tries to keep one's top spinning for as long as possible, or achieve some other goal. Some tops have faceted bodies with symbols or inscriptions, and are used like dice to inject randomness into games, or for divination and ritual purposes. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
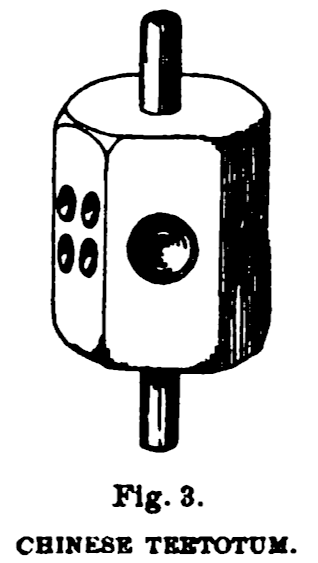
Teetotum
A teetotum (or T-totum) is a form of spinning top most commonly used for gambling games. It has a polygonal body marked with letters or numbers, which indicate the result of each spin. Usage goes back to (at least) ancient Greeks and Romans, with the popular "put and take" gambling version going back to medieval times. Description In its earliest form the body was square (in some cases via a stick through a regular six-sided die), marked on the four sides by the letters A ( Lat. ''aufer'', take) indicating that the player takes one from the pool, D (Lat. ''depone'', put down) when a fine has to be paid, N (Lat. ''nihil'', nothing), and T (Lat. ''totum'', all), when the whole pool is to be taken. Other accounts give such letters as P, N, D (''dimidium'', half), and H or T or other combinations of letters. Some other combinations that could be found were NG, ZS, TA, TG, NH, ND, SL and M, which included the Latin terms ''Zona Salve'' ("save all"), ''Tibi Adfer'' ("take all"), '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nun (letter)
Nun is the fourteenth letter of the Semitic abjads, including Phoenician Nūn , Hebrew Nun , Aramaic Nun , Syriac Nūn ܢܢ, and Arabic Nūn (in abjadi order). Its numerical value is 50. It is the third letter in Thaana (), pronounced as "noonu". In all languages, it represents the alveolar nasal /n/. The Phoenician letter gave rise to the Greek nu (Ν), Etruscan , Latin N, and Cyrillic Н. Origins Nun is believed to be derived from an Egyptian hieroglyph of a snake (the Hebrew word for snake, ''nachash'' begins with a Nun and snake in Aramaic is ''nun'') or eel. Some have hypothesized a hieroglyph of fish in water as its origin (in Arabic, ' means large fish or whale). The Phoenician letter was named "fish", but the glyph has been suggested to descend from a hypothetical Proto-Canaanite "snake", based on the name in Ethiopic, ultimately from a hieroglyph representing a snake, I10 (see Middle Bronze Age alphabets). Hebrew Nun Hebrew spelling: ;The letter in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Klezmer
Klezmer ( yi, קלעזמער or ) is an instrumental musical tradition of the Ashkenazi Jews of Central and Eastern Europe. The essential elements of the tradition include dance tunes, ritual melodies, and virtuosic improvisations played for listening; these would have been played at weddings and other social functions. The musical genre incorporated elements of many other musical genres including Ottoman (especially Greek and Romanian) music, Baroque music, German and Slavic folk dances, and religious Jewish music. As the music arrived in the United States, it lost some of its traditional ritual elements and adopted elements of American big band and popular music. Among the European-born klezmers who popularized the genre in the United States in the 1910s and 1920s were Dave Tarras and Naftule Brandwein; they were followed by American-born musicians such as Max Epstein, Sid Beckerman and Ray Musiker. After the destruction of Jewish life in Eastern Europe during the Holoca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sefer Torah
A ( he, סֵפֶר תּוֹרָה; "Book of Torah"; plural: ) or Torah scroll is a handwritten copy of the Torah, meaning the five books of Moses (the first books of the Hebrew Bible). The Torah scroll is mainly used in the ritual of Torah reading during Jewish prayers. At other times, it is stored in the holiest spot within a synagogue, the Torah ark, which is usually an ornate curtained-off cabinet or section of the synagogue built along the wall that most closely faces Jerusalem, the direction Jews face when praying. The text of the Torah is also commonly printed and bound in book form for non-ritual functions, called a (plural ) ("five-part", for the five books of Moses), and is often accompanied by commentaries or translations. History The En-Gedi Scroll is an ancient Hebrew parchment found in 1970 at Ein Gedi, Israel. Radiocarbon testing dates the scroll to the third or fourth century CE (210–390 CE), although paleographical considerations suggest that the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Torah
The Torah (; hbo, ''Tōrā'', "Instruction", "Teaching" or "Law") is the compilation of the first five books of the Hebrew Bible, namely the books of Genesis, Exodus, Leviticus, Numbers and Deuteronomy. In that sense, Torah means the same as Pentateuch or the Five Books of Moses. It is also known in the Jewish tradition as the Written Torah (, ). If meant for liturgic purposes, it takes the form of a Torah scroll (''Sefer Torah''). If in bound book form, it is called '' Chumash'', and is usually printed with the rabbinic commentaries (). At times, however, the word ''Torah'' can also be used as a synonym for the whole of the Hebrew Bible or Tanakh, in which sense it includes not only the first five, but all 24 books of the Hebrew Bible. Finally, Torah can even mean the totality of Jewish teaching, culture, and practice, whether derived from biblical texts or later rabbinic writings. The latter is often known as the Oral Torah. Representing the core of the Jewish spir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seleucid Empire
The Seleucid Empire (; grc, Βασιλεία τῶν Σελευκιδῶν, ''Basileía tōn Seleukidōn'') was a Greek state in West Asia that existed during the Hellenistic period from 312 BC to 63 BC. The Seleucid Empire was founded by the Macedonian general Seleucus I Nicator, following the division of the Macedonian Empire originally founded by Alexander the Great. After receiving the Mesopotamian region of Babylonia in 321 BC, Seleucus I began expanding his dominions to include the Near Eastern territories that encompass modern-day Iraq, Iran, Afghanistan, Syria, all of which had been under Macedonian control after the fall of the former Persian Achaemenid Empire. At the Seleucid Empire's height, it had consisted of territory that had covered Anatolia, Persia, the Levant, and what are now modern Iraq, Kuwait, Afghanistan, and parts of Turkmenistan. The Seleucid Empire was a major center of Hellenistic culture. Greek customs and language were privileged; the wide v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antiochus IV
Antiochus IV Epiphanes (; grc, Ἀντίοχος ὁ Ἐπιφανής, ''Antíochos ho Epiphanḗs'', "God Manifest"; c. 215 BC – November/December 164 BC) was a Greek Hellenistic king who ruled the Seleucid Empire from 175 BC until his death in 164 BC. He was a son of King Antiochus III the Great. Originally named Mithradates (alternative form ''Mithridates''), he assumed the name Antiochus after he ascended the throne. Notable events during Antiochus's reign include his near-conquest of Ptolemaic Egypt, his persecution of the Jews of Judea and Samaria, and the rebellion of the Jewish Maccabees. Antiochus's accession to the throne was controversial, and he was seen as a usurper by some. After the death of his brother Seleucus IV Philopator in 175 BC, the "true" heir should have been Seleucus's son Demetrius I. However, Demetrius I was very young and a hostage in Rome at the time, and Antiochus seized the opportunity to declare himself king instead, successfully ral ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)


