|
Dravidianism
Dravidian nationalism, or Dravidianism, developed in Madras Presidency which comprises the four major ethno-linguistic groups in South India. This idea was popularized during the 1930s to 1950s by a series of widespread and popular movements and organizations that contended that the South Indians (Dravidian people) formed a racial and a cultural entity that was different from the North Indians. Dravidianists argue that the Brahmins and other upper castes were originally Aryan migrants from outside of India, and that they imposed their language, Sanskrit, religion and heritage on the Dravidian people. The claim is based on widespread evidence of the genetic differences between North and South Indians, the linguistic differences between the two regions, and the fact that Indo Aryan Languages share a common ancestor with European languages such as English and likely originated outside of India. The hypothesis has ancient origins based on Sangam literature and the concept of Tami ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
All India Anna Dravida Munnetra Kazhagam
The All India Anna Dravida Munnetra Kazhagam (; AIADMK, also abbreviated as ADMK), also shortened to Anna Dravida Munnetra Kazhagam, is an Indian Regionalism (politics), regional political party with great influence in the Federated state, state of Tamil Nadu and the union territory of Puducherry (union territory), Puducherry. It is a Dravidian parties, Dravidian party founded by the former chief minister of Tamil Nadu M. G. Ramachandran (M.G.R.) at Madurai on 17 October 1972 as a breakaway faction from the Dravida Munnetra Kazhagam after M. Karunanidhi expelled him from the party for demanding an account as the party treasurer. The party is adhering to the policies of socialism and secularism based on the principles of C. N. Annadurai (Anna) collectively coined as ''Annaism'' by M.G.R. The party has won a seven-time majority in the Tamil Nadu Legislative Assembly and has emerged as the most successful political outfit in the state's history. It is currently the main Official Op ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marumalarchi Dravida Munnetra Kazhagam
The Marumalarchi Dravida Munnetra Kazhagam (; MDMK) is a political party active in the Indian state of Tamil Nadu. It was established by Vaiko in 1994 after he left the Dravida Munnetra Kazhagam. The headquarters of the party is called Thayagam, which is located at Rukmini Lakshmipathi Salai, Egmore, Chennai. History Formation Vaiko was a member of Rajya Sabha and a party activist of Dravida Munnetra Kazhagam (DMK). Vaiko was a member of the party from his initial student days and actively participated in the party agitations and courted imprisonment several times. He was elected thrice to the Rajya Sabha. In 1994, he was forced out of the parent body as he was seen as a threat to DMK chief Karunanidhi's son, M.K. Stalin. Vaiko along with some district secretaries announced the decision to start a rival party, which became the MDMK. Support for Sri Lankan Tamils Vaiko voiced support for Tamils during the Sri Lankan Civil War, including for the Liberation Tigers of Tamil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dravida Munnetra Kazhagam
The Dravida Munnetra Kazhagam (; ; DMK) is an Indian political party based in the state of Tamil Nadu, where it is currently the ruling party, and the union territory of Puducherry (union territory), Puducherry, where it is currently the main opposition. The DMK was founded on 17 September 1949 by C. N. Annadurai (Anna) as a breakaway faction from the Dravidar Kazhagam headed by Periyar. DMK was headed by Annadurai as the general secretary from 1949 until his death on 4 February 1969. He also served as the chief minister of Tamil Nadu from 1967 to 1969. Under Annadurai, in 1967, DMK became the first party, other than the Indian National Congress, to win the state-level elections with a clear majority on its own in any state in India. M. Karunanidhi (Kalaignar) followed Annadurai as the first president of the party from 1969 until his death on 7 August 2018. He also served as the Chief Minister for five non-consecutive terms, in two of which he was dismissed by the Union governm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Madras Presidency
The Madras Presidency or Madras Province, officially called the Presidency of Fort St. George until 1937, was an administrative subdivision (province) of British India and later the Dominion of India. At its greatest extent, the presidency included most of southern India, including all of present-day Andhra Pradesh, almost all of Tamil Nadu and parts of Kerala, Karnataka, Odisha and Telangana in the modern day. The city of Madras was the winter capital of the presidency and Ooty (Udagamandalam) was the summer capital. The Madras State was neighboured by the Kingdom of Mysore to the northwest, the Kingdom of Cochin and Kingdom of Travancore to the southwest, the Kingdom of Pudukkottai in the center, and the Hyderabad State to the north. Some parts of the presidency were also flanked by Bombay State ( Konkan Districts) and Central States (modern Madhya Pradesh). In 1639, the English East India Company purchased the village of Madraspatnam and one year later it establis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Far-right Politics
Far-right politics, often termed right-wing extremism, encompasses a range of ideologies that are marked by ultraconservatism, authoritarianism, ultranationalism, and Nativism (politics), nativism. This political spectrum situates itself on the far end of the right-wing politics, right, distinguished from more mainstream right-wing ideologies by its opposition to Liberal democracy, liberal democratic norms and emphasis on Exclusivism, exclusivist views. Far-right ideologies have historically included fascism, Nazism, and Falangism, while contemporary manifestations also incorporate neo-fascism, neo-Nazism, white supremacy, and various other movements characterized by chauvinism, xenophobia, and theocratic or reactionary beliefs. Key to the far-right worldview is the notion of societal purity, often invoking ideas of a homogeneous "national" or "ethnic" community. This view generally promotes organicism, which perceives society as a unified, natural entity under threat from D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1930s Establishments In British India
Year 193 ( CXCIII) was a common year starting on Monday of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Sosius and Ericius (or, less frequently, year 946 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 193 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years. Events By place Roman Empire * January 1 – Year of the Five Emperors: The Roman Senate chooses Publius Helvius Pertinax, against his will, to succeed the late Commodus as Emperor. Pertinax is forced to reorganize the handling of finances, which were wrecked under Commodus, to reestablish discipline in the Roman army, and to suspend the food programs established by Trajan, provoking the ire of the Praetorian Guard. * March 28 – Pertinax is assassinated by members of the Praetorian Guard, who storm the imperial palace. The Empire is auctioned off; Marcus Didius Julianus the highest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Delhi
New Delhi (; ) is the Capital city, capital of India and a part of the Delhi, National Capital Territory of Delhi (NCT). New Delhi is the seat of all three branches of the Government of India, hosting the Rashtrapati Bhavan, New Parliament House, New Delhi, Sansad Bhavan, and the Supreme Court of India, Supreme Court. New Delhi is a Municipal governance in India, municipality within the NCT, administered by the New Delhi Municipal Council (NDMC), which covers mostly Lutyens' Delhi and a few adjacent areas. The municipal area is part of a larger List of districts in India, administrative district, the New Delhi district. Although colloquially ''Delhi'' and ''New Delhi'' are used interchangeably to refer to the National Capital Territory of Delhi, both are distinct entities, with the municipality and the New Delhi district forming a relatively small part within the megacity of Delhi. The National Capital Region (India), National Capital Region is an even larger entity, compris ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Government Of India
The Government of India (ISO 15919, ISO: Bhārata Sarakāra, legally the Union Government or Union of India or the Central Government) is the national authority of the Republic of India, located in South Asia, consisting of States and union territories of India, 36 states and union territories. The government is led by the president of India (currently ) who largely exercises the executive powers, and selects the Prime Minister of India, prime minister of India and other ministers for aid and advice. Government has been formed by the The prime minister and their senior ministers belong to the Union Council of Ministers, its executive decision-making committee being the Cabinet (government), cabinet. The government, seated in New Delhi, has three primary branches: the legislature, the executive and the judiciary, whose powers are vested in bicameral Parliament of India, Union Council of Ministers (headed by prime minister), and the Supreme Court of India respectively, with a p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Self-determination
Self-determination refers to a people's right to form its own political entity, and internal self-determination is the right to representative government with full suffrage. Self-determination is a cardinal principle in modern international law, binding, as such, on the United Nations as an authoritative interpretation of the Charter of the United Nations, Charter's norms. The principle does not state how the decision is to be made, nor what the outcome should be (whether independence, federation, protectorate, protection, some form of autonomy or full Cultural assimilation, assimilation), and the right of self-determination does not necessarily include a right to an independent state for every ethnic group within a former colonial territory. Further, no right to secession is recognized under international law. The concept emerged with the rise of nationalism in the 19th century and came into prominent use in the 1860s, spreading rapidly thereafter. During and after World War ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
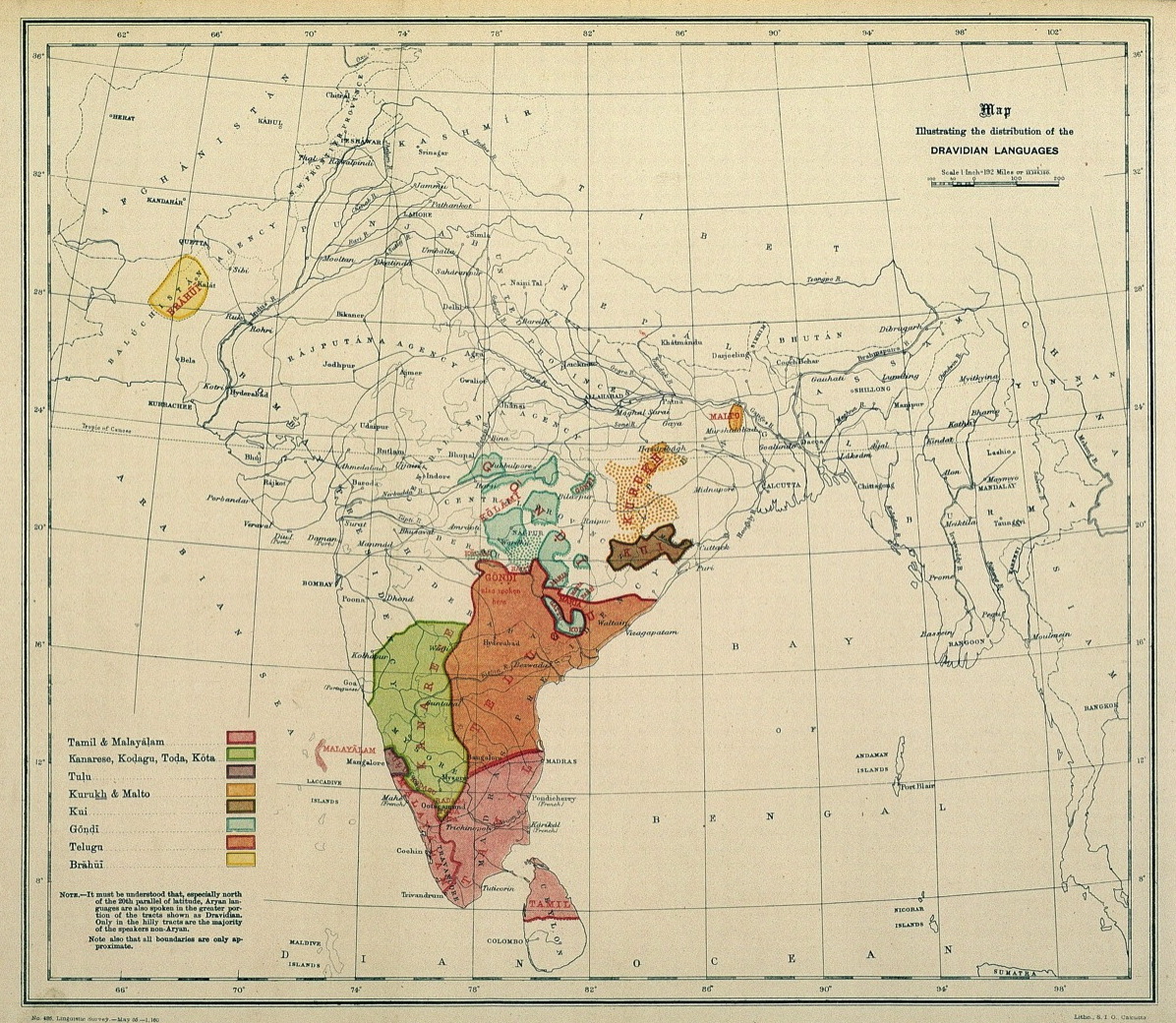
Dravidian Languages
The Dravidian languages are a language family, family of languages spoken by 250 million people, primarily in South India, north-east Sri Lanka, and south-west Pakistan, with pockets elsewhere in South Asia. The most commonly spoken Dravidian languages are (in descending order) Telugu language, Telugu, Tamil language, Tamil, Kannada, and Malayalam, all of which Classical languages of India, have long literary traditions. Smaller literary languages are Tulu language, Tulu and Kodava language, Kodava. Together with several smaller languages such as Gondi language, Gondi, these languages cover the southern part of India and the northeast of Sri Lanka, and account for the overwhelming majority of speakers of Dravidian languages. Malto language, Malto and Kurukh language, Kurukh are spoken in isolated pockets in eastern India. Kurukh is also spoken in parts of Nepal, Bhutan and Bangladesh. Brahui language, Brahui is mostly spoken in the Balochistan region of Pakistan, Sistan and Baluc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dravida Nadu
The Dravida Nadu movement was a separatist movement seeking to create a homeland for the Dravidians by establishing a sovereign state in the predominantly Dravidian-speaking southern regions of British India consisting of Telangana, Andhra Pradesh, Tamil Nadu, Karnataka and Kerala. It was started by the Justice Party under Periyar and later the Dravida Munnetra Kazhagam (DMK) led by C. N. Annadurai. Initially, the demand of Dravida Nadu proponents was limited to Tamil-speaking regions, but it was later expanded to include other Indian states with a majority of Dravidian-speakers (Andhra Pradesh, Telangana, Kerala and Karnataka). Some of the proponents also included parts of Ceylon (Sri Lanka), Orissa and Maharashtra. Other names for the proposed sovereign state included "South India", "Deccan Federation" and "Dakshinapath". The movement for Dravida Nadu was at its height from the 1940s to 1960s, but due to fears of Tamil hegemony, it failed to find any support outside Tam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hindu Nationalism
Hindu nationalism has been collectively referred to as the expression of political thought, based on the native social and cultural traditions of the Indian subcontinent. "Hindu nationalism" is a simplistic translation of . It is better described as "Hindu polity". The native thought streams became highly relevant in Indian history when they helped form a distinctive identity about the Indian polityChatterjee Partha (1986) and provided a basis for questioning colonialism.Peter van der Veer, Hartmut Lehmann, Nation and religion: perspectives on Europe and Asia, Princeton University Press, 1999 p. 90 These also inspired Indian nationalism, Indian nationalists during the Indian independence movement, independence movement based on armed struggle,Li Narangoa, R. B. Cribb ''Imperial Japan and National Identities in Asia'', 1895–1945, Published by Routledge, 2003 p. 78 coercive politics,Bhatt, Chetan, ''Hindu Nationalism: Origins, Ideologies and Modern Myths'', Berg Publishers (20 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |