|
Douglas T. Ross
Douglas Taylor "Doug" Ross (21 December 1929 – 31 January 2007) was an American computer scientist pioneer, and chairman of SofTech, Inc. He is most famous for originating the term CAD for computer-aided design, and is considered to be the father of Automatically Programmed Tools ( APT), a programming language to drive numerical control in manufacturing. His later work focused on a pseudophilosophy he developed and named Plex. Biography Ross was born in China, where his parents both worked as medical missionaries, and he then grew up in the United States in Canandaigua, New York. He received a Bachelor of Science (B.Sc.) ''cum laude'' in mathematics from Oberlin College in 1951, and a Master of Science (M.Sc.) in electrical engineering from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) in 1954. Afterward, he began but didn't finish his Ph.D., at MIT due to his pressing work as head of MIT's Computer Applications Group. In the 1950s, he participated in the MIT Whirlwind I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computer Science
Computer science is the study of computation, information, and automation. Computer science spans Theoretical computer science, theoretical disciplines (such as algorithms, theory of computation, and information theory) to Applied science, applied disciplines (including the design and implementation of Computer architecture, hardware and Software engineering, software). Algorithms and data structures are central to computer science. The theory of computation concerns abstract models of computation and general classes of computational problem, problems that can be solved using them. The fields of cryptography and computer security involve studying the means for secure communication and preventing security vulnerabilities. Computer graphics (computer science), Computer graphics and computational geometry address the generation of images. Programming language theory considers different ways to describe computational processes, and database theory concerns the management of re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canandaigua, New York
Canandaigua () is a city in Ontario County, New York, United States. Its population was 10,576 at the 2020 census. It is the county seat of Ontario County; some administrative offices are at the county complex in the adjacent town of Hopewell.Google Maps (3019 County Complex Drive, Canandaigua, New York) Retrieved Jan. 14, 2015.Ontario County, New York Retrieved Jan. 14, 2015. The city is surrounded by the [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lincoln Laboratory
The MIT Lincoln Laboratory, located in Lexington, Massachusetts, is a United States Department of Defense federally funded research and development center chartered to apply advanced technology to problems of national security. Research and development activities focus on long-term technology development as well as rapid system prototyping and demonstration. Its core competencies are in sensors, integrated sensing, signal processing for information extraction, decision-making support, and communications. These efforts are aligned within ten mission areas. The laboratory also maintains several field sites around the world. The laboratory transfers much of its advanced technology to government agencies, industry, and academia, and has launched more than 100 start-ups. History Origins At the urging of the United States Air Force, the Lincoln Laboratory was created in 1951 at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) as part of an effort to improve the U.S. air defense syste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marchant Calculator
The Marchant Calculating Machine Company was founded in 1911 by Rodney and Alfred Marchant in Oakland, California. The company built mechanical, and then electromechanical calculators which had a reputation for reliability. First models were similar to the Odhner Arithmometer, Odhner arithmometer. In 1918, employee Carl Friden designed a new model in response to patent challenges. It was a great success, and Friden became the chief designer until he left in 1934 to found his own company. In 1958 the company was acquired by the Smith Corona typewriter company in a diversification move that proved unsound; the company, which was now known as SCM, tried to stay competitive by introducing the SCM Cogito 240SR electronic calculator (designed by Manhattan Project veteran Stan Frankel) in 1965. Within a few years a tidal wave of cheaper electronic calculators had devastated their business, and by the mid-1980s, SCM's typewriter business, too, had been ruined by the advent of inexpensive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computer (job Description)
The term "computer", in use from the early 17th century (the first known written reference dates from 1613), meant "one who computes": a person performing mathematical calculations, before electronic calculators became available. Alan Turing described the "human computer" as someone who is "supposed to be following fixed rules; he has no authority to deviate from them in any detail." Teams of people, often women from the late nineteenth century onwards, were used to undertake long and often tedious calculations; the work was divided so that this could be done in parallel. The same calculations were frequently performed independently by separate teams to check the correctness of the results. Since the end of the 20th century, the term "human computer" has also been applied to individuals with prodigious powers of mental arithmetic, also known as mental calculators. Origins in sciences Astronomers in Renaissance times used that term about as often as they called themselves " math ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Real-time Computing
Real-time computing (RTC) is the computer science term for Computer hardware, hardware and software systems subject to a "real-time constraint", for example from Event (synchronization primitive), event to Event (computing), system response. Real-time programs must guarantee response within specified time constraints, often referred to as "deadlines".Mordechai Ben-Ari, Ben-Ari, Mordechai; "Principles of Concurrent and Distributed Programming", ch. 16, Prentice Hall, 1990, , p. 164 The term "real-time" is also used in Computer simulation, simulation to mean that the simulation's clock runs at the same speed as a real clock. Real-time responses are often understood to be in the order of milliseconds, and sometimes microseconds. A system not specified as operating in real time cannot usually ''guarantee'' a response within any timeframe, although ''typical'' or ''expected'' response times may be given. Real-time processing ''fails'' if not completed within a specified deadline rela ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MIT Electrical Engineering And Computer Science Department
The Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science at MIT is an engineering department of the Massachusetts Institute of Technology in Cambridge, Massachusetts. It offers degrees of Master of Science, Master of Engineering, Doctor of Philosophy, and Doctor of Science. History The curriculum for the electrical engineering program was created in 1882, and was the first such program in the country. It was initially taught by the physics faculty. In 1902, the Institute set up a separate Electrical Engineering department. The department was renamed to Electrical Engineering and Computer Science in 1975, to highlight the new addition of computer science to the program. Current faculty Professors * Silvio Micali * Harold Abelson * Anant Agarwal * Akintunde I. Akinwande * Dimitri A. Antoniadis * Arvind * Arthur B. Baggeroer * Hari Balakrishnan Dimitri P. BertsekasRobert C. BerwickDuane S. BoningRodney A. BrooksVincent W. S. ChanAnantha P. Chandrakasan* Shafira Goldwasser P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pascal (programming Language)
Pascal is an imperative and procedural programming language, designed by Niklaus Wirth as a small, efficient language intended to encourage good programming practices using structured programming and data structuring. It is named after French mathematician, philosopher and physicist Blaise Pascal. Pascal was developed on the pattern of the ALGOL 60 language. Wirth was involved in the process to improve the language as part of the ALGOL X efforts and proposed a version named ALGOL W. This was not accepted, and the ALGOL X process bogged down. In 1968, Wirth decided to abandon the ALGOL X process and further improve ALGOL W, releasing this as Pascal in 1970. On top of ALGOL's scalars and arrays, Pascal enables defining complex datatypes and building dynamic and recursive data structures such as lists, trees and graphs. Pascal has strong typing on all objects, which means that one type of data cannot be converted to or interpreted as another without explicit conversions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ada (programming Language)
Ada is a structured, statically typed, imperative, and object-oriented high-level programming language, inspired by Pascal and other languages. It has built-in language support for '' design by contract'' (DbC), extremely strong typing, explicit concurrency, tasks, synchronous message passing, protected objects, and non-determinism. Ada improves code safety and maintainability by using the compiler to find errors in favor of runtime errors. Ada is an international technical standard, jointly defined by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO), and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC). , the standard, ISO/IEC 8652:2023, is called Ada 2022 informally. Ada was originally designed by a team led by French computer scientist Jean Ichbiah of Honeywell under contract to the United States Department of Defense (DoD) from 1977 to 1983 to supersede over 450 programming languages then used by the DoD. Ada was named after Ada Lovelace (1815–185 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
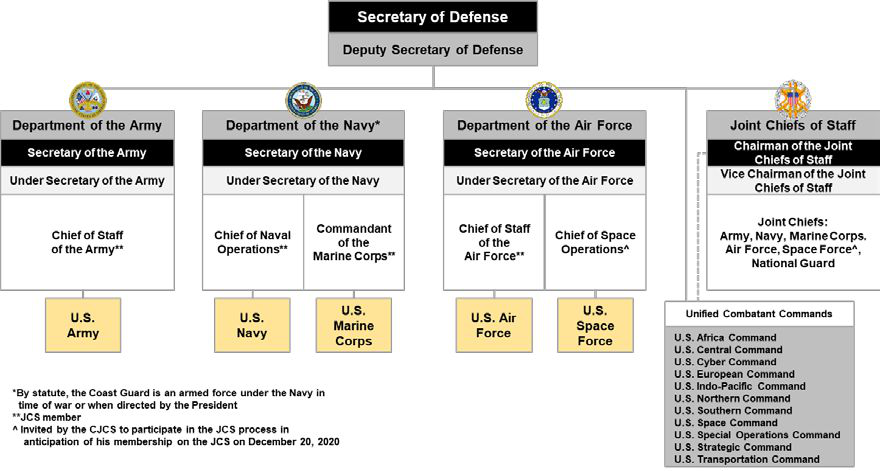
United States Department Of Defense
The United States Department of Defense (DoD, USDOD, or DOD) is an United States federal executive departments, executive department of the federal government of the United States, U.S. federal government charged with coordinating and supervising the six U.S. armed services: the United States Army, Army, United States Navy, Navy, United States Marine Corps, Marines, United States Air Force, Air Force, United States Space Force, Space Force, the United States Coast Guard, Coast Guard for some purposes, and related functions and agencies. As of November 2022, the department has over 1.4 million active-duty uniformed personnel in the six armed services. It also supervises over 778,000 National Guard (United States), National Guard and reservist personnel, and over 747,000 civilians, bringing the total to over 2.91 million employees. Headquartered at the Pentagon in Arlington County, Virginia, just outside Washington, D.C., the Department of Defense's stated mission is "to provid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Compiler
In computing, a compiler is a computer program that Translator (computing), translates computer code written in one programming language (the ''source'' language) into another language (the ''target'' language). The name "compiler" is primarily used for programs that translate source code from a high-level programming language to a lower level language, low-level programming language (e.g. assembly language, object code, or machine code) to create an executable program.Compilers: Principles, Techniques, and Tools by Alfred V. Aho, Ravi Sethi, Jeffrey D. Ullman - Second Edition, 2007 There are many different types of compilers which produce output in different useful forms. A ''cross-compiler'' produces code for a different Central processing unit, CPU or operating system than the one on which the cross-compiler itself runs. A ''bootstrap compiler'' is often a temporary compiler, used for compiling a more permanent or better optimised compiler for a language. Related software ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Whirlwind I
Whirlwind I was a Cold War-era vacuum-tube computer developed by the MIT Servomechanisms Laboratory for the U.S. Navy. Operational in 1951, it was among the first digital electronic computers that operated in real-time for output, and the first that was not simply an electronic replacement of older mechanical systems. It was one of the first computers to calculate in bit-parallel (rather than bit-serial), and was the first to use magnetic-core memory. Its development led directly to the Whirlwind II design used as the basis for the United States Air Force SAGE air defense system, and indirectly to almost all business computers and minicomputers in the 1960s, particularly because of the mantra "short word length, speed, people." Background During World War II, the U.S. Navy's Naval Research Lab approached MIT about the possibility of creating a computer to drive a flight simulator for training bomber crews. They envisioned a fairly simple system in which the computer w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |