|
Douglas DC-7
The Douglas DC-7 is a retired American transport aircraft built by the Douglas Aircraft Company from 1953 to 1958. A derivative of the DC-6, it was the last major piston engine-powered transport made by Douglas, being developed shortly after the earliest jet airliner—the de Havilland Comet—entered service and only a few years before the jet-powered Douglas DC-8 first flew in 1958. Larger numbers of both DC-7B and DC-7C variants were also built. Unlike other far more successful propeller-driven Douglas aircraft, such as the DC-3 and DC-6, no examples of the DC-7 remain in service as of 2020. Design and development In 1945, Pan American World Airways requested a DC-7, a civil version of the Douglas C-74 Globemaster military transport. Pan Am soon canceled their order. That proposed DC-7 was unrelated to the later DC-6-derived airliner. American Airlines revived the designation when they requested an aircraft that could fly across the United States coast-to-coast non-stop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Douglas Aircraft Company
The Douglas Aircraft Company was an American aerospace manufacturer, aerospace and military, defense company based in Southern California. Founded in 1921 by Donald Wills Douglas Sr., it merged with McDonnell Aircraft in 1967 to form McDonnell Douglas, where it operated as a division. History 1920s The company was founded as the Douglas Company by Donald Wills Douglas Sr. on July 22, 1921, in Santa Monica, California, following dissolution of the Davis-Douglas Company. An early claim to fame was the first aerial circumnavigation, first circumnavigation of the world by air in Douglas airplanes in 1924. In 1923, the U.S. Army Air Service was interested in carrying out a mission to circumnavigate the Earth for the first time by aircraft, a program called "World Flight". Donald Douglas proposed a modified Douglas DT to meet the Army's needs. The two-place, open cockpit DT biplane torpedo bomber had previously been produced for the United States Navy, U.S. Navy.Rumerman, Judy. "The D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trans World Airlines
Trans World Airlines (TWA) was a major airline in the United States that operated from 1930 until it was acquired by American Airlines in 2001. It was formed as Transcontinental & Western Air to operate a route from New York City to Los Angeles via St. Louis, Kansas City, and other stops, with Ford Trimotors. With American Airlines, American, United Airlines, United, and Eastern Air Lines, Eastern, it was one of the "Legacy carrier#Defunct legacy carriers, Big Four" domestic airlines in the United States formed by the Air Mail scandal, Spoils Conference of 1930. Howard Hughes acquired control of TWA in 1939, and after World War II led the expansion of the airline to serve Europe, the Middle East, and Asia, making TWA a second unofficial flag carrier of the United States after Pan American World Airways, Pan Am. Hughes gave up control in the 1960s, and the new management of TWA acquired Hilton Worldwide, Hilton International and Century 21 Real Estate, Century 21 in an attempt to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wright Aeronautical
Wright Aeronautical (1919–1929) was an American aircraft manufacturer headquartered in Paterson, New Jersey. It was the successor corporation to Wright-Martin. It built aircraft and was a supplier of aircraft engines to other builders in the golden age of aviation. Wright engines were used by Amelia Earhart and Charles Lindbergh. In 1929, the company merged with Curtiss Aeroplane and Motor Corporation to form Curtiss-Wright. History In 1916, the Wright brothers' original aviation firm, the Wright Company, merged with Glenn L. Martin's firm, the Glenn L. Martin Company of California, to form the Wright-Martin Aircraft Corporation. In September 1917, Martin resigned from Wright-Martin and re-formed an independent Glenn L. Martin Company of Ohio (later of Maryland). After World War I in 1919, Wright-Martin was renamed Wright Aeronautical. It moved to Paterson, New Jersey in 1919. In February 1919, an airplane with a Wright engine broke the world's speed record at per hour. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
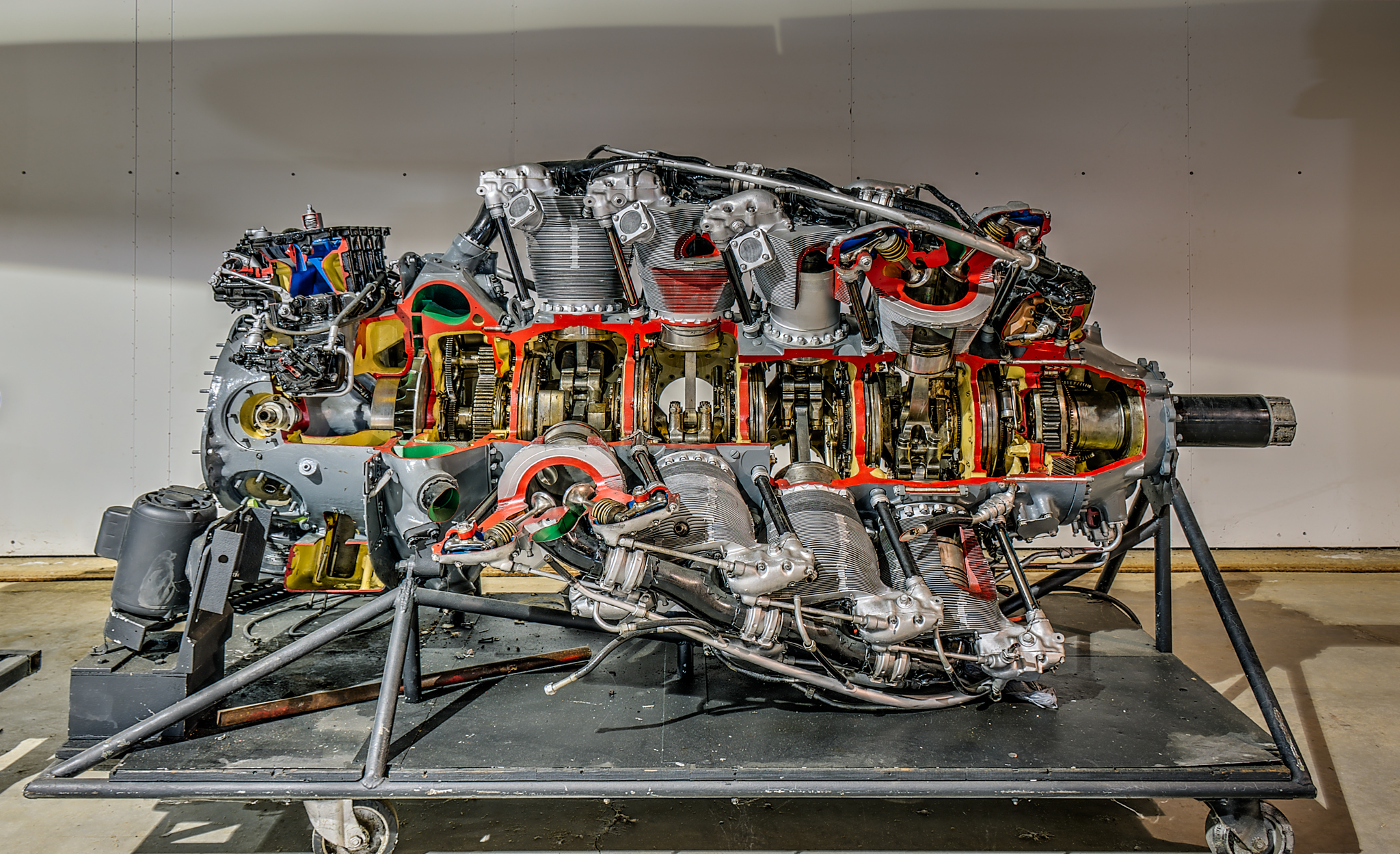
Pratt & Whitney R-4360 Wasp Major
The Pratt & Whitney R-4360 Wasp Major is an American 28-cylinder four-row radial engine, radial reciprocating engine, piston aircraft engine designed and built during World War II. At , it is the largest-displacement aviation piston engine to be mass-produced in the United States, and at the most powerful. First run in 1944, it was the last of the Pratt & Whitney Pratt & Whitney Wasp series, Wasp family, and the culmination of its maker's piston engine technology. The war was over before it could power airplanes into combat. It powered many of the last generation of large piston-engined aircraft before turbojets, but was supplanted by equivalent (and superior) powered turboprops (such as the Allison T56). Its main rival was the twin-row, 18-cylinder, nearly displacement, up to Wright R-3350 Duplex-Cyclone, first run some seven years earlier (May 1937). Design and development The R-4360 was a 28-cylinder (engine), cylinder four-row air-cooled radial engine. Each row of seven ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pratt & Whitney R-2800 Double Wasp
The Pratt & Whitney R-2800 Double Wasp is an American twin-row, 18-cylinder, air-cooled radial aircraft engine with a displacement of , and is part of the long-lived Wasp family of engines. The R-2800 saw widespread use in many important American aircraft during and after World War II. During the war years, Pratt & Whitney continued to develop new ideas to upgrade the engine, including water injection for takeoff in cargo and passenger planes and to give emergency power in combat. Design and development First run in 1937, near the time that the larger competing 18-cylinder Wright Duplex-Cyclone's development had been started in May of that year, the displacement R-2800 was first flown by 1940, one year before the Duplex-Cyclone. The Double Wasp was more powerful than the world's only other modern 18-cylinder engine, the Gnome-Rhône 18L of . The Double Wasp was much smaller in displacement than either of the other 18-cylinder designs, and heat dissipation was a gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boeing 707
The Boeing 707 is an early American long-range Narrow-body aircraft, narrow-body airliner, the first jetliner developed and produced by Boeing Commercial Airplanes. Developed from the Boeing 367-80 prototype, the initial first flew on December 20, 1957. Pan Am began regular 707 service on October 26, 1958. With versions produced until 1979, the 707 is a swept wing four-engined jet aircraft, quadjet with podded engines. Its larger fuselage cross-section allowed six-abreast economy seating, retained in the later Boeing 720, 720, Boeing 727, 727, Boeing 737, 737, and Boeing 757, 757 models. Although it was not the first commercial jetliner in service, the 707 was the first to be widespread, and is often credited with beginning the Jet Age. It dominated passenger airline, air-transport in the 1960s, and remained common through the 1970s, on Domestic flight, domestic, Transcontinental flight, transcontinental, and transatlantic flights, as well as cargo and military applications. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lockheed L-1649A Starliner
The Lockheed L-1649 Starliner is the last model of the Lockheed Constellation line of airliners. Powered by four Wright R-3350 Turbo-compound engines, it was built at Lockheed's Burbank, California plant from 1956 to 1958. Design and development Development of the Starliner began when Lockheed designed the L-1449 in response to the Douglas DC-7C Seven Seas.Breffort, Dominique. Lockheed Constellation: from Excalibur to Starliner Civilian and Military Variants. Histoire and Collecions, 2006. p.112 to 117 Powered by four 5500 hp Pratt & Whitney PT2G-3 turboprop engines, the L-1449 would have cruised faster than the DC-7C with comparable range with of fuel in a new wing. Pratt & Whitney dropped the PT2 project in March 1955 due to expected unreliability, high specific fuel consumption and high operating costs, though the T34 military version of the engine powered the Douglas C-133 freighter, which was also plagued with unreliability. The L-1449 would have been about lo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scandinavian Airlines System
The Scandinavian Airlines System (SAS), commonly known as Scandinavian Airlines, is the Flag carrier, national airline of Denmark, Norway, and Sweden. It is part of SAS Group and is headquartered in Solna Municipality, Solna, Sweden. Including its subsidiaries SAS Link and Scandinavian Airlines Connect, SAS Connect, the airline operates a fleet of 133 aircraft to 130 destinations, as of July 2024. The principal hub of SAS is Copenhagen Airport, which connects to 106 destinations worldwide. The airline's two other hubs are Stockholm Arlanda Airport with 74 destinations, and Oslo Airport, Gardermoen, Oslo Airport, with 56 destinations. Additionally, there are minor hubs at Bergen Airport, Flesland, Göteborg Landvetter Airport, Stavanger Airport, and Trondheim Airport. In 2017, SAS carried 28.6 million passengers, achieving revenues of 40 billion Swedish krona, Swedish kronor. This made it the list of largest airlines in Europe, eighth-largest airline in Europe and the largest in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bristol Britannia
The Bristol Type 175 Britannia is a retired United Kingdom, British flight length, medium-to-long-range airliner built by the Bristol Aeroplane Company in 1952 to meet British civilian aviation needs. During development two prototypes were lost and the turboprop engines proved susceptible to inlet atmospheric icing, icing, which delayed entry into service while solutions were sought. By the time development was completed, "pure" jet airliners from France, the United Kingdom, and the United States were about to enter service, and consequently, only 85 Britannias were built before production ended in 1960. Nevertheless, the Britannia is considered one of the landmarks in turboprop-powered airliner design and was popular with passengers. It became known as "The Whispering Giant" for its quiet exterior noise and smooth flying, although the passenger interior remained less tranquil. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lockheed L-1049
The Lockheed L-1049 Super Constellation is an American aircraft, a member of the Lockheed Constellation aircraft line. The aircraft was colloquially referred to as the Super Connie. The L-1049 was Lockheed's response to the successful Douglas DC-6 airliner, first flying in 1950. The aircraft was produced for both the United States Navy as the WV / R7V and U.S. Air Force as the C-121 for transport, electronics, and airborne early warning and control aircraft. Development Beginning in 1943, Lockheed planned stretched variants of the Constellation family. The first was the L-049 with a fuselage lengthened by and the second the L-749 stretched . Douglas launched a stretched version of its DC-6 airliner as a cargo transport, designated DC-6A, for both military and civilian operators. Douglas was soon to launch a passenger version (the DC-6B) of this new aircraft. The DC-6B could carry 23 more passengers than Lockheed's current production L-749 Constellation. In 1950, Lockheed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parasitic Drag
Parasitic drag, also known as profile drag, is a type of aerodynamic drag that acts on any object when the object is moving through a fluid. Parasitic drag is defined as the combination of '' form drag'' and '' skin friction drag''. It is named as such because it is not useful, in contrast with lift-induced drag which is created when an airfoil generates lift. All objects experience parasitic drag, regardless of whether they generate lift. Parasitic drag comprises all types of drag except lift-induced drag, and the total drag on an aircraft or other object which generates lift is the sum of parasitic drag and lift-induced drag. Form drag Form drag arises because of the shape of the object. The general size and shape of the body are the most important factors in form drag; bodies with a larger presented cross-section will have a higher drag than thinner bodies; sleek ("streamlined") objects have lower form drag. Form drag follows the drag equation, meaning that it increases wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |