 |
Double Data Rate SDRAM
Double Data Rate Synchronous Dynamic Random-Access Memory (DDR SDRAM) is a double data rate (DDR) synchronous dynamic random-access memory (SDRAM) class of memory integrated circuits used in computers. DDR SDRAM, also retroactively called DDR1 SDRAM, has been superseded by DDR2 SDRAM, DDR3 SDRAM, DDR4 SDRAM and DDR5 SDRAM. None of its successors are Forward compatibility, forward or Backward compatibility, backward compatible with DDR1 SDRAM, meaning DDR2, DDR3, DDR4 and DDR5 memory modules will not work on DDR1-equipped motherboards, and vice versa. Compared to single data rate (Synchronous dynamic random-access memory#SDR, SDR) SDRAM, the DDR SDRAM External memory interface, interface makes higher transfer rates possible through more strict control of the timing of the electrical data and clock signals. Implementations often have to use schemes such as phase-locked loops and self-calibration to reach the required timing accuracy. The interface uses double data rate, double pum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Desktop DDR Memory Comparison
A desktop traditionally refers to: * The surface of a desk (often to distinguish office appliances that fit on a desk, such as photocopiers and printers, from larger equipment covering its own area on the floor) Desktop may refer to various computer terms: * Desktop computer, a personal computer designed to fit on a desk * Desktop metaphor, a style of graphical user interface modeled after a physical work surface **Desktop environment, software that provides a comprehensive computer user interface ** .desktop file, providing configuration details for a program in a desktop environment **Remote desktop software, software that provides remote access to a computer's desktop * Client (computing), sometimes referred to as a desktop to distinguish the client from a server * Desktop (word processor), a program for the ZX Spectrum See also * * *Laptop A laptop computer or notebook computer, also known as a laptop or notebook, is a small, portable personal computer (PC). Lapto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Forward Compatibility
Forward compatibility or upward compatibility is a design characteristic that allows a system to accept input intended for a later version of itself. The concept can be applied to entire systems, electrical interfaces, telecommunication signals, data communication protocols, file formats, and programming languages. A standard supports forward compatibility if a product that complies with earlier versions can " gracefully" process input designed for later versions of the standard, ignoring new parts which it does not understand. The objective for forward compatible technology is for old devices to recognise when data has been generated for new devices. Forward compatibility for the older system usually means backward compatibility for the new system, i.e. the ability to process data from the old system; the new system usually has ''full'' compatibility with the older one, by being able to both process and generate data in the format of the older system. Forward compatibilit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Megabit
The bit is the most basic Units of information, unit of information in computing and digital communication. The name is a portmanteau of binary digit. The bit represents a truth value, logical state with one of two possible value (computer science), values. These values are most commonly represented as either , but other representations such as ''true''/''false'', ''yes''/''no'', ''on''/''off'', or ''+''/''−'' are also widely used. The relation between these values and the physical states of the underlying Data storage device, storage or computing device, device is a matter of convention, and different assignments may be used even within the same device or computer program, program. It may be physically implemented with a two-state device. A contiguous group of binary digits is commonly called a ''bit string'', a bit vector, or a single-dimensional (or multi-dimensional) ''bit array''. A group of eight bits is called one ''byte'', but historically the size of the byte is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Double Data Rate
In computing, double data rate (DDR) describes a computer bus that transfers data on both the rising and falling edges of the clock signal and hence doubles the memory bandwidth by transferring data twice per clock cycle. This is also known as double pumped, dual-pumped, and double transition. The term toggle mode is used in the context of NAND flash memory. Overview The simplest way to design a clocked electronic circuit is to make it perform one transfer per full cycle (rise and fall) of a clock signal. This, however, requires that the clock signal changes twice per transfer, while the data lines change at most once per transfer. When operating at a high bandwidth, signal integrity limitations constrain the clock frequency. By using both edges of the clock, the data signals operate with the same limiting frequency, thereby doubling the data transmission rate. This technique has been used for microprocessor front-side busses, Ultra-3 SCSI, expansion buses ( AGP, PCI ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
MB/s
In telecommunications, data transfer rate is the average number of bits ( bitrate), characters or symbols ( baudrate), or data blocks per unit time passing through a communication link in a data-transmission system. Common data rate units are multiples of bits per second (bit/s) and bytes per second (B/s). For example, the data rates of modern residential high-speed Internet connections are commonly expressed in megabits per second (Mbit/s). Standards for unit symbols and prefixes Unit symbol The ISQ symbols for the bit and byte are ''bit'' and ''B'', respectively. In the context of data-rate units, one byte consists of 8 bits, and is synonymous with the unit octet. The abbreviation bps is often used to mean bit/s, so that when a ''1 Mbps'' connection is advertised, it usually means that the maximum achievable bandwidth is 1 Mbit/s (one million bits per second), which is 0.125 MB/s ( megabyte per second), or about 0.1192 MiB/s ( mebibyte per second). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Bandwidth (computing)
In computing, bandwidth is the maximum rate of data transfer across a given path. Bandwidth may be characterized as network bandwidth, data bandwidth, or digital bandwidth. This definition of ''bandwidth'' is in contrast to the field of signal processing, wireless communications, modem data transmission, digital communications, and electronics, in which ''bandwidth'' is used to refer to the signal bandwidth measured in hertz, meaning the frequency range between lowest and highest attainable frequency while meeting a well-defined impairment level in signal power. The actual bit rate that can be achieved depends not only on the signal bandwidth but also on the noise on the channel. Network capacity The term ''bandwidth'' sometimes defines the net bit rate ''peak bit rate'', ''information rate'', or physical layer ''useful bit rate'', channel capacity, or the maximum throughput of a logical or physical communication path in a digital communication system. For example, bandwi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Signal Integrity
Signal integrity or SI is a set of measures of the quality of an electrical signal. In digital electronics, a stream of binary values is represented by a voltage (or current) waveform. However, digital signals are fundamentally analog signal, analog in nature, and all signals are subject to effects such as electrical noise, noise, distortion, and loss. Over short distances and at low bit rates, a simple conductor can transmit this with sufficient fidelity. At high bit rates and over longer distances or through various mediums, various effects can degrade the electrical signal to the point where errors occur and the system or device fails. Signal integrity engineering is the task of analyzing and mitigating these effects. It is an important activity at all levels of electronics packaging and assembly, from internal connections of an integrated circuit (IC), A survey of the field of electronic design automation. Portions of IC section of this article were derived (with permission) fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Data Bus
In computer architecture, a bus (historically also called a data highway or databus) is a communication system that transfers data between components inside a computer or between computers. It encompasses both hardware (e.g., wires, optical fiber) and software, including communication protocols. At its core, a bus is a shared physical pathway, typically composed of wires, traces on a circuit board, or busbars, that allows multiple devices to communicate. To prevent conflicts and ensure orderly data exchange, buses rely on a communication protocol to manage which device can transmit data at a given time. Buses are categorized based on their role, such as system buses (also known as internal buses, internal data buses, or memory buses) connecting the CPU and memory. Expansion buses, also called peripheral buses, extend the system to connect additional devices, including peripherals. Examples of widely used buses include PCI Express (PCIe) for high-speed internal connections ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
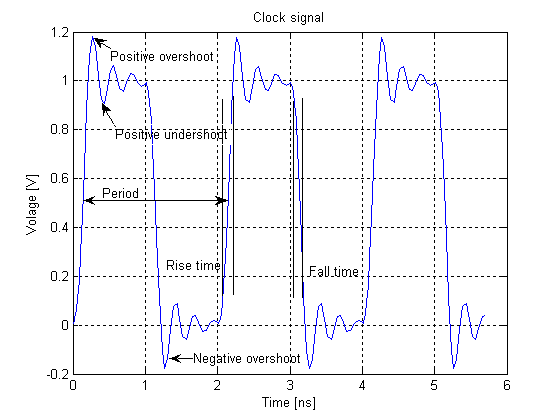 |
Clock Signal
In electronics and especially synchronous digital circuits, a clock signal (historically also known as ''logic beat'') is an electronic logic signal (voltage or current) which oscillates between a high and a low state at a constant frequency and is used like a metronome to synchronize actions of digital circuits. In a synchronous logic circuit, the most common type of digital circuit, the clock signal is applied to all storage devices, flip-flops and latches, and causes them all to change state simultaneously, preventing race conditions. A clock signal is produced by an electronic oscillator called a clock generator. The most common clock signal is in the form of a square wave with a 50% duty cycle. Circuits using the clock signal for synchronization may become active at either the rising edge, falling edge, or, in the case of double data rate, both in the rising and in the falling edges of the clock cycle. Digital circuits Most integrated circuits (ICs) of suffi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Phase-locked Loop
A phase-locked loop or phase lock loop (PLL) is a control system that generates an output signal whose phase is fixed relative to the phase of an input signal. Keeping the input and output phase in lockstep also implies keeping the input and output frequencies the same, thus a phase-locked loop can also track an input frequency. Furthermore, by incorporating a frequency divider, a PLL can generate a stable frequency that is a multiple of the input frequency. These properties are used for clock synchronization, demodulation, frequency synthesis, clock multipliers, and signal recovery from a noisy communication channel. Since 1969, a single integrated circuit can provide a complete PLL building block, and nowadays have output frequencies from a fraction of a hertz up to many gigahertz. Thus, PLLs are widely employed in radio, telecommunications, computers (e.g. to distribute precisely timed clock signals in microprocessors), grid-tie inverters (electronic power converters used ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
External Memory Interface
An external memory interface is a bus protocol for communication from an integrated circuit, such as a microprocessor, to an external memory device located on a circuit board. The memory is referred to as external because it is not contained within the internal circuitry of the integrated circuit and thus is externally located on the circuit board. The external memory interface enables the processor to interface with third level caches, peripherals, and external memory. Some common external memory interfaces include: * DDR * DDR2 * GDDR Graphics DDR SDRAM (GDDR SDRAM) is a type of synchronous dynamic random-access memory (SDRAM) specifically designed for applications requiring high bandwidth, e.g. graphics processing units (GPUs). GDDR SDRAM is distinct from the more widely kno ... References {{reflist Computer memory ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |