|
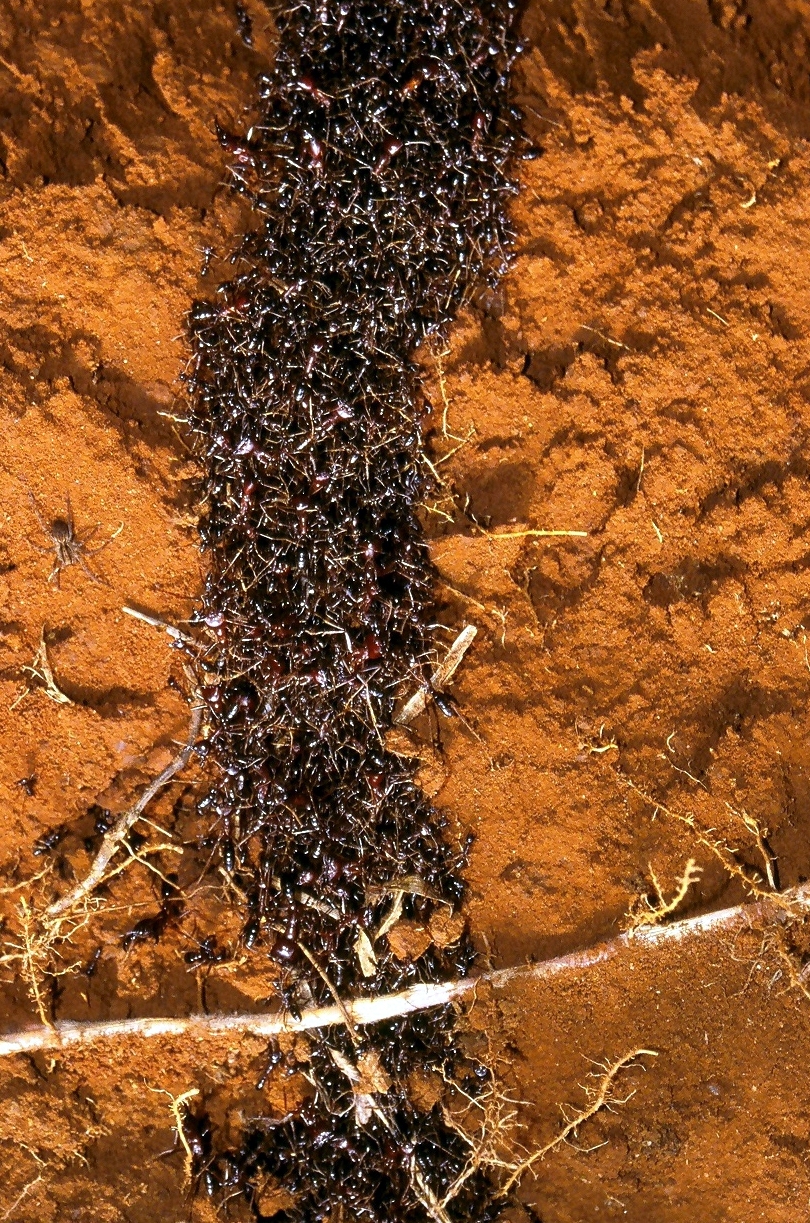
Dorylus
''Dorylus'', also known as driver ants, safari ants, or siafu, is a large genus of army ants found primarily in central and east Africa, although the range also extends to southern Africa and tropical Asia. The term siafu is a loanword from Swahili, and is one of numerous similar words from regional Bantu languages used by indigenous peoples to describe various species of these ants. Unlike the New World members of the former subfamily Ecitoninae (now Dorylinae), members of this genus form temporary subterranean bivouacs in underground cavities which they excavate and inhabit - either for a few days or up to three months. Also, unlike some New World army ants, driver ants are not specialized predators of other species of ant, instead being more generalistic with a diet consisting of a diversity of arthropods. Their colonies are enormous compared to other ant species, and can contain over 20 million individuals. As with their American counterparts, workers exhibit caste polymorphis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dorylus Gribodoi
''Dorylus gribodoi'' is a West African species of army ants in the genus ''Dorylus''. Habitat and distribution The species occurs in West Africa, from Guinea and Liberia to Cameroon. It is restricted to humid habitats such as rainforest and gallery forest in mixed savanna–forest landscapes and occurs at least up to 1600 m above sea level. Biology Raids are conducted in the leaf-litter stratum. Workers retreat in tunnels when disturbed or exposed to sun. Limited observations indicate that the species seems to prey almost exclusively on earthworms, but this information has to be viewed with caution since variation in prey composition can be considerable in other ''Dorylus'' species. Common chimpanzee, Chimpanzees are known to feed on ''D. gribodoi'' at two sites (Bossou in Guinea and Taï in Ivory Coast); they either use sticks to "dip" for ant workers at trails or nests or open nests and take brood and workers with their hands. Nests are much less conspicuous than those of dri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Army Ant
The name army ant (or legionary ant or ''marabunta'') is applied to over 200 ant species in different lineages. Because of their aggressive predatory foraging groups, known as "raids", a huge number of ants forage simultaneously over a limited area. Another shared feature is that, unlike most ant species, army ants do not construct permanent nests; an army ant colony moves almost incessantly over the time it exists. All species are members of the true ant family, Formicidae, but several groups have independently evolved the same basic behavioural and ecological syndrome. This syndrome is often referred to as "legionary behaviour", and may be an example of convergent evolution. Most New World army ants belong to the genera ''Cheliomyrmex'', ''Neivamyrmex'', ''Nomamyrmex'', ''Labidus'', and ''Eciton''. The largest genus is ''Neivamyrmex'', which contains more than 120 species; the most predominant species is ''Eciton burchellii''; its common name "army ant" is considered to be t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dorylinae
Dorylinae is an ant subfamily, with distributions in both the Old World and New World. Brady ''et al.'' (2014) Synonym (taxonomy), synonymized the previous dorylomorph subfamilies (Aenictinae, Aenictogitoninae, Cerapachyinae, Ecitoninae, and Leptanilloidinae) under Dorylinae, while Borowiec (2016) reviewed and revised the genera, resurrecting many genera which had previously been merged. Dorylinae genera are suggested to have evolved sometime between , subsequently undergoing rapid adaptive radiation events during their early history. Dorylinae ants including Eciton species, exhibit army ant behavior. Non-army Doryline ants like ''Yunodorylus'' provides evolution of the army ant adaptive syndrome, including group foraging, nomadism, and specialized queens. Genera *''Acanthostichus'' Mayr, 1887 *''Aenictogiton'' Emery, 1901 *''Aenictus'' Shuckard, 1840 *''Cerapachys'' Smith, 1857 *''Cheliomyrmex'' Mayr, 1870 *''Chrysapace'' Crawley, 1924 *''Cylindromyrmex'' Mayr, 1870 *''Dorylus' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alate
Alate (Latin ''ālātus'', from ''āla'' (“wing”)) is an adjective and noun used in entomology and botany to refer to something that has wings or winglike structures. In entomology In entomology, "alate" usually refers to the winged form of a social insect, especially ants or termites, though it can also be applied to aphids and some thrips. Alate females are referred to as gyne The gyne (, from Greek γυνή, "woman") is the primary reproductive female caste of social insects (especially ants, wasps, and bees of order Hymenoptera, as well as termites). Gynes are those destined to become queens, whereas female workers ...s, and are typically those destined to become queens. A " dealate" is an adult insect that shed or lost its wings ("dealation"). In botany In botany, "alate" refers to wing-like structures on some seeds that use wind dispersal. It is also used to describe flattened ridges which run longitudinally on stems. References External links * Insect ec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eldana
''Eldana'' is a genus of moths of the family Pyralidae containing only one species, the African sugar-cane borer (''Eldana saccharina''), which is commonly found in Equatorial Guinea, Ghana, Mozambique, Sierra Leone and South Africa. Adults have a wingspan of 35mm. This species is particularly relevant to humans because the larvae are a pest of the '' Saccharum'' species as well as several grain crops such as sorghum and maize. Other recorded host plants are cassava, rice and '' Cyperus'' species. When attacking these crops, ''E. saccharina'' bores into the stems of their host plant, causing severe damage to the crop. This behavior is the origin of the ''E. saccharrina's'' common name, the African sugar-cane borer. The African sugar-cane borer is a resilient pest, as it can survive crop burnings. Other methods such as intercropping and parasitic wasps have been employed to prevent further damage to crops. Taxonomy The only member of the genus ''Eldana'', ''E. saccharina'' was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genus
Genus (; : genera ) is a taxonomic rank above species and below family (taxonomy), family as used in the biological classification of extant taxon, living and fossil organisms as well as Virus classification#ICTV classification, viruses. In binomial nomenclature, the genus name forms the first part of the binomial species name for each species within the genus. :E.g. ''Panthera leo'' (lion) and ''Panthera onca'' (jaguar) are two species within the genus ''Panthera''. ''Panthera'' is a genus within the family Felidae. The composition of a genus is determined by taxonomy (biology), taxonomists. The standards for genus classification are not strictly codified, so different authorities often produce different classifications for genera. There are some general practices used, however, including the idea that a newly defined genus should fulfill these three criteria to be descriptively useful: # monophyly – all descendants of an ancestral taxon are grouped together (i.e. Phylogeneti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sting (biology)
A stinger (or sting) is a sharp organ found in various animals (typically insects and other arthropods) capable of injecting venom, usually by piercing the epidermis of another animal. An insect sting is complicated by its introduction of venom, although not all stings are venomous. Bites, which can introduce saliva as well as additional pathogens and diseases, are often confused with stings, and vice versa. Specific components of venom are believed to give rise to an allergic reaction, which in turn produces skin lesions that may vary from a small itching weal, or slightly elevated area of the skin, to large areas of inflamed skin covered by vesicles and crusted lesions. Stinging insects produce a painful swelling of the skin, the severity of the lesion varying according to the location of the sting, the identity of the insect and the sensitivity of the subject. Many species of bees and wasps have two poison glands, one gland secreting a toxin in which formic acid is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pheromone
A pheromone () is a secreted or excreted chemical factor that triggers a social response in members of the same species. Pheromones are chemicals capable of acting like hormones outside the body of the secreting individual, to affect the behavior of the receiving individuals. There are ''alarm signal, alarm pheromones'', ''food trail pheromones'', ''sex pheromones'', and many others that affect behavior or physiology. Pheromones are used by many organisms, from basic unicellular prokaryotes to complex multicellular eukaryotes. Their use among insects has been particularly well documented. In addition, some vertebrates, plants and ciliates communicate by using pheromones. The ecological functions and evolution of pheromones are a major topic of research in the field of chemical ecology. Background The portmanteau word "pheromone" was coined by Peter Karlson and Martin Lüscher in 1959, based on the Greek language, Greek () and (). Pheromones are also sometimes classified as ec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surgical Staple
Surgical staples are specialized Staple (fastener), staples used in surgery in place of surgical suture, sutures to close skin wounds or to resection (surgery), resect and/or anastomosis, connect parts of an Organ (biology), organ (e.g. bowels, stomach or lungs). The use of staples over sutures reduces the local inflammatory response, width of the wound, and time it takes to close a defect. A more recent development, from the 1990s, uses clips instead of staples for some applications; this does not require the staple to penetrate. History The technique was pioneered by "father of surgical stapling", Hungarian surgeon Hümér Hültl. Hultl's prototype stapler of 1908 weighed , and required two hours to assemble and load. The technology was refined in the 1950s in the Soviet Union, allowing for the first commercially produced re-usable stapling devices for creation of bowel and Surgical anastomosis, anastomoses. Mark M. Ravitch brought a sample of stapling device after attendin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laceration
A wound is any disruption of or damage to living tissue, such as skin, mucous membranes, or organs. Wounds can either be the sudden result of direct trauma (mechanical, thermal, chemical), or can develop slowly over time due to underlying disease processes such as diabetes mellitus, venous/arterial insufficiency, or immunologic disease. Wounds can vary greatly in their appearance depending on wound location, injury mechanism, depth of injury, timing of onset ( acute vs chronic), and wound sterility, among other factors. Treatment strategies for wounds will vary based on the classification of the wound, therefore it is essential that wounds be thoroughly evaluated by a healthcare professional for proper management. In normal physiology, all wounds will undergo a series of steps collectively known as the wound healing process, which include hemostasis, inflammation, proliferation, and tissue remodeling. Age, tissue oxygenation, stress, underlying medical conditions, and certain me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
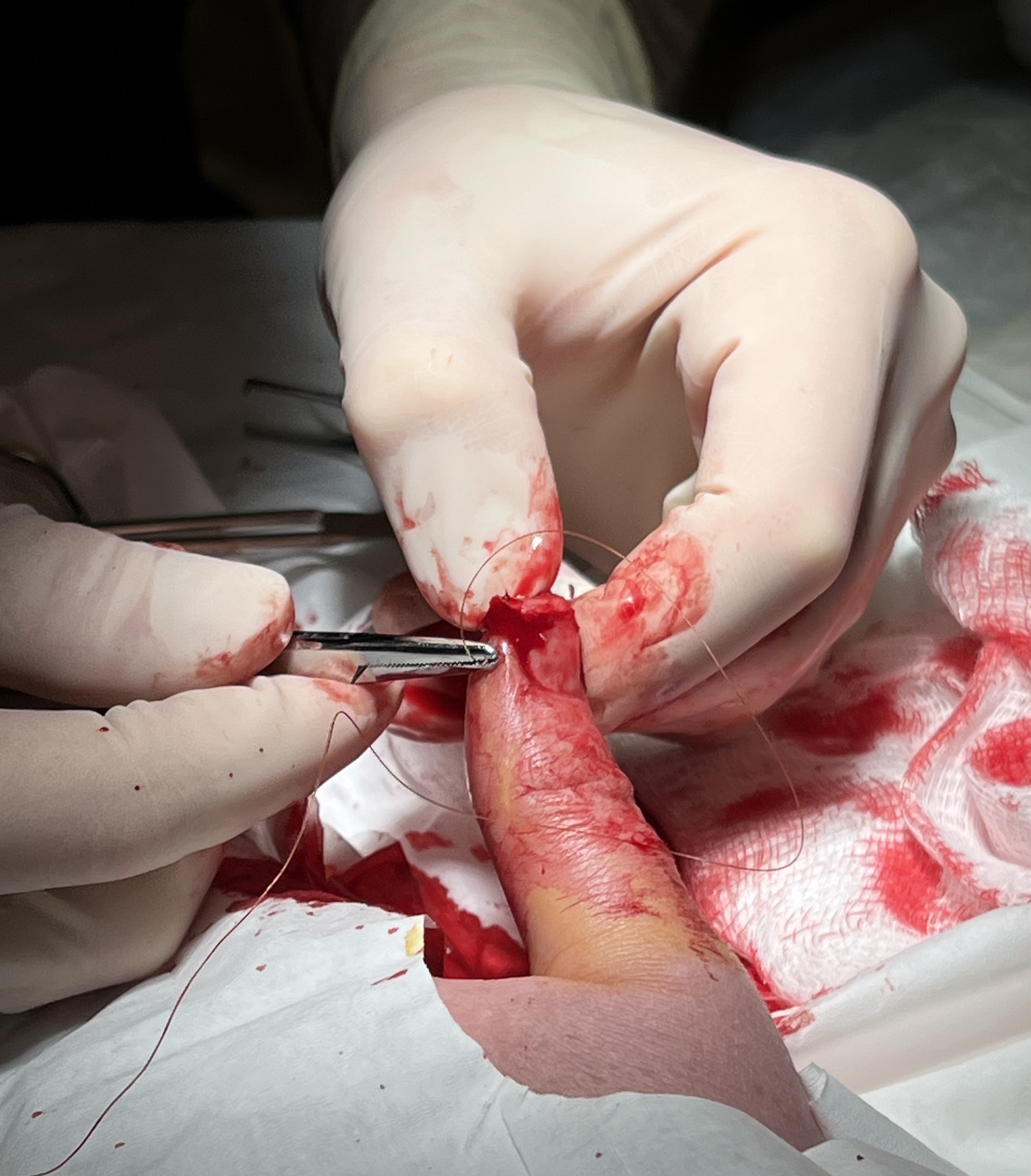
Surgical Suture
A surgical suture, also known as a stitch or stitches, is a medical device used to hold Tissue (biology), body tissues together and approximate wound edges after an injury or surgery. Application generally involves using a Sewing needle, needle with an attached length of thread (yarn), thread. There are numerous types of suture which differ by needle shape and size as well as thread material and characteristics. Selection of surgical suture should be determined by the characteristics and location of the wound or the specific body tissues being approximated. In selecting the needle, thread, and suturing technique to use for a specific patient, a medical care provider must consider the tensile strength of the specific suture thread needed to efficiently hold the tissues together depending on the mechanical and shear forces acting on the wound as well as the thickness of the tissue being approximated. One must also consider the elasticity of the thread and ability to adapt to differe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |