|
Dorthe Dahl-Jensen
Dorthe Dahl-Jensen (born 8 September 1958, Copenhagen, Denmark) is a Danish palaeoclimatology professor and researcher at the Centre for Ice and Climate at the Niels Bohr Institute, University of Copenhagen in Denmark. Her primary field is the study of ice and climate, specifically the reconstruction of climate records from ice cores and borehole data; ice flow models to date ice cores; continuum mechanical properties of anisotropic ice; ice in the Solar System; and the history and evolution of the Greenland Ice Sheet. Education and career Dahl-Jensen has an M.Sc. In Geophysics (1984) and a Ph.D. in Geophysics (1988) from the University of Copenhagen. As a student in 1980, Dahl-Jensen took part in ice-core drilling at the Dye 3 site on the Greenland ice sheet, a project led by Willi Dansgaard. Although Dansgaard had a rule that no women were allowed at the drilling site, he allowed Dahl-Jensen to participate. She and her drilling partner Jørgen Peder Steffensen later married. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Copenhagen
Copenhagen ( ) is the capital and most populous city of Denmark, with a population of 1.4 million in the Urban area of Copenhagen, urban area. The city is situated on the islands of Zealand and Amager, separated from Malmö, Sweden, by the Øresund strait. The Øresund Bridge connects the two cities by rail and road. Originally a Vikings, Viking fishing village established in the 10th century in the vicinity of what is now Gammel Strand, Copenhagen became the capital of Denmark in the early 15th century. During the 16th century, the city served as the ''de facto'' capital of the Kalmar Union and the seat of the Union's monarchy, which governed most of the modern-day Nordic countries, Nordic region as part of a Danish confederation with Sweden and Norway. The city flourished as the cultural and economic centre of Scandinavia during the Renaissance. By the 17th century, it had become a regional centre of power, serving as the heart of the Danish government and Military history ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geophysics
Geophysics () is a subject of natural science concerned with the physical processes and Physical property, properties of Earth and its surrounding space environment, and the use of quantitative methods for their analysis. Geophysicists conduct investigations across a wide range of scientific disciplines. The term ''geophysics'' classically refers to solid earth applications: Earth's figure of the Earth, shape; its gravitational, Earth's magnetic field, magnetic fields, and electromagnetic fields; its structure of the Earth, internal structure and Earth#Chemical composition, composition; its geodynamics, dynamics and their surface expression in plate tectonics, the generation of magmas, volcanism and rock formation. However, modern geophysics organizations and pure scientists use a broader definition that includes the water cycle including snow and ice; geophysical fluid dynamics, fluid dynamics of the oceans and the atmosphere; atmospheric electricity, electricity and magnetism in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Academia Europaea
The Academia Europaea is a pan-European Academy of humanities, letters, law, and sciences. The Academia was founded in 1988 as a functioning Europe-wide Academy that encompasses all fields of scholarly inquiry. It acts as co-ordinator of European interests in national research agencies. History The concept of a 'European Academy of Sciences' was raised at a meeting in Paris of the European Ministers of Science in 1985. The initiative was taken by the Royal Society (United Kingdom) which resulted in a meeting in London in June 1986 of Arnold Burgen (United Kingdom), Hubert Curien (France), Umberto Colombo (Italy), David Magnusson (Sweden), Eugen Seibold (Germany) and Ruurd van Lieshout (the Netherlands) – who agreed to the need for a new body. The meeting also included Brian Flowers and John Kendrew. Another, larger meeting took place in October 1986 with participants representing some countries in the Council of Europe and was in support for the development of a Eur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hans Oerlemans
Johannes "Hans" Oerlemans (born October 8, 1950 in Eethen) is a Dutch climatologist specialized in glaciology and sea level. He has been a professor of meteorology in the Faculty of Physics and Astronomy at Utrecht University since 1989. He was elected a member of the Royal Netherlands Academy of Arts and Sciences in 1994. In 2001 he won the Spinoza Prize. In 2010 he was made a Knight of the Order of the Netherlands Lion. In 2022 he was awarded the Balzan Prize The International Balzan Prize Foundation awards four annual monetary prizes to people or organizations who have made outstanding achievements in the fields of humanities, natural sciences, culture, as well as for endeavours for peace and the b ... for Glaciation and Ice Sheet Dynamics together with Dorthe Dahl-Jensen. References External links * 1950 births Living people Dutch climatologists Knights of the Order of the Netherlands Lion Members of the Royal Netherlands Academy of Arts and Sciences People fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Danish Academy Of Sciences And Letters
The Royal Danish Academy of Sciences and Letters ({{Langx, da, Det Kongelige Danske Videnskabernes Selskab or ''Videnskabernes Selskab'') is a Danish academy of science. The Royal Danish Academy was established on 13 November 1742, and was created with the purpose of strengthening the position of Science in Denmark as well as promoting interdisciplinary understanding. The Royal Danish Academy works as a body of cooperation and a meeting place for prominent scientists from all areas of basic scientific research. Its core activities consist of organizing the biweekly meetings for the academy's members, publishing scientific works, advising, and communicating, organizing and conducting events and lectures of a scientific character (e.g. public lectures and symposiums) as well as participating in international cooperation with other scientific academies and with scientific organizations like for example ISC and EASAC. Since 1745, the Royal Danish Academy has had its own publishing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
European Geosciences Union
The European Geosciences Union (EGU) is a non-profit international union in the fields of Earth, planetary, and space sciences whose vision is to "realise a sustainable and just future for humanity and for the planet". The organisation has headquarters in Munich, Germany. Membership is open to individuals who are professionally engaged in or associated with these fields and related studies, including students, early career scientists and retired seniors. The EGU publishes 19 public peer-reviewed open-access scientific journals and a number of other science publications. It also organises several topical meetings, as well training events and summer schools, and provides support and funding for numerous education and outreach activities. Its most prominent event is the EGU General Assembly, an annual conference that brings together over 18,000 scientists from all over the world. The meeting's sessions cover a wide range of topics, including volcanology, planetary exploration, the E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swedish Society For Anthropology And Geography
The Swedish Society for Anthropology and Geography (SSAG; ) is a scientific learned society founded in December 1877. It was established after a rearrangement of various sections of the Anthropological Society, which was formed in 1873 by Hjalmar Stolpe, Hans Hildebrand, Oscar Montelius, and Gustaf Retzius. The society functions as a link between science and the public, especially in the subjects of anthropology and geography. It awards research fellowships, organizes excursions and lectures, and hands out awards including the Vega Medal and Retzius Medal. In 1880, the society published the first edition of the Swedish yearbook ''Ymer'', and it has published the international journal ''Geografiska Annaler'' since 1919, a publication that is divided between physical geography and human geography. In 2018, it established ''Kritisk Etnografi'', an academic journal of ethnography. Society awards The society created the Vega Medal in 1881, on the occasion of Adolf Erik Nordenski ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
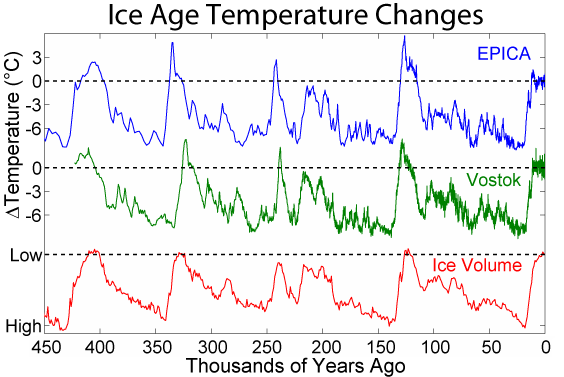
European Project For Ice Coring In Antarctica
The European Project for Ice Coring in Antarctica (EPICA) is a multinational European project for deep ice core drilling in Antarctica. Its main objective is to obtain full documentation of the climatic and atmospheric record archived in Antarctic ice by drilling and analyzing two ice cores and comparing these with their Greenland counterparts ( GRIP and GISP). Evaluation of these records will provide information about the natural climate variability and mechanisms of rapid climatic changes during the last glacial epoch. Deep drilling took place at two sites in Antarctica: Concordia Station on dome C and Kohnen Station. The European Science Foundation EPICA Programme (1996–2005) provides co-ordination for EPICA drilling activities on dome C and Kohnen Station, which are supported by the European Commission and by national contributions from Belgium, Denmark, France, Germany, Italy, the Netherlands, Norway, Sweden, Switzerland and the United Kingdom. In 2008 the project re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Guardian
''The Guardian'' is a British daily newspaper. It was founded in Manchester in 1821 as ''The Manchester Guardian'' and changed its name in 1959, followed by a move to London. Along with its sister paper, ''The Guardian Weekly'', ''The Guardian'' is part of the Guardian Media Group, owned by the Scott Trust Limited. The trust was created in 1936 to "secure the financial and editorial independence of ''The Guardian'' in perpetuity and to safeguard the journalistic freedom and liberal values of ''The Guardian'' free from commercial or political interference". The trust was converted into a limited company in 2008, with a constitution written so as to maintain for ''The Guardian'' the same protections as were built into the structure of the Scott Trust by its creators. Profits are reinvested in its journalism rather than distributed to owners or shareholders. It is considered a newspaper of record in the UK. The editor-in-chief Katharine Viner succeeded Alan Rusbridger in 2015. S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Before Present
Before Present (BP) or "years before present (YBP)" is a time scale used mainly in archaeology, geology, and other scientific disciplines to specify when events occurred relative to the origin of practical radiocarbon dating in the 1950s. Because the "present" time changes, standard practice is to use 1January 1950 as the commencement date (epoch) of the age scale, with 1950 being labelled as the "standard year". The abbreviation "BP" has been interpreted retrospectively as "Before Physics", which refers to the time before nuclear weapons testing artificially altered the proportion of the carbon isotopes in the atmosphere, which scientists must account for when using radiocarbon dating for dates of origin that may fall after this year. In a convention that is not always observed, many sources restrict the use of BP dates to those produced with radiocarbon dating; the alternative notation "RCYBP" stands for the explicit "radio carbon years before present". Usage The BP scale is s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interglacial Period
An interglacial period (or alternatively interglacial, interglaciation) is a geological interval of warmer global average temperature lasting thousands of years that separates consecutive glacial periods within an ice age. The current Holocene interglacial began at the end of the Pleistocene, about 11,700 years ago. Pleistocene During the 2.5 million years of the Pleistocene, numerous glacials, or significant advances of continental ice sheets, in North America and Europe, occurred at intervals of approximately 40,000 to 100,000 years. The long glacial periods were separated by more temperate and shorter interglacials. During interglacials, such as the present one, the climate warms and the tundra recedes polewards following the ice sheets. Forests return to areas that once supported tundra vegetation. Interglacials are identified on land or in shallow epicontinental seas by their paleontology. Floral and faunal remains of species pointing to temperate climate and indicating a s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eemian
The Last Interglacial, also known as the Eemian, was the interglacial period which began about 130,000 years ago at the end of the Penultimate Glacial Period and ended about 115,000 years ago at the beginning of the Last Glacial Period. It corresponds to Marine Isotope Stage 5e. It was the second-to-latest interglacial period of the current Ice Age, the most recent being the Holocene which extends to the present day (having followed the last glacial period). During the Last Interglacial, the proportion of in the atmosphere was about 280 parts per million. The Last Interglacial was one of the warmest periods of the last 800,000 years, with temperatures comparable to and at times warmer (by up to on average 2 degrees Celsius) than the contemporary Holocene interglacial, with the maximum sea level being up to 6 to 9 metres higher than at present, with global ice volume likely also being smaller than the Holocene interglacial. The Last Interglacial is known as the Eemian in nort ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |