|
Doris Entwisle
Doris R. Entwisle (1924–2013) was an educational sociologist known for her research on the impact of sociological factors on academic achievement, notably the longitudinal Beginning School Studies conducted in Baltimore, MD. She held the position of professor of sociology and engineering studies at Johns Hopkins University. Entwisle was awarded the Senior Distinguished Contributions Award by Society for Research in Child Development in 1997. She was named a Fellow of the John Simon Guggenheim Memorial Foundation in 1976 and the American Educational Research Association in 2008. ''The Long Shadow: Family Background, Disadvantaged Urban Youth, and the Transition to Adulthood'', co-authored by Entwisle, Karl Alexander and Linda Olson, received the Grawemeyer Award in Education from the University of Louisville in 2015. This book detailed how socioeconomic factors shaped the life outcomes of 800 Baltimore youths. One major finding was that white youth held an advantage over black ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sociology Of Education
The sociology of education is the study of how public institutions and individual experiences affect education and its outcomes. It is mostly concerned with the public schooling systems of modern industrial societies, including the expansion of higher, further, adult, and continuing education.Gordon Marshall (ed) ''A Dictionary of Sociology'' (Article: Sociology of Education), Oxford University Press, 1998 Education is seen as a fundamentally optimistic human endeavour characterised by aspirations for progress and betterment.Schofield, K. (1999)''The Purposes of Education, Queensland State Education: 2010''Accessed 2002, Oct 28. It is understood by many to be a means of overcoming handicaps, achieving greater equality, and acquiring wealth and social status.Sargent, M. (1994) ''The New Sociology for Australians'' (3rd ed.), Longman Cheshire, Melbourne Education is perceived as a place where children can develop according to their unique needs and potential. Not only can chil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Sociologists
American(s) may refer to: * American, something of, from, or related to the United States of America, commonly known as the "United States" or "America" ** Americans, citizens and nationals of the United States of America ** American ancestry, people who self-identify their ancestry as "American" ** American English, the set of varieties of the English language native to the United States ** Native Americans in the United States, indigenous peoples of the United States * American, something of, from, or related to the Americas, also known as "America" ** Indigenous peoples of the Americas * American (word), for analysis and history of the meanings in various contexts Organizations * American Airlines, U.S.-based airline headquartered in Fort Worth, Texas * American Athletic Conference, an American college athletic conference * American Recordings (record label), a record label that was previously known as Def American * American University, in Washington, D.C. Sports teams S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
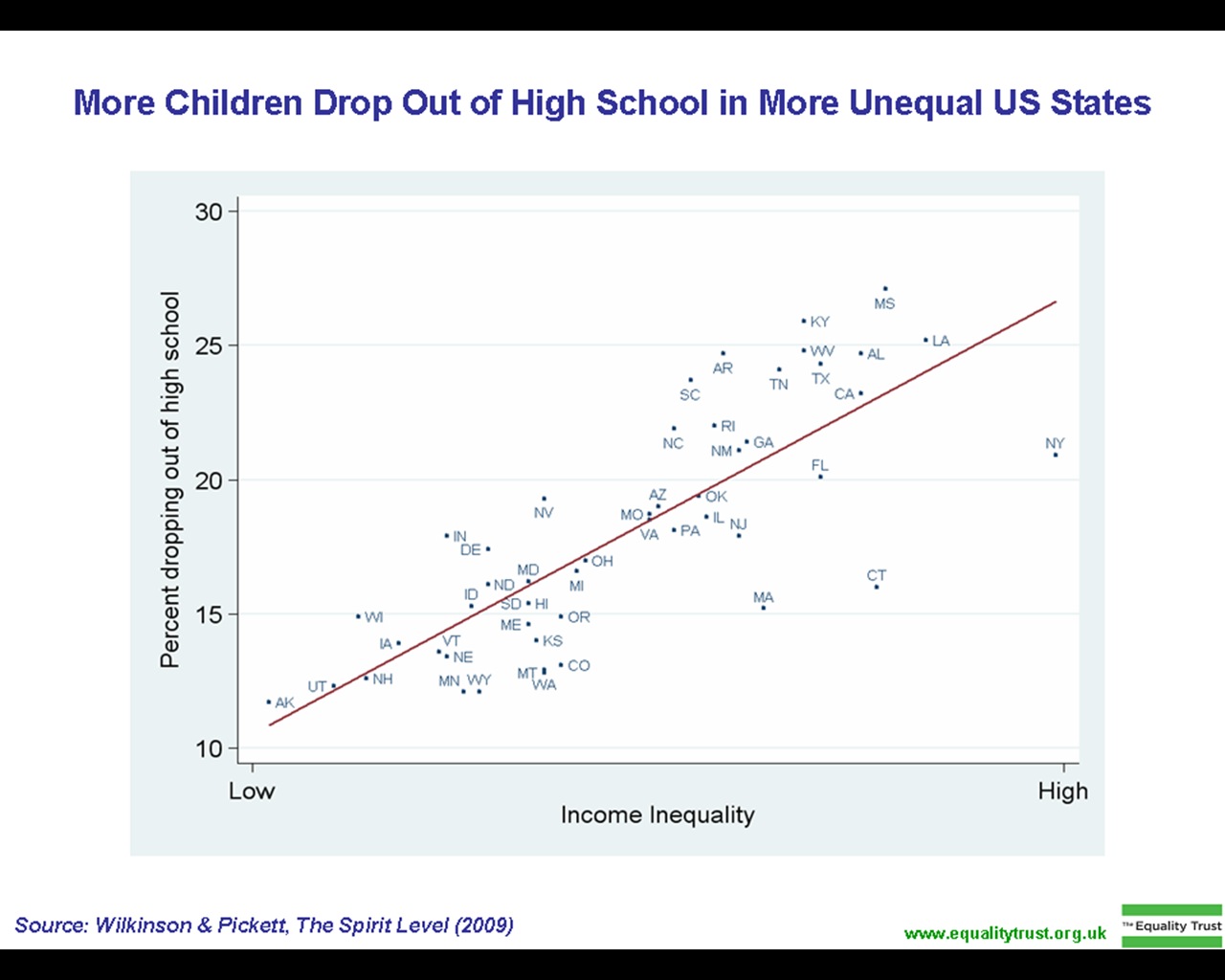
Dropping Out
Dropping out refers to leaving high school, college, university or another group for practical reasons, necessities, inability, apathy, or disillusionment with the system from which the individual in question leaves. Canada In Canada, most individuals graduate from grade 12 by the age of 18, according to Jason Gilmore who collects data on employment and education using the Labour Force Survey (LFS), the official survey used to collect unemployment data in Canada (2010). Using this tool, assessing educational attainment and school attendance can calculate a dropout rate (Gilmore, 2010). It was found by the LFS that by 2009, one in twelve 20- to 24-year-old adults did not have a high school diploma (Gilmore, 2010). The study also found that men still have higher dropout rates than women, and that students outside of major cities and in the northern territories also have a higher risk of dropping out. Although since 1990 dropout rates have gone down from 20% to a low of 9% in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Socioeconomic Status
Socioeconomic status (SES) is a measurement used by economics, economists and sociology, sociologsts. The measurement combines a person's work experience and their or their family's access to economic resources and social position in relation to others. In common parlance, "socioeconomic status" is synonymous with social class. However, academics distinguish social class from socioeconomic status, using the former to refer to one's relatively stable cultural background and the latter to refer to one's current social and economic situation which is consequently more changeable over time. When analyzing a family's SES, the household income and the education and occupations of its members are examined, whereas for an individual's SES only their own attributes are assessed. Recently, research has revealed a lesser-recognized attribute of SES as perceived financial stress, as it defines the "balance between income and necessary expenses". Perceived financial stress can be tested by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Educational Inequality
Educational Inequality is the unequal distribution of academic resources, including but not limited to school funding, qualified and experienced teachers, booksphysical facilitiesand technologies, to socially excluded communities. These communities tend to be historically disadvantaged and oppressed. Individuals belonging to these marginalized groups are often denied access to schools with adequate resources and those that can be accessed are so distant from these communities. Inequality leads to major differences in the educational success or efficiency of these individuals and ultimately suppresses social and economic mobility. Inequality in education is broken down into different types: regional inequality, inequality by sex, inequality by social stratification, inequality by parental income, inequality by parent occupation, and many more. Measuring educational efficacy varies by country and even provinces/states within the country. Generally, grades, GPA test scores, other sc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Summer Learning Loss
Summer learning loss or ''summer slide'', is the loss of academic skills and knowledge over the course of summer vacation in countries that have lengthy breaks in the school year, such as the US and Canada. Schools see evidence of this because students are often given a standardised test prior to the summer break and again when they return to school in the autumn. Research studies produce different results as to the extent of the loss, however they all appear to agree that the loss in learning varies across age and grade, subject matter, and family income and socioeconomic status. In 2017, one review of the research in the U.S.A. concluded that a) ''on average'' students lost one month of learning over the summer months, b) students lost more of their math ability than their reading ability, c) students in higher grades lost more of their learning in general than those in lower grades, d) students from low income households lost reading ability, but students in middle and high inco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Noun
In grammar, a noun is a word that represents a concrete or abstract thing, like living creatures, places, actions, qualities, states of existence, and ideas. A noun may serve as an Object (grammar), object or Subject (grammar), subject within a phrase, clause, or sentence.Example nouns for: * Living creatures (including people, alive, dead, or imaginary): ''mushrooms, dogs, Afro-Caribbeans, rosebushes, Mandela, bacteria, Klingons'', etc. * Physical objects: ''hammers, pencils, Earth, guitars, atoms, stones, boots, shadows'', etc. * Places: ''closets, temples, rivers, Antarctica, houses, Uluru, utopia'', etc. * Actions of individuals or groups: ''swimming, exercises, cough, explosions, flight, electrification, embezzlement'', etc. * Physical qualities: ''colors, lengths, porosity, weights, roundness, symmetry, solidity,'' etc. * Mental or bodily states: ''jealousy, sleep, joy, headache, confusion'', etc. In linguistics, nouns constitute a lexical category (part of speech) defined ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adverb
An adverb is a word or an expression that generally modifies a verb, an adjective, another adverb, a determiner, a clause, a preposition, or a sentence. Adverbs typically express manner, place, time, frequency, degree, or level of certainty by answering questions such as ''how'', ''in what way'', ''when'', ''where'', ''to what extent''. This is called the adverbial function and may be performed by an individual adverb, by an adverbial phrase, or by an adverbial clause. Adverbs are traditionally regarded as one of the parts of speech. Modern linguists note that the term ''adverb'' has come to be used as a kind of "catch-all" category, used to classify words with various types of syntactic behavior, not necessarily having much in common except that they do not fit into any of the other available categories (noun, adjective, preposition, etc.). Functions The English word ''adverb'' derives (through French) from Latin ''adverbium'', from ''ad-'' ('to'), ''verbum'' ('word', 'ver ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |