|
Don John (horse)
Don John (1835–1857) was a British Thoroughbred racehorse and sire best known for winning the classic St Leger Stakes in 1838. In a racing career which lasted from May 1837 until April 1839 he ran ten times and won nine races, although three of his victories were walkovers when no rival appeared to oppose him. He was one of the leading British two-year-olds of 1837, when his three wins included the Champagne Stakes at Doncaster Racecourse. In the following year he returned to Doncaster where he recorded an emphatic win in the St Leger and then defeated a strong field of older horses in the Doncaster Cup. In the following year he was campaigned at Newmarket where he was beaten for the first time by Grey Momus in the Port Stakes. After one more win he suffered serious leg injuries which ended his racing career. He was retired to stud where he became a successful breeding stallion. Background Don John was a bay horse standing 15 hands three inches high with a white sock on hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Frederick Herring
John Frederick Herring Sr. (12 September 1795 – 23 September 1865), also known as John Frederick Herring I, was a painter, sign maker and coachman in Victorian England.John Frederick Herring Sr. on Art.Net" (biography & selected works),John Frederick Herring Sr. (biography) Berger Collection (BCET) Berger Collection Educational Trust, 2006. Archived at Internet Archive. He painted the 1848 "Pharoah's Chariot Horses" (''archaic spelling "Pharoah"''). He amended his signature "SR" (senior) in 1836, with the growing fame of his teenage son (1 of 4) |
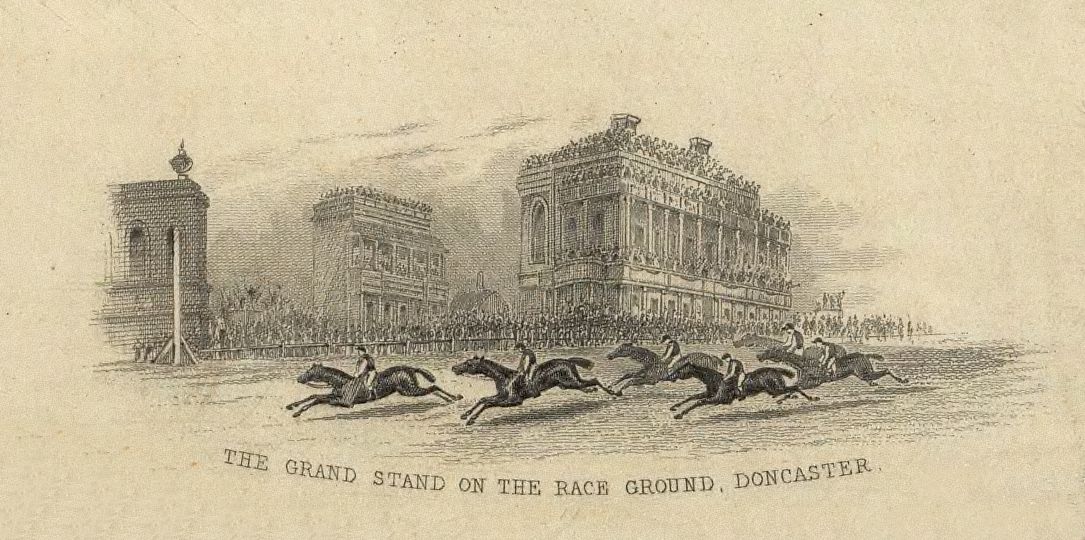
Doncaster Racecourse
Doncaster Racecourse (also known as the Town Moor course) is a racecourse in Doncaster, South Yorkshire, England. It hosts two of Great Britain's 36 annual Group 1 flat races, the St Leger Stakes and the Racing Post Trophy. History Doncaster is one of the oldest (and the largest in physical capacity) established centres for horse racing in Britain, with records of regular race meetings going back to the 16th century. A map of 1595 already shows a racecourse at Town Moor. In 1600 the corporation tried to put an end to the races because of the number of ruffians they attracted, but by 1614 it acknowledged failure and instead marked out a racecourse. Doncaster is home to two of the World's oldest horse races: The Doncaster Cup The earliest important race in Doncaster's history was the Doncaster Gold Cup, first run over Cantley Common in 1766. The Doncaster Cup is the oldest continuing regulated horse race in the world. Together with the Goodwood Cup and Ascot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northumberland Plate
The Northumberland Plate is a flat handicap horse race in Great Britain open to horses aged three years or older. It is run at Newcastle over a distance of 2 miles and 56 yards (3,270 metres), and it is scheduled to take place each year in late June or early July. History The event was established in 1833, and the inaugural running was won by Tomboy. It was initially held at Town Moor, and it was part of a meeting first staged at Killingworth in 1623. It was transferred to its present venue at Gosforth Park in 1882. The Northumberland Plate originally took place on a Wednesday, and for many years the meeting was a holiday for local mine workers. The race became popularly known as the "Pitmen's Derby". The meeting ceased to be a holiday in 1949, and the race was switched to a Saturday in 1952. The Northumberland Plate is now one of the richest two-mile handicaps in the world. It was sponsored by John Smith's from 2003 to 2016, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Scott (jockey)
William Scott (1797–1848) was a British jockey. Known as "Bill", he was a brother of the renowned trainer John Scott who frequently conditioned horses that he rode. Based at his brother's Whitewall Stables in Malton, North Yorkshire, Bill Scott won nineteen of the British Classic Races, including the St. Leger Stakes a record nine times of which four were in a row from 1838 through 1841. He was already a jockey of some national renown by the early 1830s, being described as the " Chifney of the north". "For hand, seat and science in a race, he is very little inferior to anyone." He was also "possessed of considerable property (part in right of his wife)". In 1836, Scott won the first of his three Epsom Oaks aboard Cyprian, a filly owned and trained by his brother John. He also owned (and trained) Sir Tatton Sykes whom he rode to victory in the 1846 2,000 Guineas, his third win as a jockey in that Classic. He also rode Sir Tatton Sykes to his ninth victory in that year's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malton, North Yorkshire
Malton is a market town, civil parish and electoral ward in North Yorkshire, England. Historically part of the North Riding of Yorkshire, the town is the location of the offices of Ryedale District Council and has a population of around 13,000 people, measured for both the civil parish and the electoral ward at the 2011 Census as 4,888. The town is located to the north of the River Derwent which forms the historic boundary between the North and East Ridings of Yorkshire. Facing Malton on the other side of the Derwent is Norton. The Karro Food Group (formerly known as Malton Bacon Factory), Malton bus station and Malton railway station are located in Norton-on-Derwent. Malton is the local area's commercial and retail centre. In the town centre there are small traditional independent shops and high street names. The market place has recently become a meeting area with a number of coffee bars and cafés opening all day to complement the public houses. Malton has been des ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bloomsbury (horse)
Bloomsbury (1836 –1861) was a British Thoroughbred racehorse and sire. In a career that lasted from May 1839 to July 1841 he ran ten times and won four races. His most important win came on his first racecourse appearance when he won the 1839 Derby. He went on to win important races at Ascot and Liverpool before his retirement after his five-year-old season. He was later exported to stand as a stallion in Germany. Bloomsbury's controversial origins were the subject of two formal objections and a court case which led to a crisis in English racing. Background Bloomsbury was a bay horse described as looking "coarse" but very powerful, standing 15.3 hands high, bred by Mr Cattle, a farmer from Sheriff Hutton. The colt was sired by Mulatto the winner of the 1827 Doncaster Cup who went on to be a good, but unexceptional sire. Bloomsbury's dam, Arcot Lass, was one of the few mares to produce two Derby winners: her son St. Giles had won the race in 1832. According to one account, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yearling (horse)
A yearling is a young horse either male or female that is between one and two years old.Ensminger, M. E. ''Horses & Tack: A Complete One Volume Reference on Horses and Their Care'' Rev. ed. Boston:Houghton Mifflin Co. 1991 p. 470 Yearlings are comparable in development to a very early adolescent and are not fully mature physically. While they may be in the earliest stages of sexual maturity, they are considered too young to be breeding stock. Yearlings may be further defined by sex, using the term "colt" to describe any male horse under age four, and filly for any female under four. Development and training Generally, the training of yearlings consists of basic gentling on the ground; most are too young to be ridden or driven. Yearlings are often full of energy and quite unpredictable. Even though they are not fully mature, they are heavier and stronger than a human and require knowledgeable handling. Many colts who are not going to be used as breeding stallions are gelded ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Ridsdale
Robert Ridsdale (1783–1857) was a wealthy English race horse breeder and gambler, whose horse St. Giles, owned in partnership with prize-fighter, John Gully, won The Derby in 1832. According to the ''Biographical Encyclopaedia of British Flat Racing'' “His methods were based on the corruption of trainers, jockey and stable employee and for some years he was a powerful influence for evil in the sport”. His partnership with Gully ended on acrimonious and violent terms. Early life Ridsdale came from humble beginnings, but stories about his early life vary; some say he was working in a Doncaster hotel as a boot-black and others that he was a groom in York. They all agree that he was offered a job in service by John George Lambton, who later became the 1st Earl of Durham. Ridsdale worked as a groom and became involved with Lambton's horse racing and gambling, getting to know jockeys, trainers and the betting market. His time with Lambton enabled him to develop the so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guinea (coin)
The guinea (; commonly abbreviated gn., or gns. in plural) was a coin, minted in Great Britain between 1663 and 1814, that contained approximately one-quarter of an ounce of gold. The name came from the Guinea region in West Africa, from where much of the gold used to make the coins was sourced. It was the first English machine-struck gold coin, originally representing a value of 20 shillings in sterling specie, equal to one pound, but rises in the price of gold relative to silver caused the value of the guinea to increase, at times to as high as thirty shillings. From 1717 to 1816, its value was officially fixed at twenty-one shillings. In the Great Recoinage of 1816, the guinea was demonetised and the word "guinea" became a colloquial or specialised term. Although the coin itself no longer circulated, the term ''guinea'' survived as a unit of account in some fields. Notable usages included professional fees (medical, legal, etc.), which were often invoiced in guineas, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sock (horse Marking)
Markings on horses are usually distinctive white areas on an otherwise dark base coat color. Most horses have some markings, and they help to identify the horse as a unique individual. Markings are present at birth and do not change over the course of the horse's life. Most markings have pink skin underneath most of the white hairs, though a few faint markings may occasionally have white hair with no underlying pink skin. Markings may appear to change slightly when a horse grows or sheds its winter coat, however this difference is simply a factor of hair coat length; the underlying pattern does not change. On a gray horse, markings visible at birth may become hidden as the horse turns white with age, but markings can still be determined by trimming the horse's hair closely, then wetting down the coat to see where there is pink skin and black skin under the hair. Recent studies have examined the genetics behind white markings and have located certain genetic loci that influence ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hand (unit)
The hand is a non- SI unit of measurement of length standardized to . It is used to measure the height of horses in many English-speaking countries, including Australia, Canada, the Republic of Ireland, the United Kingdom, and the United States. It was originally based on the breadth of a human hand. The adoption of the international inch in 1959 allowed for a standardized imperial form and a metric conversion. It may be abbreviated to "h" or "hh". Although measurements between whole hands are usually expressed in what appears to be decimal format, the subdivision of the hand is not decimal but is in base 4, so subdivisions after the radix point are in quarters of a hand, which are inches. Thus, 62 inches is fifteen and a half hands, or 15.2 hh (normally said as "fifteen-two", or occasionally in full as "fifteen hands two inches"). Terminology "Hands" may be abbreviated to "h", or "hh". The "hh" form is sometimes interpreted as standing for "hands high". When spoke ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bay (horse)
Bay is a hair coat color of horses, characterized by a reddish-brown or brown body color with a black point coloration on the mane, tail, ear edges, and lower legs. Bay is one of the most common coat colors in many horse breeds. The black areas of a bay horse's hair coat are called "black points", and without them, a horse is not a bay horse. Black points may sometimes be covered by white markings; however such markings do not alter a horse's classification as "bay". Bay horses have dark skin – except under white markings, where the skin is pink. Genetically, bay occurs when a horse carries both the Agouti gene and a black base coat. While the basic genetics that create bay coloring are fairly simple, the genes themselves and the mechanisms that cause shade variations within the bay family are quite complex and, at times, disputed. The genetics of dark shades of bay are still under study. The genetic mechanism that produces seal brown has yet to be isolated. Sooty ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |