|
Domus Severiana
The Domus Severiana is the modern name given to the final extension to the imperial palaces on the Palatine Hill in Rome, built to the south-east of the Stadium Palatinum in the Domus Augustana of Septimius Severus. It included the Baths of Septimius Severus (Latin: ''Balneum Palatii''). All that remains of the building are the imposing brick substructures at the corner of the hill, which created an artificial platform at the same level as the palace of Domitian, extending it, since the emperors had run out of space on the hill. There are very few remains of the building itself, which was then built on the terrace supported by the substructures. It had a view of Rome from the Circus Maximus and the Aventine Hill to the Caelian Hill and the Baths of Caracalla. They were part of an imperial baths complex or thermae, now visible in the remains below the exedra of the Stadium Palatinum, which may have been built under Domitian and which was rebuilt by Maxentius. They were fed by a br ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maxentius
Marcus Aurelius Valerius Maxentius ( 283 – 28 October 312) was a Roman emperor from 306 until his death in 312. Despite ruling in Italy and North Africa, and having the recognition of the Senate in Rome, he was not recognized as a legitimate emperor by his fellow emperors. He was the son of former Emperor Maximian and the son-in-law of Emperor Galerius. The latter part of his reign was preoccupied with civil war, allying with Maximinus against Licinius and Constantine. The latter defeated him at the Battle of the Milvian Bridge in 312, where Maxentius, with his army in flight, purportedly perished by drowning in the Tiber river. Maxentius was the last emperor permanently to reside in Rome. He attempted to embellish, restore and improve the ancient capital, carrying out important building works, including the Temple of the Divine Romulus (dedicated to his deceased son), the Basilica of Maxentius, which was completed by Constantine, the villa and the circus of Maxentius. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Roman Buildings And Structures In Rome
Ancient history is a time period from the History of writing, beginning of writing and recorded human history through late antiquity. The span of recorded history is roughly 5,000 years, beginning with the development of Sumerian language, Sumerian cuneiform script. Ancient history covers all continents inhabited by humans in the period 3000 BCAD 500, ending with the Early Muslim conquests, expansion of Islam in late antiquity. The three-age system periodises ancient history into the Stone Age, the Bronze Age, and the Iron Age, with recorded history generally considered to begin with the Bronze Age. The start and end of the three ages vary between world regions. In many regions the Bronze Age is generally considered to begin a few centuries prior to 3000 BC, while the end of the Iron Age varies from the early first millennium BC in some regions to the late first millennium AD in others. During the time period of ancient history, the world population was Exponential growth, e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buildings And Structures Completed In The 2nd Century
A building or edifice is an enclosed structure with a roof, walls and windows, usually standing permanently in one place, such as a house or factory. Buildings come in a variety of sizes, shapes, and functions, and have been adapted throughout history for numerous factors, from building materials available, to weather conditions, land prices, ground conditions, specific uses, prestige, and aesthetic reasons. To better understand the concept, see ''Nonbuilding structure'' for contrast. Buildings serve several societal needs – occupancy, primarily as shelter from weather, security, living space, privacy, to store belongings, and to comfortably live and work. A building as a shelter represents a physical separation of the human habitat (a place of comfort and safety) from the ''outside'' (a place that may be harsh and harmful at times). buildings have been objects or canvasses of much artistic expression. In recent years, interest in sustainable planning and building practi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Ancient Monuments In Rome
This is a list of ancient monuments from Roman Republic, Republican and Roman Empire, Imperial periods in the city of Rome, Italy. Amphitheaters * Amphitheater of Caligula * Amphitheatrum Castrense * Amphitheater of Nero * Amphitheater of Statilius Taurus * Colosseum Baths * Baths of Agrippa * Baths of Caracalla * Baths of Commodus * Baths of Constantine (Rome), Baths of Constantine * Baths of Decius * Baths of Diocletian * Baths of Licinius Sura * Baths of Nero and Alexander * Baths of Septimius Severus * Baths of Titus * Baths of Trajan (later misnamed the Baths of Domitian) Circuses * Circus Flaminius * Circus Maximus * Circus of Maxentius * Circus of Nero * Circus Varianus Gardens * Gardens of Lucullus * Gardens of Maecenas * Gardens of Sallust * Horti Aciliorum * Horti Agrippinae * Horti Caesaris * Horti Domitiae * Horti Lamiani * Horti Liciniani * Horti Lolliani * Horti Pompeiani * Horti Tauriani Porticoes * Porticus Aemilia * Porticus Deorum Consentium * Porticu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
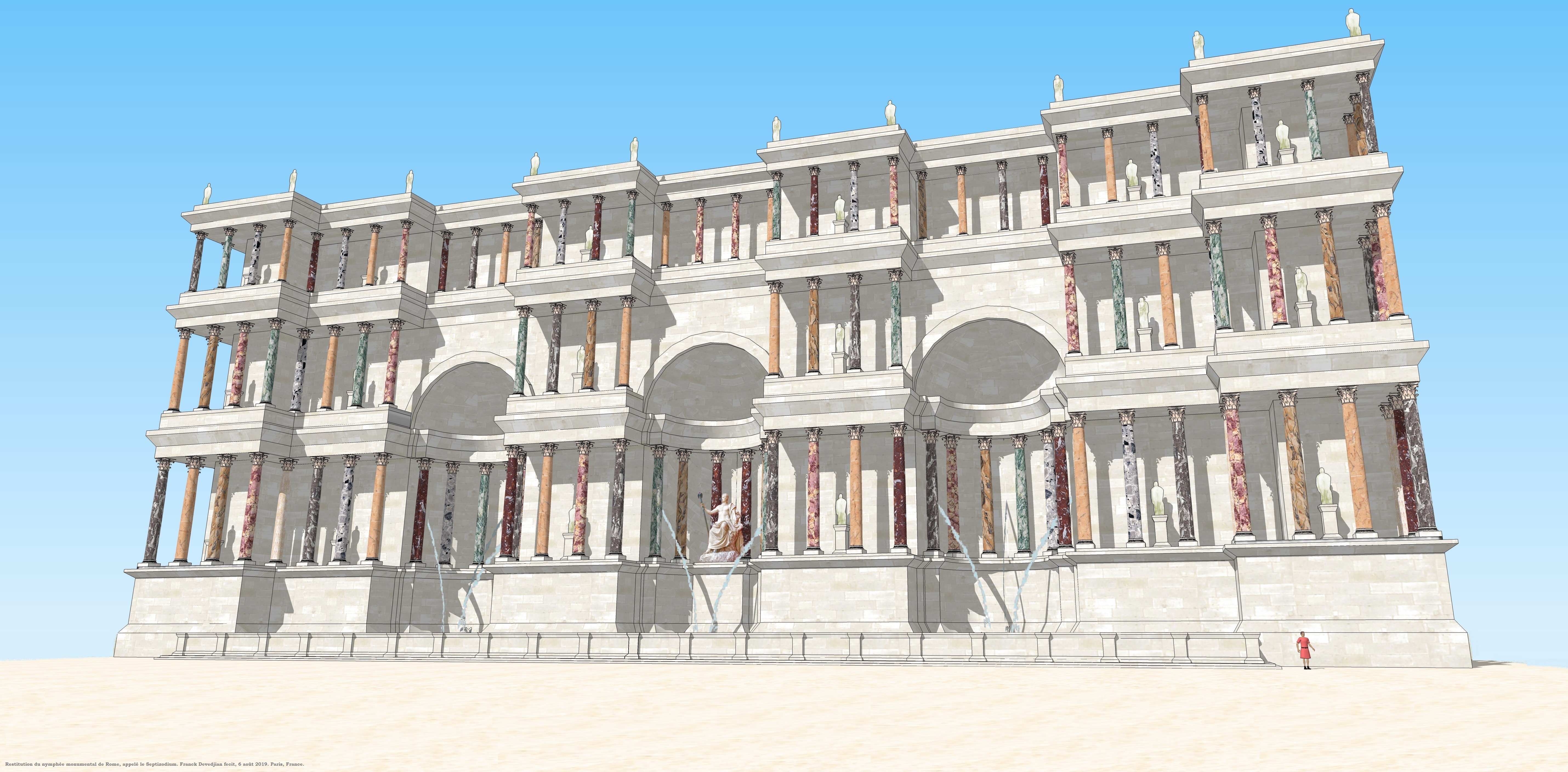
Septizodium
The Septizodium (also called ''Septizonium'', ''Septicodium'', or ''Septisolium'') was a building in ancient Rome. It was built in 203 AD by Emperor Septimius Severus. The origin of the name "Septizodium" is from ''Septisolium'', from the Latin for temple of seven suns, and was probably named for the seven planetary deities (Saturn, Sol, Luna, Mars, Mercury, Jupiter, and Venus) or for the fact that it was originally divided into seven parts. The building had no known practical purpose and was probably meant to be a decorative façade, known as a nymphaeum. Ancient and medieval sources describe its purpose as being to impress Severus' fellow north Africans as they entered the city, as it was located at the place where the Via Appia passes the Palatine and leads east towards the Forum Romanum. Other examples of septizodia are known, all from Africa. Ammianus Marcellinus refers to the building in an ambiguous passage: "The plebs...had come together at the Septemzodium, a popular ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
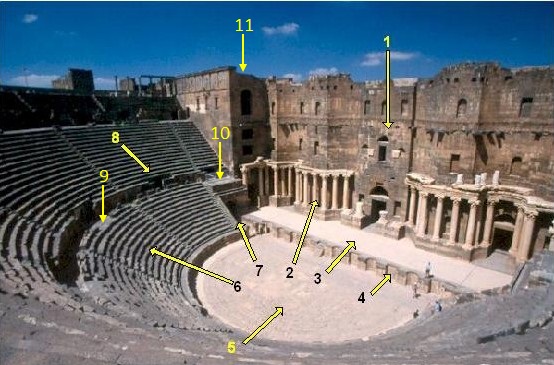
Scaenae Frons
The scaenae frons () is the elaborately decorated permanent architectural background of a Roman theatre (structure), Roman theatre stage. The form may have been intended to resemble the facades of imperial palaces. It could support a permanent roof or awnings. The Roman scaenae frons was also used both as the backdrop to the stage and behind as the actors' dressing room. Largely through reconstruction or restoration, there are a number of well-preserved examples. This form was influenced by Greek theatre#Architecture, Greek theatre, which had an equivalent but simpler ''Skene (theatre), skene'' building (meaning "tent", showing the original nature of it). This led to the stage or space before the ''skene'' being called the proscenium. In the Hellenistic period the ''skene'' became more elaborate, perhaps with columns, but also used to support painted scenery. The Roman scaenae frons was also used both as the backdrop to the stage and behind as the actors' dressing room. It no l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Via Appia
The Appian Way (Latin and Italian: Via Appia) is one of the earliest and strategically most important Roman roads of the ancient republic. It connected Rome to Brindisi, in southeast Italy. Its importance is indicated by its common name, recorded by Statius, of ('the Appian Way, the queen of the long roads'). The road is named after Appius Claudius Caecus, the Roman censor who, during the Samnite Wars, began and completed the first section as a military road to the south in 312 BC."Appian Way" in '' Chambers's Encyclopædia''. London: George Newnes, 1961, Vol. 1, p. 490. In July 2024, the Appian Way entered the UNESCO World Heritage List. Origins Development The Appian Way was a Roman road that the Republic used as a main route for military supplies for its conquest of southern Italy in 312 BC and for improvements in communication. The Appian Way — essential to the Romans — was the first long road built specifically to transport troops outside the sma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aqua Claudia
Aqua Claudia ("the Claudius, Claudian water") was an ancient Roman aqueduct that, like the Aqua Anio Novus, was begun by Emperor Caligula (37–41 AD) in 38 AD and finished by Emperor Claudius (41–54 AD) in 52 AD. It was the eighth aqueduct to supply Rome and together with Aqua Anio Novus, Aqua Anio Vetus and Aqua Marcia, it is regarded as one of the "four great aqueducts of Rome". = The aqueduct went through at least two major repairs. Tacitus suggests that the aqueduct was in use by AD 47. An inscription from the time of emperor Vespasian suggests that Aqua Claudia was used for ten years, then failed and was out of use for nine years. The first repairs took place during the reign of Vespasian in 71 AD. The aqueduct was repaired again in 81 AD by emperor Titus. Additionally, brick stamps from 123 AD testify to some restorations during the rule of emperor Hadrian. Honorary inscriptions from the 5th century show that repairs were done during the rule of Arcadius and the rule of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Domitian
Domitian ( ; ; 24 October 51 – 18 September 96) was Roman emperor from 81 to 96. The son of Vespasian and the younger brother of Titus, his two predecessors on the throne, he was the last member of the Flavian dynasty. Described as "a ruthless but efficient autocrat", his authoritarian style of ruling put him at sharp odds with the Roman Senate, Senate, whose powers he drastically curtailed. Domitian had a minor and largely ceremonial role during the reigns of his father and brother. After the death of his brother, Domitian was declared emperor by the Praetorian Guard. His 15-year reign was the longest since Tiberius. As emperor, Domitian strengthened the economy by revaluing the Roman currency, Roman coinage, expanded the border defenses of the empire, and initiated a massive building program to restore the damaged city of Rome. Significant wars were fought in Britain, where his general Gnaeus Julius Agricola, Agricola made significant gains in his attempt to conquer Ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palatine Hill
The Palatine Hill (; Classical Latin: ''Palatium''; Neo-Latin: ''Collis/Mons Palatinus''; ), which relative to the seven hills of Rome is the centremost, is one of the most ancient parts of the city; it has been called "the first nucleus of the Roman Empire". The site is now mainly a large open-air museum whilst the Palatine Museum houses many finds from the excavations here and from other ancient Italian sites. Imperial palaces were built there, starting with Augustus. Before imperial times the hill was mostly occupied by the houses of the rich. The hill originally had two summits separated by a depression: the higher summit was called ''Palatium''; the lower ''Germalus'' (or ''Cermalus''). Using the Forma Urbis Romae, Forma Urbis its perimeter enclosed ; while the Regionary Catalogues of the 4th century enclose . Etymology According to Livy (59 BC – AD 17) the Palatine hill got its name from the Arcadia (ancient region), Arcadian settlers from Pallantium, named fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermae
In ancient Rome, (from Greek , "hot") and (from Greek ) were facilities for bathing. usually refers to the large Roman Empire, imperial public bath, bath complexes, while were smaller-scale facilities, public or private, that existed in great numbers throughout Rome. Most Roman cities had at least one – if not many – such buildings, which were centers not only for bathing, but socializing and reading as well. Bathhouses were also provided for wealthy private Roman villa, villas, domus, town houses, and castra, forts. They were supplied with water from an adjacent river or stream, or within cities by aqueduct (watercourse), aqueduct. The water would be heated by fire then channelled into the caldarium (hot bathing room). The design of baths is discussed by Vitruvius in ''De architectura'(V.10) Terminology '','' '','' '','' and may all be translated as 'bath' or 'baths', though Latin sources distinguish among these terms. or , derived from the Greek language, G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |