|
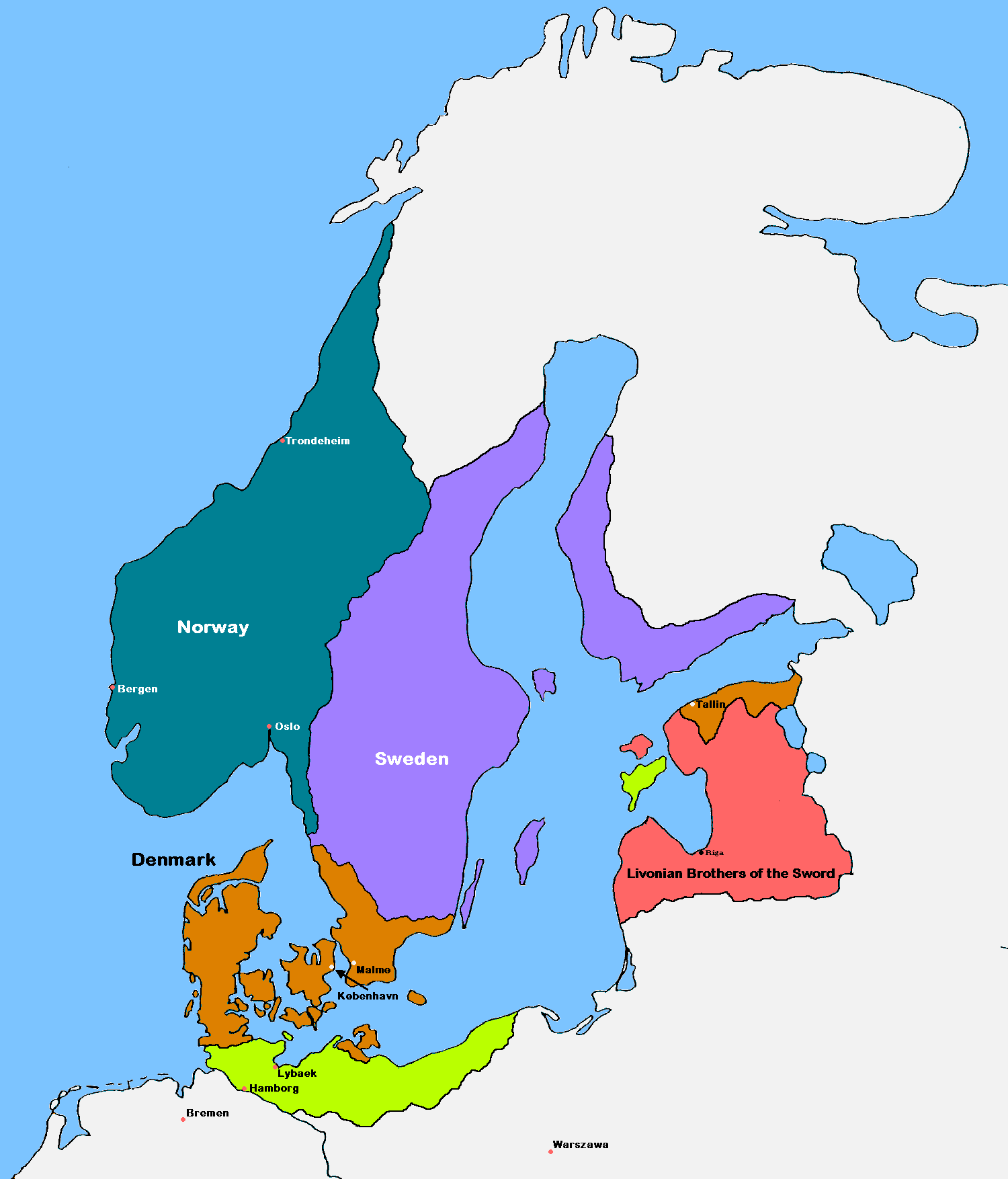
Dominium Maris Baltici
The establishment of a , . ("Baltic Sea dominion") was one of the primary political aims of the Kingdom of Denmark, Danish and Kingdom of Sweden, Swedish kingdoms in the Late Middle Ages, late medieval and Early Modern era, early modern eras. Throughout the Northern Wars the Danish and Swedish navies played a secondary role, as the ''dominium'' was contested through control of key coasts by land warfare. Etymology The term, which is commonly used in historiography, was probably coined in 1563 by the King of Poland, Sigismund II Augustus, referring to the hegemonial ambitions of his Swedish adversaries in the Livonian War. The first written reference stems from the Treaty of the Hague (1614), Dutch-Swedish treaty of 5 (Old Style and New Style dates, O.S.) / 15 (Old Style and New Style dates, N.S.) April 1614, concluded in The Hague.Treaty of The Hague, 5 (15) April 1614, article VIII of the Dutch version: "[...] sijne Koninghlijcke Majesteyt ende de Croon Sweeden, in haere Hooghey ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medieval Norway
The history of Norway has been influenced to an extraordinary degree by the terrain and the climate of the region. About 10,000 BC, following the retreat inland of the great ice sheets, the earliest inhabitants migrated north into the territory which is now Norway. They traveled steadily northwards along the coastal areas, warmed by the Gulf Stream. They were hunter-gatherers whose diet included seafood and game, particularly reindeer as staple foods. Between 5,000 BC and 4,000 BC the earliest agricultural settlements appeared around the Oslofjord. Gradually, between 1,500 BC and 500 BC, agricultural settlements spread to the entire south Norway, while the inhabitants of the regions north of Trøndelag continued to hunt and fish. The Neolithic period started in 4,000 BC. The Migration Period caused the first chieftains to take control and hilltop forts to be constructed. From the 8th century Norwegians started expanding across the seas to the British Isles and later Iceland and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treaty Of The Hague (1614)
The Treaty of the Hague (1614) was a defensive and maritime treaty signed between the Netherlands and Sweden in 1614. It had some special significance due to the fact it was connected to a somewhat earlier alliance between the Dutch and Lübeck Stipulations * A defensive alliance to last 15 years is established between Sweden and the Dutch. * The two powers pledge to try and protect their liberties and rights in the Baltic Sea and North Sea. * Both countries would exchange ambassadors to each other. * The Dutch recognize the Swedish claim to ''Dominium maris baltici The establishment of a , . ("Baltic Sea dominion") was one of the primary political aims of the Kingdom of Denmark, Danish and Kingdom of Sweden, Swedish kingdoms in the Late Middle Ages, late medieval and Early Modern era, early modern eras. Th ...'' References {{reflist Treaties Treaties of Sweden Treaties of the Dutch Republic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hanseatic League
The Hanseatic League was a Middle Ages, medieval commercial and defensive network of merchant guilds and market towns in Central Europe, Central and Northern Europe, Northern Europe. Growing from a few Northern Germany, North German towns in the late 12th century, the League expanded between the 13th and 15th centuries and ultimately encompassed nearly 200 settlements across eight modern-day countries, ranging from Tallinn in Estonia in the east, Bergen (Bjørgvin) in Norway to the North to the Netherlands in the west, and extended inland as far as Cologne, Prussia (region), the Prussian regions and Kraków, Poland. The League began as a collection of loosely associated groups of German traders and towns aiming to expand their commercial interests, including protection against robbery. Over time, these arrangements evolved into the League, offering traders toll privileges and protection on affiliated territory and trade routes. Economic interdependence and familial connections am ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Principality Of Rügen
The Principality of Rügen was a Medieval Denmark, Danish principality, formerly a duchy, consisting of the island of Rügen and the adjacent mainland from 1168 until 1325. It was governed by a local dynasty of princes of the ''Wizlawiden'' (''House of Wizlaw'') dynasty. For at least part of this period, Rügen was subject to the Holy Roman Empire. Danish conquest and conversion The Danes (Germanic tribe), Danes conquered the Rani (Slavic tribe), Rani stronghold of Cape Arkona, Arkona in 1168. The rulers of the Rani became vassals of the Danish king, and the Slavic population was gradually Christianized. In the 12th century, the Duchy of Rügen not only functioned as a bridgehead for Danish expansions into Wends, ''Vendland'', but also Rani forces successfully participated in Danish raids into Circipania and areas conquered by Pomerania's Wartislaw I in the 1120s. After Pomerania became part of the Holy Roman Empire in 1181, it sent out a navy in 1184 to subdue Rügen for the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Bornhöved (1227)
The (second) Battle of Bornhöved took place on 22 July 1227 near Bornhöved in Holstein. Count Adolf IV of Schauenburg and Holstein — leading an army consisting of troops from the cities of Lübeck and Hamburg, Dithmarschen, Holstein, and various Northern German nobles, defeated King Valdemar II of Denmark and the Welf Otto the Child. Background Valdemar and his predecessor King Canute VI of Denmark had previously conquered Holstein, Mecklenburg, Hamburg, Lübeck (1202), Ratzeburg and the coast of Pomerania, including the island of Rügen. Battle The contest was maintained with great firmness on both sides, and continued for an unusual length of time. The carnage was so great that its combatants are said to have fought knee deep in blood. The King of Denmark had one of his eyes shot out, and had several horses killed under him, but his troops and their allies fought with so much bravery that the victory would have been theirs had not the contingent from Dithmar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Danish Empire And Campaigns 1168-1227
Danish may refer to: * Something of, from, or related to the country of Denmark People * A Danish person, also called a "Dane", can be a national or citizen of Denmark (see Demographics of Denmark) * Culture of Denmark * Danish people or Danes, people with a Danish ancestral or ethnic identity * A member of the Danes, a Germanic tribe * Danish (name), a male given name and surname Language * Danish language, a North Germanic language used mostly in Denmark and Northern Germany * Danish tongue or Old Norse, the parent language of all North Germanic languages Food * Danish cuisine * Danish pastry, often simply called a "Danish" See also * Dane (other) * * Gdańsk Gdańsk is a city on the Baltic Sea, Baltic coast of northern Poland, and the capital of the Pomeranian Voivodeship. With a population of 486,492, Data for territorial unit 2261000. it is Poland's sixth-largest city and principal seaport. Gdań ... * List of Danes * Languages of Denmark {{disambi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Northern War
In the Great Northern War (1700–1721) a coalition led by the Tsardom of Russia successfully contested the supremacy of the Swedish Empire in Northern Europe, Northern, Central Europe, Central and Eastern Europe. The initial leaders of the anti-Swedish alliance were Peter the Great, Peter I of Russia, Frederick IV of Denmark, Frederick IV of Denmark–Norway and Augustus II the Strong of Electorate of Saxony, Saxony–Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, Poland–Lithuania. Frederick IV and Augustus II were defeated by Sweden, under Charles XII, and forced out of the alliance in 1700 and 1706 respectively, but rejoined it in 1709 after the defeat of Charles XII at the Battle of Poltava. George I of Great Britain and the Electorate of Hanover joined the coalition in 1714 for Hanover and in 1717 for Britain, and Frederick William I of Prussia, Frederick William I of Brandenburg-Prussia joined it in 1715. Charles XII led the Swedish army. Swedish allies included Holstein-Gottorp, sev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth Navy
Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth Navy was the navy of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth and existed from 1627 to 1643. History The Commonwealth Navy was small and played a relatively minor role in the history of the Commonwealth. Juliusz Bardach, Boguslaw Lesnodorski, and Michal Pietrzak, ''Historia panstwa i prawa polskiego''. Warsaw: Paristwowe Wydawnictwo Naukowe, 1987, p.231 Despite having access to the Baltic Sea and temporarily to the Black Sea, neither Poland nor Lithuania had any significant navy until the first naval commission was established by Sigismund II Augustus during the Northern Seven Years' War in 1568. Sigismund III Vasa's plans for fleet creation At the turn of the seventeenth century, Poland became ruled by the House of Vasa, and was involved in Polish-Swedish wars, a series of wars with Sweden (see also dominium maris baltici). Vasa kings attempted to create a proper fleet, but their attempts met with repeated failures, due to lack of funds in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth
The Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, also referred to as Poland–Lithuania or the First Polish Republic (), was a federation, federative real union between the Crown of the Kingdom of Poland, Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, existing from 1569 to 1795. This state was among the largest, most populated countries of 16th- to 18th-century Europe. At its peak in the early 17th century, the Commonwealth spanned approximately and supported a multi-ethnic population of around 12 million as of 1618. The official languages of the Commonwealth were Polish language, Polish and Latin Language, Latin, with Catholic Church, Catholicism as the state religion. The Union of Lublin established the Commonwealth as a single entity on 1 July 1569. The two nations had previously been in a personal union since the Union of Krewo, Krewo Agreement of 1385 (Polish–Lithuanian union) and the subsequent marriage of Queen Jadwiga of Poland to Grand Duke Jogaila of Lithuania, who was cr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire, also known as the Holy Roman Empire of the German Nation after 1512, was a polity in Central and Western Europe, usually headed by the Holy Roman Emperor. It developed in the Early Middle Ages, and lasted for a millennium until its Dissolution of the Holy Roman Empire, dissolution in 1806 during the Napoleonic Wars. For most of its history the Empire comprised the entirety of the modern countries of Germany, Czechia, Austria, the Netherlands, Belgium, Switzerland, Slovenia, and Luxembourg, most of north-central Italy, and large parts of modern-day east France and west Poland. On 25 December 800, Pope Leo III crowned the Frankish king Charlemagne Roman emperor, reviving the title more than three centuries after the fall of the Western Roman Empire in 476. The title lapsed in 924, but was revived in 962 when Otto I, OttoI was crowned emperor by Pope John XII, as Charlemagne's and the Carolingian Empire's successor. From 962 until the 12th century, the empire ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
France
France, officially the French Republic, is a country located primarily in Western Europe. Overseas France, Its overseas regions and territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the Atlantic Ocean#North Atlantic, North Atlantic, the French West Indies, and List of islands of France, many islands in Oceania and the Indian Ocean, giving it Exclusive economic zone of France, one of the largest discontiguous exclusive economic zones in the world. Metropolitan France shares borders with Belgium and Luxembourg to the north; Germany to the northeast; Switzerland to the east; Italy and Monaco to the southeast; Andorra and Spain to the south; and a maritime border with the United Kingdom to the northwest. Its metropolitan area extends from the Rhine to the Atlantic Ocean and from the Mediterranean Sea to the English Channel and the North Sea. Its Regions of France, eighteen integral regions—five of which are overseas—span a combined area of and hav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |