|
Dominican Republic–Spain Relations
Dominican Republic–Spain relations are the bilateral relations between the Dominican Republic and the Spain, Kingdom of Spain. Both nations are members of the Association of Academies of the Spanish Language and the Organization of Ibero-American States. History Spanish colonization The first Europeans to arrive to what is now present day Dominican Republic was in December 1492 when explorer Christopher Columbus arrived to the island of Hispaniola. The Spanish built a fort named La Navidad. The Spanish settlers on Hispaniola soon began fighting amongst themselves. They raped Taíno women and forced them to work as their servants. After several months of this abuse, the Taínos attacked the settlement and killed the Spanish settlers; the fort was burned to the ground. In 1493, Columbus built the first permanent European settlement in the Americas and called it "La Isabela", named after Spanish Queen Isabella I of Castile. Soon after Columbus's arrival to Hispaniola, most of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bilateral Relations
Bilateralism is the conduct of political, economic, or cultural relations between two sovereign states. It is in contrast to unilateralism or multilateralism, which is activity by a single state or jointly by multiple states, respectively. When states recognize one another as sovereign states and agree to diplomatic relations, they create a bilateral relationship. States with bilateral ties will exchange diplomatic agents such as ambassadors to facilitate dialogues and cooperations. Economic agreements, such as free trade agreements (FTAs) or foreign direct investment (FDI), signed by two states, are a common example of bilateralism. Since most economic agreements are signed according to the specific characteristics of the contracting countries to give preferential treatment to each other, not a generalized principle but a situational differentiation is needed. Thus through bilateralism, states can obtain more tailored agreements and obligations that only apply to particular con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
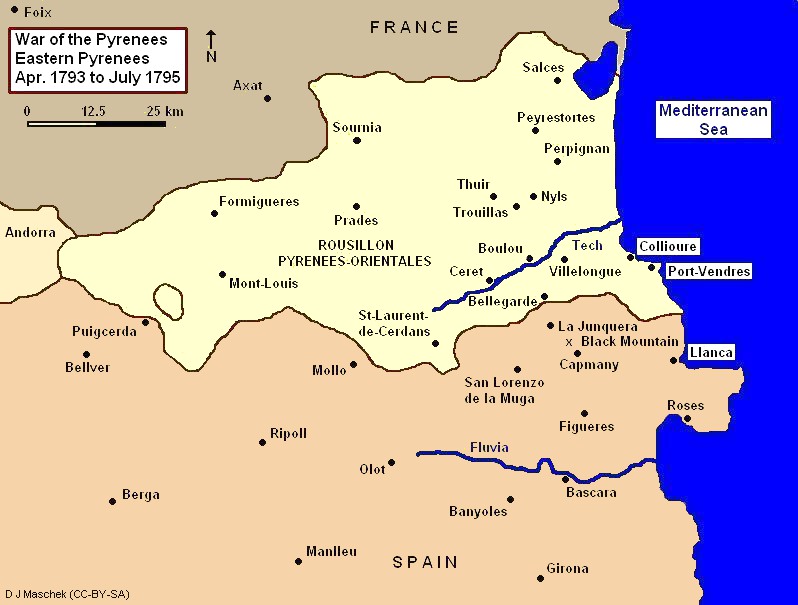
War Of The Pyrenees
The War of the Pyrenees, also known as War of Roussillon or War of the Convention, was the Pyrenees, Pyrenean front of the First Coalition's war against the First French Republic. It pitted Revolutionary France against the kingdoms of History of Spain (1700–1810), Spain and Kingdom of Portugal, Portugal from March 1793 to July 1795 during the French Revolutionary Wars. The war was fought in the eastern and western Pyrenees, at the French port of Toulon, and at sea. In 1793, a Spanish army invaded Roussillon in the eastern Pyrenees and maintained itself on French soil through April 1794. The French Revolutionary Army drove the Spanish Army back into Catalonia and inflicted a serious defeat in November 1794. After February 1795, the war in the eastern Pyrenees became a stalemate. In the western Pyrenees, the French began to win in 1794. By 1795, the French army controlled a portion of northeast Spain. The war was brutal in at least two ways. The Committee of Public Safety dec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cortes Generales
The (; ) are the Bicameralism, bicameral legislative chambers of Spain, consisting of the Congress of Deputies (the lower house) and the Senate of Spain, Senate (the upper house). The Congress of Deputies meets in the Palacio de las Cortes, Madrid, Palacio de las Cortes. The Senate meets in the Palacio del Senado. Both are in Madrid. The Cortes are elected through universal, free, equal, direct and secret suffrage, with the exception of some senatorial seats, which are elected indirectly by the legislatures of the Autonomous communities of Spain, autonomous communities. The are composed of 615 members: 350 Deputies and 265 Senators. The members of the serve four-year terms, and they are representatives of the Spanish people. In both chambers, the seats are divided by constituencies that correspond with the Provinces of Spain, fifty provinces of Spain, plus Ceuta and Melilla. However, each island or group of islands within the Canary Islands, Canary and Balearic Islands, Bal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Puerto Plata, Dominican Republic
Puerto Plata, officially known as San Felipe de Puerto Plata; () is a major coastal city in the Dominican Republic, and capital of the Provinces of the Dominican Republic, province of Puerto Plata (province), Puerto Plata. The city is a major trading port. Puerto Plata has resorts such as Playa Dorada and Costa Dorada, which are located east of the city proper. There are 100,000 hotel beds in the city. The first aerial tramway of the Caribbean is located in Puerto Plata, in which visitors can ride up to the Pico Isabel de Torres, a 793-meter (2600-foot) high mountain within the city. The city's history dates back to the early 16th century, when Spanish colonists founded a small colonial settlement in the region. During the first decades of the existence of the Captaincy General of Santo Domingo, the settlement was considered the main commercial and maritime port of the island. In 1605, it was depopulated and destroyed by order of Philip III of Spain to counter raids by English priv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Santiago De Los Caballeros
Santiago de los Caballeros ("James, son of Zebedee, Saint James of the Knights"), often shortened to Santiago, is the second-largest city in the Dominican Republic and the fourth-largest city in the Caribbean by population. It is the capital of Santiago Province (Dominican Republic), Santiago Province and the largest major metropolis in the Cibao region of the country. Santiago is the largest Caribbean city that is not a capital city, and the largest non-coastal metropolis in the Caribbean islands. It is approximately northwest of the capital, Santo Domingo, with an average altitude of . The city has a population of 1,074,684 inhabitants (2022). Santiago's metropolitan area population composed by the municipalities of Santiago-Licey al Medio, Licey Al Medio-Baitoa-Tamboril, Dominican Republic, Tamboril-Puñal-Villa González is 1,261,852 as of 2022, making it the Dominican Republic's second-largest. Founded in 1495 during the first wave of European colonization of the Americas, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dominican Restoration War
The Dominican Restoration War or the Dominican War of Restoration (), called War of Santo Domingo in Spain (''Guerra de Santo Domingo''),Losada, J. C. (2012). ''Batallas decisivas de la historia de España.'' Ed. Aguilar, pgs. 371-386. was a Guerrilla warfare, guerrilla war between 1863 and 1865 in the Dominican Republic between Dominican nationalists and Spain, the latter of which Spanish occupation of the Dominican Republic, had recolonized the country 17 years after its independence. The war resulted in the restoration of Dominican sovereignty, the withdrawal of Spanish forces, the separation of the Captaincy General of Santo Domingo from Spain, and the establishment of a second republic in the Dominican Republic. During the period of the First Dominican Republic, the nation endured repeated attacks from Haiti, and annexation attempts from France, Spain, Great Britain, and the United States, all of which threatened national sovereignty. Also posing a threat to the nation was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pedro Santana
Pedro Santana y Familias, 1st Marquess of Las Carreras (June 29, 1801June 14, 1864) was a Dominican soldier and politician who served three times as the president of the First Dominican Republic (1844–1861) and was the first governor-general during the period of annexation of the Dominican Republic to Spain (1861–1865), accomplished at Santana's request. Called " Libertador de la Patria" in life, Santana is today considered a dictator because of his authoritarian rule. Santana was one of the signatories of the Manifesto of January 16, 1844 that proclaimed Dominican independence on February 27, 1844. He would assume the leadership of the southern expeditionary army and gain prominence for his victory in the Battle of Azua. He led a coup d'état against the Central Governing Board and was named president on a provisional basis. During his government, the first constitution of the Dominican Republic was promulgated, and he was designated the first constitutional president ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monumento A La Guerra De Restauración De La República Dominicana
{{disambiguation ...
Monumento may refer to: * ''Monumento'' (album), a 2008 album by Dakrya * "Monumento", a 2018 song by Kyla from ''The Queen of R&B'' * Monumento, a district in Caloocan, Philippines where the Bonifacio Monument is located ** Monumento LRT station, Manila LRT station serving the said area See also ''Monumento'' means monument in Portuguese, Spanish, and Filipino. For relevant articles in Wikipedia see: * Monuments of Portugal * Monument (Spain) The current legislation regarding historical monuments in Spain dates from 1985. However, ''Monumentos nacionales'' (to use the original term) were first designated in the nineteenth century. It was a fairly broad category for national heritage sit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dominican War Of Independence
The Dominican War of Independence () was a war of independence that began when the Dominican Republic declared independence from the Republic of Haiti on February 27, 1844 and ended on January 24, 1856. Before the war, the island of Hispaniola had been united for 22 years when the newly independent nation, previously known as the Captaincy General of Santo Domingo, was unified with the Republic of Haiti in 1822. The criollo class within the country overthrew the Spanish crown in 1821 before unifying with Haiti a year later. The First Dominican Republic was proclaimed at the Puerta de la Misericordia after the blunderbluss shot by the patrician Matías Ramón Mella in the early morning of February 27, 1844 and by the raising of the tricolor flag at the Puerta del Conde by the patrician Francisco del Rosario Sánchez, both inspired by the ideals of their leader, Juan Pablo Duarte, ending the 22 years of Haitian rule. In response, Charles Rivière-Hérard issued the first Ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gran Colombia
Gran Colombia (, "Great Colombia"), also known as Greater Colombia and officially the Republic of Colombia (Spanish language, Spanish: ''República de Colombia''), was a state that encompassed much of northern South America and parts of Central America from 1819 to 1831. It included present-day Colombia, mainland Ecuador (i.e. excluding the Galápagos Islands), Panama, and Venezuela, along with the Caribbean coasts of Nicaragua and Costa Rica, parts of northern Peru, northwestern Brazil, and Guyana–Venezuela territorial dispute, claimed the Essequibo region. The terms Gran Colombia and Greater Colombia are used historiography, historiographically to distinguish it from the current Colombia, Republic of Colombia, which is also the official name of the former state. However, Diplomatic recognition, international recognition of the legitimacy of the Gran Colombian state ran afoul of European opposition to the independence of states in the Americas. Austrian Empire, Austria, Bourb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Republic Of Spanish Haiti
The Republic of Spanish Haiti (), also called the Independent State of Spanish Haiti () was the independent state that succeeded the Captaincy General of Santo Domingo after independence was declared on 1 December 1821 by José Núñez de Cáceres. The republic lasted only from 1 December 1821 to 9 February 1822 when it was annexed by the Republic of Haiti. History Background As a result of the Peace of Basel, the part of Hispaniola under Spanish administration was ceded to France, and merged with the French colony of Saint Domingue. When the Haitian Revolution triumphed and independence was declared by Jean-Jacques Dessalines, the eastern part of the island remained under French control until the ''criollos'' revolted and Santo Domingo was reconquered by an Anglo-Spanish alliance in 1809. After Santo Domingo was restored to Spanish rule, however, the government could not afford to exercise its full powers on the colony, its resources severely depleted by both the Pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
José Núñez De Cáceres
José Núñez de Cáceres y Albor (March 14, 1772 – September 11, 1846) was a People of the Dominican Republic, Dominican revolutionary and writer. He is known for being the leader of the first Dominican independence movement against Spanish Empire, Spain in 1821. His revolutionary activities preceded the Dominican War of Independence. Before its independence, while Spain exercised a España Boba, perfunctory rule over the east side of Hispaniola, Núñez de Cáceres pioneered the use of literature as a weapon for social protest and anti-colonial politics. He was also the first Dominican fabulist and one of the first ''Criollo people, criollo'' storytellers in Spanish America. Many of his works appeared in his own satirical newspaper, ''El Duende (newspaper), El Duende'', the second newspaper created in Santo Domingo. He was only president of the short-lived Republic of Spanish Haiti, which existed from December 1, 1821, to February 9, 1822. This period was known as the Españ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |