|
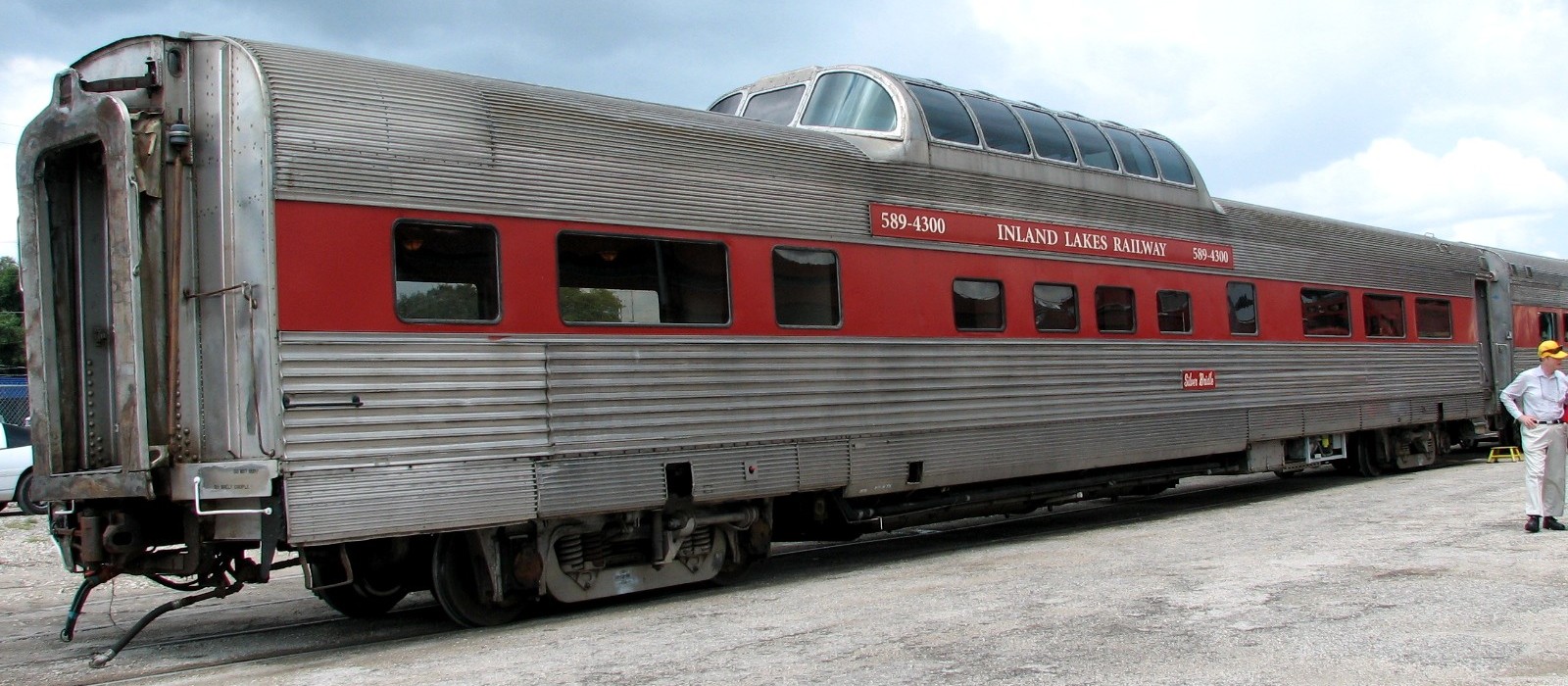
Dome Car
A dome car is a type of railway Passenger car (rail), passenger car that has a glass dome on the top of the car where passengers can ride and see in all directions around the train. It also can include features of a Coach (rail), coach, lounge car, dining car, sleeping car or observation car, observation. Beginning in 1945, dome cars were primarily used in the United States and Canada, though a small number were constructed in Europe for Trans Europ Express service. In North America, dome cars were manufactured by the Budd Company, Pullman Standard and American Car & Foundry. Southern Pacific Railroad built its own dome cars in its Sacramento, California, shops. In the 1990s Colorado Railcar began producing dome cars. Generally, seats in the dome were considered "non-revenue" like lounge car seats. Configuration A portion of the car, usually in the center of the car but offset towards one end, is split between two levels. The offset results in floorplans having a "long end" and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colorado Railcar
Colorado Railcar was a manufacturer of railroad railroad car, rolling stock—railcars and diesel multiple unit commuter vehicles. Both products came in single- and double-level versions. It shut down in 2008, with its assets being purchased by US Railcar. History The company was first organized as Rader Railcar. Founded by Tom Rader in 1988, the company changed its name to Colorado Railcar in November 1997. Rader and his company were featured in the PBS-aired documentary ''Dome Car Magic'' in 2006. In 2008, it was announced that sometime in 2007 TriMet had to directly pay Colorado Railcar's suppliers in order to financially support the company. On December 23, 2008, Colorado Railcar ceased operations, and creditors began dissolving the company after a "major liquidity problem". The shut-down was at least partially caused by the State of Vermont's cancellation of a deal to buy several DMUs for the ''Vermonter (train), Vermonter'' train. In 2009, private investors affiliated wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
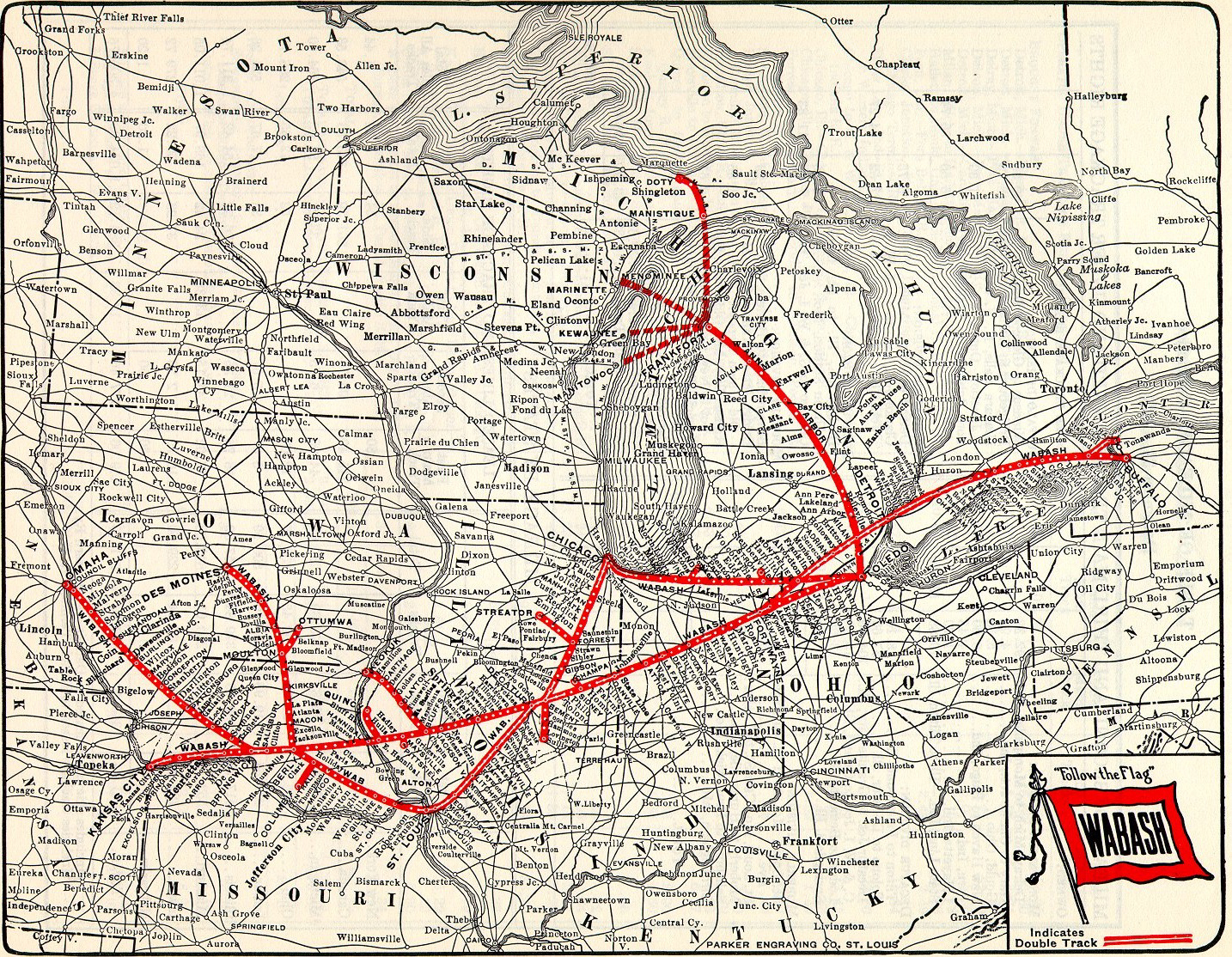
Wabash Railroad
The Wabash Railroad was a Class I railroad that operated in the mid-central United States. It served a large area, including track in the states of Ohio, Indiana, Illinois, Iowa, Michigan, and Missouri and the province of Ontario. Its primary connections included Chicago, Illinois; Kansas City, Missouri; Detroit, Michigan; Buffalo, New York; St. Louis, Missouri; and Toledo, Ohio. The Wabash's major freight traffic advantage was the direct line from Kansas City to Detroit, without going through St. Louis or Chicago. Despite being merged into the Norfolk and Western Railway (N&W) in 1964, the Wabash company continued to exist on paper until the N&W merged into the Norfolk Southern Railway (NS) in 1982. At the end of 1960 Wabash operated 2,423 miles of road on 4,311 miles of track, not including Ann Arbor Railroad (1895–1976), the Ann Arbor Railroad and the New Jersey, Indiana and Illinois Railroad; that year it reported 6,407 million net ton-miles of revenue freight and 164& ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roomette
A roomette is a type of sleeping car compartment in a railroad passenger train. The term was first used in North America, and was later carried over into Australia and New Zealand. Roomette rooms are relatively small, and were originally generally intended for use by a single person; contemporary roomettes on Amtrak, however, include two sleeping berths. By country Australia In Australia, a roomette is designed for use by one person. The width of each compartment is typically slightly less than half the width of the sleeping car it is in, with a corridor running down the centre and the compartments on both sides. The number of roomettes in a sleeping car can vary slightly, but it is commonly 16, 18, or 20. The bed in a roomette folds into one of the end walls of the compartment when not in use, and a seat folds upwards to replace it. Thus the bed is Parallel (geometry), parallel to the side of the train, in contrast to twinette berths, which are perpendicular to it. Becau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
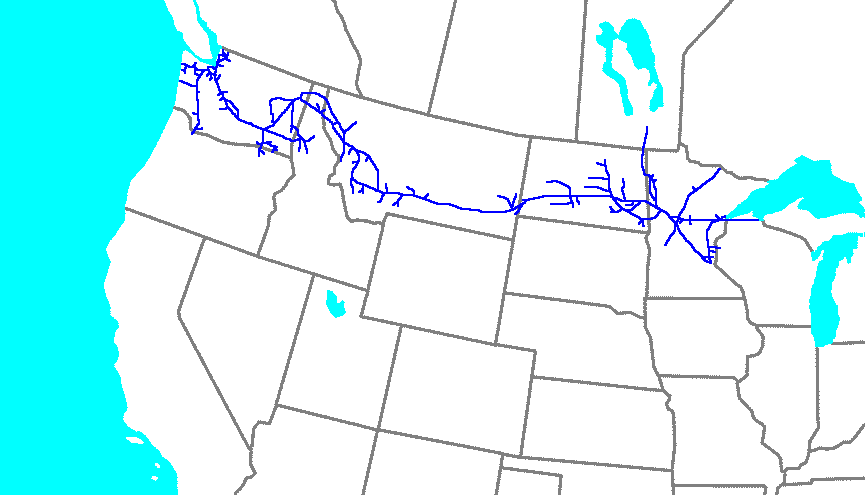
Northern Pacific Railway
The Northern Pacific Railway was an important American transcontinental railroad that operated across the northern tier of the Western United States, from Minnesota to the Pacific Northwest between 1864 and 1970. It was approved and chartered by the 38th Congress of the United States in the national / federal capital of Washington, D.C., during the last years of the American Civil War (1861-1865), and received nearly of adjacent land grants, which it used to raise additional money in Europe (especially in President Henry Villard's home country of the new German Empire), for construction funding. Construction began in 1870 and the main line opened all the way from the Great Lakes to the Pacific Ocean, just south of the United States-Canada border when Ulysses S. Grant, drove in the final "golden spike" completing the line in western Montana Territory (future State of Montana in 1889), on September 8, 1883. The railroad had about of track and served a large area, including ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Denver Zephyr
The ''Denver Zephyr'' was a streamlined passenger train operated by the Chicago, Burlington and Quincy Railroad between Chicago, Illinois, and Denver, Colorado. In peak years it ran to Colorado Springs. It operated from 1936 to 1973. The ''Denver Zephyr'' continued operating after the Burlington Northern Railroad merger in 1970. BN conveyed the train to Amtrak in 1971; Amtrak merged it with the Denver–Oakland '' City of San Francisco'' to form the ''San Francisco Zephyr'' and dropped the "Denver" name in 1973. The first Denver Zephyrs The first Zephyr service to Denver began May 31, 1936, with the trainsets of the ''Pioneer Zephyr'' and the '' Mark Twain Zephyr'', trains 9900 and 9903. This new service was known as the ''Advance Denver Zephyr'' and operated on a 16-hour schedule. The trains did not have sleepers, but introduced hostesses called " Zephyrettes". In the meantime, after the success of the 3-car and 4-car ''Pioneer Zephyr'', '' Twin Zephyrs'', and ''Mark Twa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Royal Zephyr
The ''American Royal Zephyr'' was a streamlined passenger train service operated by the Chicago, Burlington and Quincy Railroad between Chicago and Kansas City. This CB&Q ''Zephyr'' was named for the American Royal, one of the Midwest's largest and oldest livestock exhibition, professional rodeo, and horse show. The ''American Royal Zephyr'' made its inaugural run on February 1, 1953, as an all-new overnight streamliner between Chicago and Kansas City. The new train was prompted by the completion the previous October of the $16-million "Kansas City Shortcut", 49 miles of new track that made the route shorter, flatter, and straighter. The new alignment shaved 2 hours off of the previous shortest route, and made CB&Q optimistic that it could compete successfully against its entrenched rival, the AT&SF, on this busy route. ''American Royal Zephyr'' #56 departed Kansas City at 10:00 pm, arriving in Chicago at 7:30 am. Westbound counterpart #55 operated on a mirrored schedule, de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kansas City Zephyr
The ''Kansas City Zephyr'' was a streamliner passenger train service operated by the Chicago, Burlington and Quincy Railroad (CB&Q) between Chicago and Kansas City. Overview The largest fleet of named streamliners in the United States were the Burlington's Zephyrs. Competing in markets against the famed Eagles, Chiefs, 400's, Cities and Hiawathas on almost every route, the polished Zephyrs covered almost every route on the mainline of the Burlington and for years held the speed/distance title in the record books. The ''Kansas City Zephyr'' made its inaugural run on February 1, 1953, as an all-new daylight streamliner between Chicago and Kansas City. The new train was prompted by the completion the previous October of the $16-million "Kansas City Shortcut", 49 miles of new track that made the route shorter, flatter, and straighter. The new alignment shaved two hours off of the previous shortest route, and made CB&Q optimistic that it could compete successfully against its ent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
California Zephyr
The ''California Zephyr'' is a Amtrak Long Distance, long-distance passenger train operated by Amtrak between Chicago, Illinois, Chicago and the San Francisco Bay Area (at Emeryville station, Emeryville), via Omaha, Nebraska, Omaha, Denver, Salt Lake City, and Reno, Nevada, Reno. At , it is Amtrak's longest daily route, and second-longest overall after the ''Texas Eagle's'' triweekly continuation from San Antonio, Texas, San Antonio to Los Angeles, with travel time between the termini taking approximately 52 hours. Amtrak claims the route as one of its most scenic, with views of the upper Colorado River valley in the Rocky Mountains, and the Sierra Nevada (U.S.), Sierra Nevada. The modern train is the second iteration of a train named ''California Zephyr''; the California Zephyr (1949–1970), original train was privately operated and ran on a different route through Nevada and California. During fiscal year 2023, the ''California Zephyr'' carried 328,458 passengers, an increa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chicago, Burlington & Quincy Railroad
The Chicago, Burlington and Quincy Railroad was a railroad that operated in the Midwestern United States. Commonly referred to as the Burlington Route, the Burlington, CB&Q, or as the Q, it operated extensive trackage in the states of Colorado, Illinois, Iowa, Missouri, Nebraska, Wisconsin, Wyoming, and also in Texas through subsidiaries Colorado and Southern Railway, Fort Worth and Denver Railway, and Burlington-Rock Island Railroad. Its primary connections included Chicago, Minneapolis–Saint Paul, St. Louis, Kansas City, and Denver. Because of this extensive trackage in the midwest and mountain states, the railroad used the advertising slogans "Everywhere West", "Way of the ''Zephyrs''", and "The Way West". In 1967, it reported 19,565 million net ton-miles of revenue freight and 723 million passenger miles; corresponding totals for C&S were 1,100 and 10 and for FW&D were 1,466 and 13. At the end of the year, CB&Q operated 8,538 route-miles, C&S operated 708, and FW&D opera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
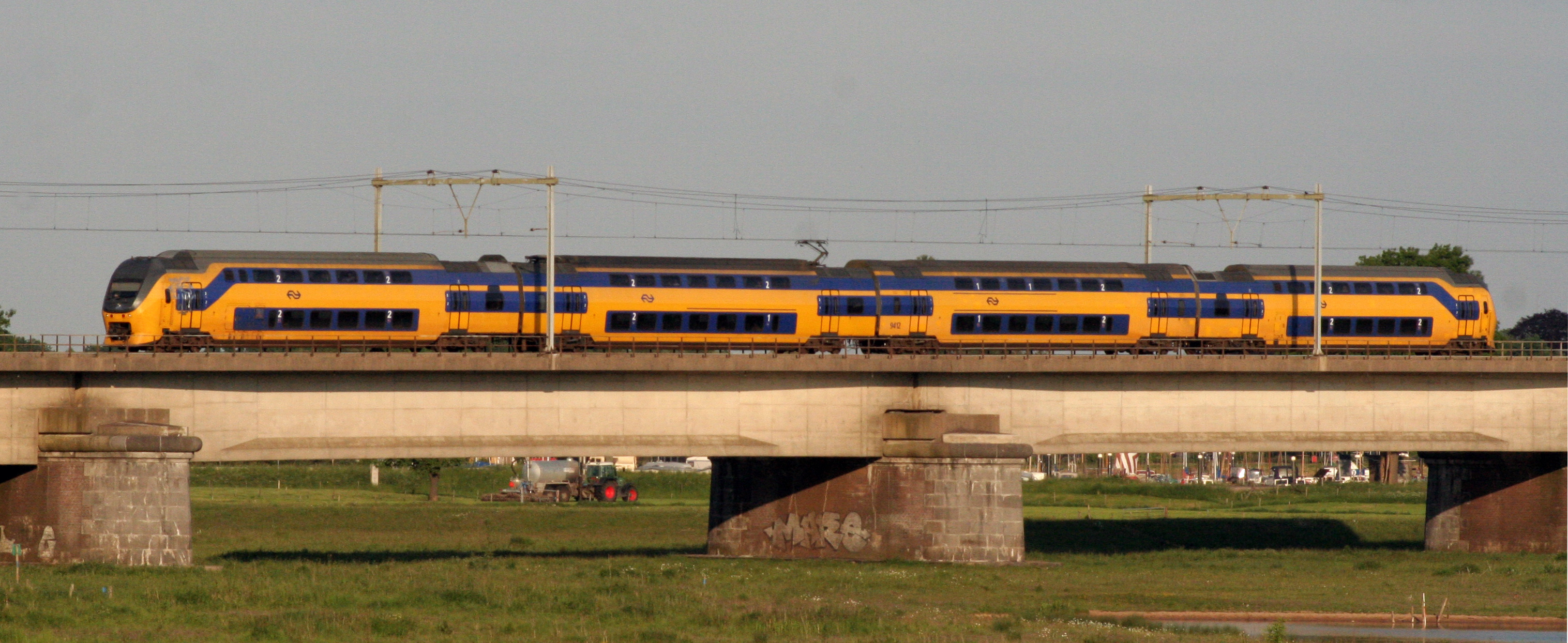
NS VIRM
VIRM trains, full name Verlengd InterRegio Materieel (), are a series of electric multiple unit (EMU) double-deck trains operated by Nederlandse Spoorwegen or NS (''Dutch Railways''), the principal railway operator in the Netherlands. NS has 178 of these double-deckers – 98 four-carriage sets, and 80 six-carriage sets. The trains were built between 1994 and 2009 – for the most part by Talbot, part of Bombardier Inc., with some railcars built by De Dietrich. The VIRM trains evolved out of the previously existing DD-IRM series (DubbelDeks InterRegio Materieel or ''Double-deck interregional rolling stock''). The first batch of 81 VIRM trains was created by lengthening all the existing DD-IRM combinations by one or two railcars. Three-unit trainsets were augmented by one carriage to transform them into a four-unit VIRM, and the four-unit sets received two more carriages, to create six-unit VIRM trains. Names * VIRM (Verlengd InterRegio Materieel) * DD-IRM (Dubbeldeksinterregi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dumbwaiter (elevator)
A dumbwaiter is a small freight elevator or lift intended to carry food. Dumbwaiters found within modern structures, including both commercial, public and private buildings, are often connected between multiple floors. When installed in restaurants, schools, hospitals, retirement homes or private homes, they generally terminate in a kitchen. Limited Preview, ''Google Books'', accessed August 26, 2008. The term seems to have been popularized in the United States in the 1840s, after the model of earlier "dumbwaiters" now known as serving trays and lazy Susans. Quinion, Michael. ''World Wide Words'':Lazy Susan. 24 Apr 2010. Accessed 11 Aug 2013. The mechanical dumbwaiter was invented by George W. Cannon, a New York City inventor. He first filed for the patent of a brake system (US Patent no. 260776) that could be used for a dumbwaiter on January 6, 1883, Limited Preview, ''Google Books', accessed October 30, 2012. then for the patent on the mechanical dumbwaiter (US Patent No. 36 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |