|
Dogra Jheer
The Dogra Jheevar are a Hindu caste found in the Jammu region of Jammu and Kashmir, India. Origin The word is said to be a corruption of the Sanskrit ''dheevara'', which means someone of mixed origin. Dheevaras receive a mention in the Mahabharat. In the Dogri language, the term ''jheer'' was often used for a cook. This community may have acquired the name Jheer because members of the community were employed as cooks. The Jheer are a caste associated with water-carrying and may be connected with the Jhinwar caste of Punjab. Like the Jhinwar and the Kahar of North India, the Jheer were also employed as palanquin bearers.People of India Jammu and Kashmir Volume XXV edited by K.N Pandita, S.D.S Charak & B.R. Rizvi page 292 to 301 Manohar Publications The homeland of the Jheer is a region historically known as Duggar Des, an area stretching from Udhampur in the north and Kathua in the south. They speak the Dogri language, and their customs and traditions are similar to the local ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hindu
Hindus (; ) are people who religiously adhere to Hinduism.Jeffery D. Long (2007), A Vision for Hinduism, IB Tauris, , pages 35–37 Historically, the term has also been used as a geographical, cultural, and later religious identifier for people living in the Indian subcontinent. The term ''"Hindu"'' traces back to Old Persian which derived these names from the Sanskrit name ''Sindhu'' (सिन्धु ), referring to the river Indus. The Greek cognates of the same terms are "''Indus''" (for the river) and "''India''" (for the land of the river). The term "''Hindu''" also implied a geographic, ethnic or cultural identifier for people living in the Indian subcontinent around or beyond the Indus River, Sindhu (Indus) River. By the 16th century CE, the term began to refer to residents of the subcontinent who were not Turkic peoples, Turkic or Muslims. Hindoo is an archaic spelling variant, whose use today is considered derogatory. The historical development of Hindu self-i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kathua District
Kathua district is one of 20 administrative districts that comprise the Indian union territory of Jammu and Kashmir. It is surrounded by Jammu to the northwest, the Doda and Udhampur districts to the north, the state of Himachal Pradesh to the east, Punjab to the south, and Pakistan's working boundary to the west. Its terrain is diverse, consisting of rich agricultural areas along the Punjab/Kashmir border, plains sweeping eastward to the foothills of the Himalaya, and the mountainous Pahari region in the east.. Kathua district is divided into 8 blocks: Bani, Barnoti, Basholi, Billawar, Duggan, Ghagwal, Hiranagar, Kathua and Lohai Malhar. It has approximately 512 villages. The traditional language of Kathua is Dogri. Pahari languages are prevalent in the mountainous area of the east. The principal media of education are English, Hindi, and Urdu. History Jodh Singh of the Andotra clan(shares ancestry with Tomar and Som Rajputs) is believed to have migrated from Hastinapur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dogra
The Dogras or Dogra people, are an Indo-Aryan ethno-linguistic group in India and Pakistan consisting of the Dogri language speakers. They live predominantly in the Jammu region of Jammu and Kashmir, and in adjoining areas of Punjab, Himachal Pradesh, and northeastern Pakistan. Their historical homeland is known as Duggar. Dogra Rajputs ruled Jammu from the 19th century, when Gulab Singh was made a hereditary Raja of Jammu by Ranjit Singh, whilst his brother Dhian Singh was the empire's prime minister of Punjab, until October 1947. Through the Treaty of Amritsar (1846), they acquired Kashmir as well. The Dogra Regiment of the Indian Army primarily consists of Dogras from the Himachal Pradesh, Punjab and Jammu region. Etymology The term Dogra is thought to derive from ''Durgara'', the name of a kingdom mentioned in an eleventh century copper-plate inscription in Chamba. The inscription mentions the Raja of Chamba facing an attack by Kiras aided by the Lord of Durg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Government Of India
The Government of India ( ISO: ; often abbreviated as GoI), known as the Union Government or Central Government but often simply as the Centre, is the national government of the Republic of India, a federal democracy located in South Asia, consisting of 28 union states and eight union territories. Under the Constitution, there are three primary branches of government: the legislative, the executive and the judiciary, whose powers are vested in a bicameral Parliament, President, aided by the Council of Ministers, and the Supreme Court respectively. Through judicial evolution, the Parliament has lost its sovereignty as its amendments to the Constitution are subject to judicial intervention. Judicial appointments in India are unique in that the executive or legislature have negligible say. Etymology and history The Government of India Act 1833, passed by the British parliament, is the first such act of law with the epithet "Government of India". Basic structure The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Land Reform
Land reform is a form of agrarian reform involving the changing of laws, regulations, or customs regarding land ownership. Land reform may consist of a government-initiated or government-backed property redistribution, generally of agricultural land. Land reform can, therefore, refer to transfer of ownership from the more powerful to the less powerful, such as from a relatively small number of wealthy or noble owners with extensive land holdings (e.g., plantations, large ranches, or agribusiness plots) to individual ownership by those who work the land. Such transfers of ownership may be with or without compensation; compensation may vary from token amounts to the full value of the land. Land reform may also entail the transfer of land from individual ownership—even peasant ownership in smallholdings—to government-owned collective farms; it has also, in other times and places, referred to the exact opposite: division of government-owned collective farms into smallholdin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endogamy
Endogamy is the practice of marrying within a specific social group, religious denomination, caste, or ethnic group, rejecting those from others as unsuitable for marriage or other close personal relationships. Endogamy is common in many cultures and ethnic groups. Several religious and ethnic religious groups are traditionally more endogamous, although sometimes with the added dimension of requiring marital religious conversion. This permits an exogamous marriage, as the convert, by accepting the partner's religion, becomes accepted within the endogamous rules. Endogamy, as distinct from consanguinity, may result in transmission of genetic disorders, the so-called founder effect, within the relatively closed community. Adherence Endogamy can serve as a form of self-segregation; a community can use it to resist integrating and completely merging with surrounding populations. Minorities can use it to stay ethnically homogeneous over a long time as distinct communities ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exogamy
Exogamy is the social norm of marrying outside one's social group. The group defines the scope and extent of exogamy, and the rules and enforcement mechanisms that ensure its continuity. One form of exogamy is dual exogamy, in which two groups continually intermarry with each other. In social science, exogamy is viewed as a combination of two related aspects: biological and cultural. Biological exogamy is marriage of nonblood-related beings, regulated by forms of incest law. Cultural exogamy is marrying outside a specific cultural group; the opposite being endogamy, marriage within a social group. Biology of exogamy Exogamy often results in two individuals that are not closely genetically related marrying each other; that is, outbreeding as opposed to inbreeding. In moderation, this benefits the offspring as it reduces the risk of the offspring inheriting two copies of a defective gene. Increasing the genetic diversity of the offspring improves the chances of offspring repr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caste
Caste is a form of social stratification characterised by endogamy, hereditary transmission of a style of life which often includes an occupation, ritual status in a hierarchy, and customary social interaction and exclusion based on cultural notions of purity and pollution. * Quote: "caste ort., casta=basket ranked groups based on heredity within rigid systems of social stratification, especially those that constitute Hindu India. Some scholars, in fact, deny that true caste systems are found outside India. The caste is a closed group whose members are severely restricted in their choice of occupation and degree of social participation. Marriage outside the caste is prohibited. Social status is determined by the caste of one's birth and may only rarely be transcended." * Quote: "caste, any of the ranked, hereditary, endogamous social groups, often linked with occupation, that together constitute traditional societies in South Asia, particularly among Hindus in India. Although ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
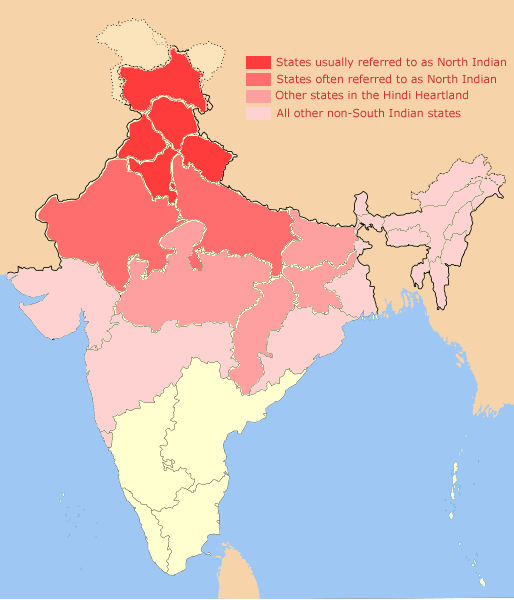
North Indian
North India is a loosely defined region consisting of the northern part of India. The dominant geographical features of North India are the Indo-Gangetic Plain and the Himalayas, which demarcate the region from the Tibetan Plateau and Central Asia. The term North India has varying definitions. The Ministry of Home Affairs in its Northern Zonal Council Administrative division included the states of Haryana, Himachal Pradesh, Punjab and Rajasthan and Union Territories of Chandigarh, Delhi, Jammu and Kashmir and Ladakh. The Ministry of Culture in its ''North Culture Zone'' includes the state of Uttarakhand but excludes Delhi whereas the Geological Survey of India includes Uttar Pradesh and Delhi but excludes Rajasthan and Chandigarh. Other states sometimes included are Bihar, Gujarat, Jharkhand, Madhya Pradesh and West Bengal. North India has been the historical centre of the Mughal Empire, the Delhi Sultanate and the British Indian Empire. It has a diverse culture, and i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dogras
The Dogras or Dogra people, are an Indo-Aryan ethno-linguistic group in India and Pakistan consisting of the Dogri language speakers. They live predominantly in the Jammu region of Jammu and Kashmir, and in adjoining areas of Punjab, Himachal Pradesh, and northeastern Pakistan. Their historical homeland is known as Duggar. Dogra Rajputs ruled Jammu from the 19th century, when Gulab Singh was made a hereditary Raja of Jammu by Ranjit Singh, whilst his brother Dhian Singh was the empire's prime minister of Punjab, until October 1947. Through the Treaty of Amritsar (1846), they acquired Kashmir as well. The Dogra Regiment of the Indian Army primarily consists of Dogras from the Himachal Pradesh, Punjab and Jammu region. Etymology The term Dogra is thought to derive from ''Durgara'', the name of a kingdom mentioned in an eleventh century copper-plate inscription in Chamba. The inscription mentions the Raja of Chamba facing an attack by Kiras aided by the Lord of Durgara ('' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Udhampur District
Udhampur is a district in the Indian Union territory of Jammu and Kashmir. Covering an area of in the Himalayan mountains, the district has its headquarters in the town of Udhampur. The Northern Command headquarters of the Indian Army is located in the district. Weather conditions Temperature varies considerably in the Udhampur District, as the altitude ranges from . Chenab, Ans, Tawi and Ujh are the main rivers. The district is rich in minerals such as coal, bauxite, gypsum and limestone. Administration Udhampur district comprises eight tehsils (Chenani, Ramnagar Tehsil, basantgarh, latti,Majalta and seventeen blocks, namely, dudu Basantgarh, Gordi, Chenani, Bajalta, Panchari, Ramnagar and Udhampur. Each block consists of a number of panchayats. Demographics The 2011 census indicates the population of the district to be 554,985. There are 871 females for every 1000 males in the district. The overall literacy rate is 54.16%, with 66.43% for males and 39.89% for fema ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jammu Division
The Jammu division (; ) is a revenue and administrative division within Jammu and Kashmir, a union territory of India. It consists of the districts of Jammu, Doda, Kathua, Ramban, Reasi, Kishtwar, Poonch, Rajouri, Udhampur and Samba. Most of the land is hilly or mountainous, including the Pir Panjal Range which separates it from the Kashmir Valley and part of the Great Himalayas in the eastern districts of Doda and Kishtwar. Its principal river is the Chenab. Jammu city is the largest city in Jammu and the winter capital of Jammu and Kashmir. It is also known as "City of Temples" as it has many temples and shrines, with glittering ''shikhars'' soaring into the sky, which dot the city's skyline, creating the ambiance of a holy and peaceful city. Home to some of the most revered Hindu shrines, such as Vaishno Devi, Jammu is a major pilgrimage centre for Hindus. A majority of Jammu's population practices Hinduism, while Islam and Sikhism enjoy a strong cultural heritage ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)